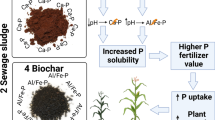
Abstract
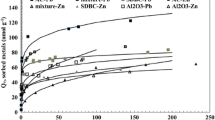
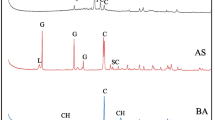
Industrial by-products are stored in large quantities in the open, leading to wasted resources and environmental pollution, and the natural environment is similarly faced with phosphate depletion and serious water and soil pollution. This study uses these by-products to produce a new sludge/biomass ash ceramsite that will be used to adsorb nitrogen and phosphorus from wastewater, and solidify heavy metals in the soil while releasing Olsen P. The sludge/biomass ash ceramsites are made using sewage sludge and biomass ash in a certain ratio calcined at high temperatures and modified for the adsorption of nitrogen and phosphorus from wastewater. Sludge/biomass ash ceramsites before and after phosphorus adsorption, biochar and biomass ash were compared to analyze their heavy metal adsorption capacity and potential as phosphate fertilizer. After phosphorus adsorption, the sludge/biomass ash ceramsites released effective phosphorus steadily and rapidly in the soil, with a greater initial release than biochar and biomass ash, and the ceramsites were in a granular form that could be easily recycled. Biochar and biomass residue, due to their surface functional groups, are better at solidifying heavy metals than sludge/biomass ash ceramsites. Biochar, biomass ash and sludge/biomass ash ceramsites significantly reduced the concentrations of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in the soil. Correlation analysis demonstrated that there was a synergistic relationship between the increase in soil Olsen P content and the change in pH, with the increase in soil Olsen P content and the increase in pH contributing to heavy metal solidification.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asrade, D. A., Kulhánek, M., Balík, J., Černý, J., & Sedlář, O. (2023). Side effect of organic fertilizing on the phosphorus transformation and balance over 27 years of maize monoculture. Field Crops Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2023.108902
Azadi, N., & Raiesi, F. (2023). Minimizing salinity-induced Pb toxicity to microbial N cycling processes in saline Pb-polluted soils amended with biochar. Pedobiologia, 96, 150861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedobi.2022.150861
Azeem, M., Ali, A., Arockiam Jeyasundar, P. G. S., Li, Y., Abdelrahman, H., Latif, A., et al. (2021). Bone-derived biochar improved soil quality and reduced Cd and Zn phytoavailability in a multi-metal contaminated mining soil. Environmental Pollution. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116800
Burton, E. D., Lamb, D. T., Hamilton, J., Miller, G., Johnston, S. G., & Karimian, N. (2022). Remediation of Pb-contaminated soil using modified bauxite refinery residue. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 437, 129339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129339
Chang, J., Cho, Y., & Lin, Y. (2022). Resources, conservation & recycling regeneration of heavy metal contaminated soils for cement production by cement kiln co-processing. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 176, 105909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105909
Chen, X., Xu, X., Wei, Y., Wang, X., & Cao, X. (2023). Constructing the active surface soil layer with ZVI-biochar amendment for simultaneous immobilization of As and Zn in both contaminated soil and groundwater: Continuous versus intermittent infiltration mode. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 445, 130518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.130518
Chen, Y., Jing, Z., Cai, K., & Li, J. (2018). Hydrothermal conversion of Cs-polluted soil into pollucite for Cs immobilization. Chemical Engineering Journal, 336, 503–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.187
Cloutier-Hurteau, B., Sauvé, S., & Courchesne, F. (2008). Influence of microorganisms on Cu speciation in the rhizosphere of forest soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 40(9), 2441–2451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.06.006
Dong, J., Mao, W. H., Zhang, G. P., Wu, F. B., & Cai, Y. (2007). Root excretion and plant tolerance to cadmium toxicity - A review. Plant, Soil and Environment, 53(5), 193–200. https://doi.org/10.17221/2205-pse
Fseha, Y. H., Sizirici, B., & Yildiz, I. (2021). The potential of date palm waste biochar for single and simultaneous removal of ammonium and phosphate from aqueous solutions. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(6), 106598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106598
Gopinath, K. P., Vo, D. V. N., Gnana Prakash, D., Adithya Joseph, A., Viswanathan, S., & Arun, J. (2021). Environmental applications of carbon-based materials: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 19(1), 557–582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01084-9
Gouma, V., Tziasiou, C., Pournara, A. D., & Giokas, D. L. (2022). A novel approach to sorbent-based remediation of soil impacted by organic micropollutants and heavy metals using granular biochar amendment and magnetic separation. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(2), 107316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107316
Hamer, U., Marschner, B., Brodowski, S., & Amelung, W. (2004). Interactive priming of black carbon and glucose mineralisation. Organic Geochemistry, 35(7), 823–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2004.03.003
Han, F., An, S. Y., Liu, L., Wang, Y., Ma, L. Q., & Yang, L. (2023). Sulfoaluminate cement-modified straw biochar as a soil amendment to inhibit Pb–Cd mobility in the soil-romaine lettuce system. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138891
He, Z., Xu, Y., Yang, X., Shi, J., Wang, X., Jin, Z., et al. (2022). Passivation of heavy metals in copper–nickel tailings by in-situ bio-mineralization: A pilot trial and mechanistic analysis. Science of the Total Environment, 838, 156504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156504
Jiang, Q., He, Y., Wu, Y., Dian, B., Zhang, J., Li, T., & Jiang, M. (2022). Solidification/stabilization of soil heavy metals by alkaline industrial wastes: A critical review. Environmental Pollution, 312, 120094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120094
Jiang, Z., Nie, K., Yu, L., Arinzechi, C., Zhao, F., Liao, Q., et al. (2023). Synchronous stabilization of As, Cd, and Pb in soil by sustained-release of iron-phosphate. Science of the Total Environment, 867, 161369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.161369
Khabbouchi, M., Hosni, K., Mezni, M., & Srasra, E. (2018). Simplified synthesis of silicophosphate materials using an activated metakaolin as a natural source of active silica. Applied Clay Science, 158, 169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2018.03.027
Lakshmana Naik, R., Rupas Kumar, M., & Bala Narsaiah, T. (2023). Removal of heavy metals (Cu & Ni) from wastewater using rice husk and orange peel as adsorbents. Materials Today: Proceedings, 72, 92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.06.112
Lan, H., Zhang, Y., Cheng, M., Li, Y., & Jing, Z. (2021). An intelligent humidity regulation material hydrothermally synthesized from ceramic waste. Journal of Building Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102336
Li, Y., Giordano, A., Ajmone-Marsan, F., & Padoan, E. (2023). Bioaccessibility of Pb in health-related size fractions of contaminated soils amended with phosphate. Science of the Total Environment, 855, 158831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158831
Liang, B., Han, G., Zeng, J., Liu, M., & Zhang, Q. (2022). Environmental implications of land use change on the fate of Zn in agricultural soils: A case study of Puding karst soils, southwest China. Environmental Research, 215(P1), 114221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114221
Lua, A. C. (2023). A comparative study of the pore characteristics and phenol adsorption performance of activated carbons prepared from oil-palm shell wastes by steam and combined steam-chemical activation. Green Chemical Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gce.2022.11.004
Luo, Y., Li, Z., Xu, H., Xu, X., Qiu, H., Cao, X., & Zhao, L. (2022). Development of phosphorus composite biochar for simultaneous enhanced carbon sink and heavy metal immobilization in soil. Science of the Total Environment, 831, 154845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154845
Marsh, A., Heath, A., Patureau, P., Evernden, M., & Walker, P. (2018). Alkali activation behaviour of un-calcined montmorillonite and illite clay minerals. Applied Clay Science, 166, 250–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2018.09.011
Mon, J., Deng, Y., Flury, M., & Harsh, J. B. (2005). Cesium incorporation and diffusion in cancrinite, sodalite, zeolite, and allophane. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 86, 277–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2005.07.030
Pu, S., Duan, W., Zhu, Z., Wang, W., Zhang, C., Li, N., et al. (2022). Environmental behavior and engineering performance of self-developed silico-aluminophosphate geopolymer binder stabilized lead contaminated soil. Journal of Cleaner Production. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134808
Sayyedan, F. S., & Enayati, M. H. (2019). On structure and oxidation behaviour of non-stoichiometric amorphous aluminium phosphate coating. Surface Engineering, 35(8), 670–676. https://doi.org/10.1080/02670844.2018.1560912
Sessitsch, A., Kuffner, M., Kidd, P., Vangronsveld, J., Wenzel, W. W., Fallmann, K., & Puschenreiter, M. (2013). The role of plant-associated bacteria in the mobilization and phytoextraction of trace elements in contaminated soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 60, 182–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.01.012
Sui, L., Tang, C., Cheng, K., & Yang, F. (2022). Biochar addition regulates soil phosphorus fractions and improves release of available phosphorus under freezing-thawing cycles. Science of the Total Environment, 848, 157748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157748
Sun, Y., Li, H., Guo, G., Semple, K. T., & Jones, K. C. (2019). Soil contamination in China: Current priorities, defining background levels and standards for heavy metals. Journal of Environmental Management, 251, 109512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109512
Suo, C., Fang, P., Cao, H., Cao, J., Liu, K., & Dong, X. (2021). Influence and microscopic mechanism of the solid waste-mixture on solidification of Cu2+-contaminated soil. Construction and Building Materials, 305, 124651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124651
Taupedi, S. B., & Ultra, V. U. (2022). Morupule fly ash as amendments in agricultural soil in Central Botswana. Environmental Technology and Innovation, 28, 102695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2022.102695
Tufail, M. A., Iltaf, J., Zaheer, T., Tariq, L., Amir, M. B., Fatima, R., et al. (2022). Recent advances in bioremediation of heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 850, 157961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157961
Wang, F., Wang, H., & Al-Tabbaa, A. (2014). Leachability and heavy metal speciation of 17-year old stabilised/solidified contaminated site soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 278, 144–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.05.102
Wang, J. L., Zhao, Y. L., Zhang, P. P., Yang, L., Xu, H., & Xi, G. (2018). Adsorption characteristics of a novel ceramsite for heavy metal removal from stormwater runoff. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 26, 96–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2017.04.011
Wang, Q., Wen, J., Hu, X., Xing, L., & Yan, C. (2021). Immobilization of Cr(VI) contaminated soil using green-tea impregnated attapulgite. Journal of Cleaner Production, 278, 123967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123967
Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Li, L., Yang, Y., Xu, C., Luo, Y., et al. (2023). Immobilization of Cd by mercapto-palygorskite in typical calcareous and acidic soil aggregates: Performance and differences. Chemosphere, 323(100), 138223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138223
Wu, L. J., Liu, C., Hu, Y. K., Tan, B., He, Y., & Li, N. (2020). Dephosphorization using ceramsites modified by coprecipitation with FeSo4 and KMnO4 and high-temperature combustion. Journal of Water Process Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101162
Wu, L., Wan, W., Shang, Z., Gao, X., Kobayashi, N., Luo, G., & Li, Z. (2018). Surface modification of phosphoric acid activated carbon by using non-thermal plasma for enhancement of Cu(II) adsorption from aqueous solutions. Separation and Purification Technology, 197, 156–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.01.007
Wu, S., Zhou, S., Bao, H., Chen, D., Wang, C., Li, B., et al. (2019). Improving risk management by using the spatial interaction relationship of heavy metals and PAHs in urban soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 364, 108–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.094
Wu, Y. J., Zhou, H., Zou, Z. J., Zhu, W., Yang, W. T., Peng, P. Q., et al. (2016). A three-year in-situ study on the persistence of a combined amendment (limestone+sepiolite) for remedying paddy soil polluted with heavy metals. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 130, 163–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.04.018
Xie, S., Tran, H. T., Pu, M., & Zhang, T. (2023). Transformation characteristics of organic matter and phosphorus in composting processes of agricultural organic waste: Research trends. Materials Science for Energy Technologies, 6, 331–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2023.02.006
Xu, G. R., Zou, J. L., & Li, G. B. (2009). Ceramsite obtained from water and wastewater sludge and its characteristics affected by (Fe2O3+CaO+MgO)/(SiO2+Al2O3). Water Research, 43, 2885–2893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.03.046
Yan, L., Chen, Q., Yang, Y., & Zhu, R. (2021). The significant role of montmorillonite on the formation of hematite nanoparticles from ferrihydrite under heat treatment. Applied Clay Science, 202, 105962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2020.105962
Yang, T., Xu, Y., Sun, G., Huang, Q., Sun, Y., Liang, X., & Wang, L. (2023). Application of ferromanganese functionalized biochar simultaneously reduces Cd and Pb uptake of wheat in contaminated alkaline soils. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 257, 114930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.114930
Yin, X., Xu, Y., Huang, R., Huang, Q., Xie, Z., Cai, Y., & Liang, X. (2017). Remediation mechanisms for Cd-contaminated soil using natural sepiolite at the field scale. Environmental Science: Processes and Impacts, 19(12), 1563–1570. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7em00262a
Yong, Y., Hua, W., & Jianhang, H. (2021). Co-treatment of electroplating sludge, copper slag, and spent cathode carbon for recovering and solidifying heavy metals. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 417, 126020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126020
You, L., Li, W., Xu, W., Zhang, C., & Hu, X. (2022). Effects of nanometer magnesium hydroxide on soil cadmium form under different cadmium levels. Asia-Pacific Journal of Chemical Engineering, 17(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/apj.2665
Zhang, J., Fan, X., Wang, X., Tang, Y., Zhang, H., Yuan, Z., et al. (2022a). Bioremediation of a saline-alkali soil polluted with Zn using ryegrass associated with Fusarium incarnatum. Environmental Pollution, 312(26), 119929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119929
Zhang, P., Xue, B., Jiao, L., Meng, X., Zhang, L., Li, B., & Sun, H. (2022b). Preparation of ball-milled phosphorus-loaded biochar and its highly effective remediation for Cd- and Pb-contaminated alkaline soil. Science of the Total Environment, 813, 152648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152648
Zhang, T., Li, T., Zhou, Z., Li, Z., Zhang, S., Wang, G., et al. (2023a). Cadmium-resistant phosphate-solubilizing bacteria immobilized on phosphoric acid-ball milling modified biochar enhances soil cadmium passivation and phosphorus bioavailability. Science of the Total Environment, 877, 162812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162812
Zhang, Y., Gao, W., Ma, L., Luan, H., Tang, J., Li, R., et al. (2023c). Long-term partial substitution of chemical fertilizer by organic amendments influences soil microbial functional diversity of phosphorus cycling and improves phosphorus availability in greenhouse vegetable production. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 341, 108193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2022.108193
Zhang, Y., Ma, J., Miao, J., Yue, L., Cheng, M., Li, Y., & Jing, Z. (2023b). Self-regulated immobilization behavior of multiple heavy metals via zeolitization towards a novel hydrothermal technology for soil remediation. Environmental Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114726
Zheng, R., Feng, X., Zou, W., Wang, R., Yang, D., Wei, W., et al. (2021). Converting loess into zeolite for heavy metal polluted soil remediation based on “soil for soil-remediation” strategy. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 412, 125199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125199
Zou, J. L., Xu, G. R., Pan, K., Zhou, W., Dai, Y., Wang, X., et al. (2012). Nitrogen removal and biofilm structure affected by COD/NH4+–N in a biofilter with porous sludge-ceramsite. Separation and Purification Technology, 94, 9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2012.03.019
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Key Research and Development Project of China (2021YFC2902002), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42272196 and 41972166), the Key Research and Development Program of Anhui Province (2023t07020006), the Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2108085QD161) and Project of Linhuan Coking Industry Company. We acknowledge editors and reviewers for polishing the language of the paper and for in-depth discussion.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HS was responsible for conducting experiments and writing manuscripts. CZ guided the experiment and writing process. SX, JS and YH participated in some experiments and manuscript correction. GL controled the overall experimental process
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, H., Zhou, C., Xu, S. et al. Study on the solidification performance and mechanism of heavy metals by sludge/biomass ash ceramsites, biochar and biomass ash. Environ Geochem Health 46, 78 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01846-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01846-8