Abstract
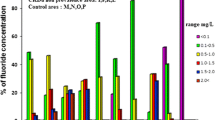
Chronic kidney disease of uncertain etiology (CKDu) is a common health issue among farming communities in the dry zone of Sri Lanka where groundwater fluoride is known to be higher than recommended levels. Excessive environmental ingestion of fluoride is widely considered as a possible factor for the onset of CKDu. This study was carried out to evaluate the serum and urine fluoride levels in biopsy-proven, non-dialysis CKDu patients. Control subjects were selected from the same area without any deteriorated kidney functions. Serum and urine fluoride levels were determined by ion-selective electrode method. Higher content of serum and urine fluoride levels were observed in patients with chronic renal failures. In CKDu cases, the serum fluoride concentrations ranged between 0.47 and 9.58 mg/L (mean 1.39 ± 1.1 mg/L), while urine levels were varied between 0.45 and 6.92 mg/L (mean 1.53 ± 0.8 mg/L). In patients, urine fluoride levels showed a significant difference with the CKDu stage; however, no difference was obtained between genders and age. In endemic controls, serum and urine fluoride levels ranged between 0.51 and 1.92 mg/L (mean = 1.07 ± 0.3 mg/L) and 0.36 and 3.80 mg/L (mean = 1.26 ± 0.6 mg/L), respectively. Significantly higher fluoride in serum and urine was noted in CKDu patients compared to endemic control groups. Higher fluoride exposure via drinking water is possibly the reason for higher fluoride in serum, while excessive urinary excretion would be due to deterioration of the kidney, suggesting a possible nephrotoxic role of environmental fluoride exposure.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdennebi, E. H., Fandi, R., & Lamnaouer, D. (1995). Human fluorosis in Morocco: Analytical and clinical investigations. Veterinary and Human Toxicology,37(5), 465–468.
Al-Wakeel, J. S., Mitwalli, A. H., Huraib, S., Al-Mohaya, S., Abu-Aisha, H., Chaudhary, A. R., et al. (1997). Serum ionic fluoride levels in haemodialysis and continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation,12(7), 1420–1424.
Anand, S., Montez-Rath, M. E., Adasooriya, D., Ratnatunga, N., Kambham, N., Wazil, A., et al. (2019). prospective biopsy-based study of CKD of unknown etiology in Sri Lanka. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology,14(2), 224–232.
Bandara, J. M. R. S., Senevirathna, D. M. A. N., Dasanayake, D. M. R. S. B., Herath, V., Bandara, J. M. R. P., Abeysekara, T., et al. (2008). Chronic renal failure among farm families in cascade irrigation systems in Sri Lanka associated with elevated dietary cadmium levels in rice and freshwater fish (Tilapia). Environmental Geochemistry and Health,30(5), 465–478.
Buzalaf, M. A. R., & Levy, S. M. (2011). Fluoride intake of children: Considerations for dental caries and dental fluorosis. In M. A. R. Buzalaf (Ed.), Fluoride and the oral environment (pp. 1–19). Basel: Karger AG Publishers.
Buzalaf, M. A. R., & Whitford, G. M. (2011). Fluoride metabolism. In M. A. R. Buzalaf (Ed.), Fluoride and the oral environment (pp. 20–36). Basel: Karger AG Publishers.
Cerdas, M. (2005). Chronic kidney disease in Costa Rica. Kidney International,68, S31–S33.
Cerklewski, F. L. (1997). Fluoride bioavailability—Nutritional and clinical aspects. Nutrition Research,17(5), 907–929.
Chandrajith, R., Abeypala, U., Dissanayake, C. B., & Tobschall, H. J. (2007). Fluoride in Ceylon tea and its implications to dental health. Environmental Geochemistry and Health,29(5), 429–434.
Chandrajith, R., Nanayakkara, S., Itai, K., Aturaliya, T. N. C., Dissanayake, C. B., Abeysekera, T., et al. (2011). Chronic kidney diseases of uncertain etiology (CKDue) in Sri Lanka: Geographic distribution and environmental implications. Environmental Geochemistry and Health,33(3), 267–278.
Chandrajith, R., Padmasiri, J. P., Dissanayake, C. B., & Prematilaka, K. M. (2012). Spatial distribution of fluoride in groundwater of Sri Lanka. Journal of the National Science Foundation of Sri Lanka,40(4), 303–309.
Cowell, D. C., & Taylor, W. H. (1981). Ionic fluoride: A study of its physiological variation in man. Annals of Clinical Biochemistry,18(2), 76–83.
Dharma-wardana, M. W. C., Amarasiri, S. L., Dharmawardene, N., & Panabokke, C. R. (2015). Chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology and ground-water ionicity: Study based on Sri Lanka. Environmental Geochemistry and Health,37(2), 221–231.
Dissanayake, C. B., & Chandrajith, R. (1999). Medical geochemistry of tropical environments. Earth Science Reviews,47(3), 219–258.
El Minshawy, O. (2011). End-stage renal disease in the El-Minia Governorate, upper Egypt: An epidemiological study. Saudi Journal of Kidney Diseases and Transplantation,22(5), 1048–1054.
Husdan, H., Vogl, R., Oreopoulos, D., Gryfe, C., & Rapoport, A. (1976). Serum ionic fluoride: Normal range and relationship to age and sex. Clinical Chemistry,22(11), 1884–1888.
Jayatilake, N., Mendis, S., Maheepala, P., & Mehta, F. R. (2013). Chronic kidney disease of uncertain aetiology: Prevalence and causative factors in a developing country. BMC Nephrology,14(1), 180.
Jha, V., Garcia-Garcia, G., Iseki, K., Li, Z., Naicker, S., Plattner, B., et al. (2013). Chronic kidney disease: Global dimension and perspectives. The Lancet,382(9888), 260–272.
Kanduti, D., Sterbenk, P., & Artnik, B. (2016). Fluoride: A review of use and effects on health. Materia Socio-Medica,28(2), 133–137.
Kumar, S., Lata, S., Yadav, J., & Yadav, J. P. (2017). Relationship between water, urine and serum fluoride and fluorosis in school children of Jhajjar District, Haryana, India. Applied Water Science,7(6), 3377–3384.
Levine, K. E., Redmon, J. H., Elledge, M. F., Wanigasuriya, K. P., Smith, K., Munoz, B., et al. (2016). Quest to identify geochemical risk factors associated with chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu) in an endemic region of Sri Lanka—A multimedia laboratory analysis of biological, food, and environmental samples. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,188, 548.
Liu, J.-L., Xia, T., Yu, Y.-Y., Sun, X.-Z., Zhu, Q., He, W., et al. (2005). The dose-effect relationship of water fluoride levels and renal damage in children. Journal of Hygiene Research,34(3), 287–288.
Luke, J. (2001). Fluoride deposition in the aged human pineal gland. Caries Research,35(2), 125–128.
Nanayakkara, S., Senevirathna, S. T. M. L. D., Abeysekera, T., Chandrajith, R., Ratnatunga, N., Gunarathne, E. D. L., et al. (2014). An integrative study of the genetic, social and environmental determinants of chronic kidney disease characterized by tubulointerstitial damages in the North Central Region of Sri Lanka. Journal of Occupational Health,56, 28–38.
O’Neill, E., Awale, G., Daneshmandi, L., Umerah, O., & Lo, K. W.-H. (2018). The roles of ions on bone regeneration. Drug Discovery Today,23(4), 879–890.
Parkins, F. M., Tinanoff, N., Moutinho, M., Anstey, M. B., & Waziri, M. H. (1974). Relationships of human plasma fluoride and bone fluoride to age. Calcified Tissue Research,16(1), 335–338.
Rafique, T., Ahmed, I., Soomro, F., Khan, M. H., & Shirin, K. (2015). Fluoride levels in urine, blood plasma and serum of people living in an endemic fluorosis area in the Thar desert, Pakistan. Journal of the Chemical Society of Pakistan,37(6), 1212–1219.
Rajapurkar, M. M., John, G. T., Kirpalani, A. L., Abraham, G., Agarwal, S. K., Almeida, A. F., et al. (2012). What do we know about chronic kidney disease in India: First report of the Indian CKD registry. BMC Nephrology,13(1), 10.
Ranasinghe, N., Kruger, E., Chandrajith, R., & Tennant, M. (2019). The heterogeneous nature of water well fluoride levels in Sri Lanka: An opportunity to mitigate the dental fluorosis. Community Dentistry and Oral Epidemiology,47, 236–242.
Reddy, D. V., & Gunasekar, A. (2013). Chronic kidney disease in two coastal districts of Andhra Pradesh, India: Role of drinking water. Environmental Geochemistry and Health,35(4), 439–454.
Schiffl, H. H., & Binswanger, U. (1980). Human urinary fluoride excretion as influenced by renal functional impairment. Nephron,26(2), 69–72.
Shimonovitz, S., Patz, D., Ever-Hadani, P., Singer, L., Zacut, D., Kidroni, G., et al. (1995). Umbilical cord fluoride serum levels may not reflect fetal fluoride status. Journal of Perinatal Medicine,23(4), 279–282.
Singer, L., & Ophaug, R. (1979). Concentrations of ionic, total, and bound fluoride in plasma. Clinical Chemistry,25(4), 523–525.
Spak, C.-J., Berg, U., & Ekstrand, J. (1985). Renal clearance of fluoride in children and adolescents. Pediatrics,75(3), 575–579.
Torra, M., Rodamilans, M., & Corbella, J. (1998). Serum and urine ionic fluoride. Biological Trace Element Research,63(1), 67–71.
Torres, C., Aragón, A., González, M., Jakobsson, K., Elinder, C. G., Lundberg, I., et al. (2010). Decreased kidney function of unknown cause in Nicaragua: A community-based survey. American Journal of Kidney Diseases,55(3), 485–496.
Ugran, V., Desai, N. N., Chakraborti, D., Masali, K. A., Mantur, P., Kulkarni, S., et al. (2017). Groundwater fluoride contamination and its possible health implications in Indi taluk of Vijayapura District (Karnataka State), India. Environmental Geochemistry and Health,39(5), 1017–1029.
Usuda, K., Kono, K., Dote, T., Watanabe, M., Shimizu, H., Tanimoto, Y., et al. (2009). Fluoride analysis and fluoride related health problems in clinical, experimental, occupational and environmental aspects: A narrative review. Biomedical Research on Trace Elements,20(4), 274–283.
VanDervort, D. R., López, D. L., Orantes Navarro, C. M., & Rodríguez, D. S. (2014). Spatial distribution of unspecified chronic kidney disease in El Salvador by crop area cultivated and ambient temperature. MEDICC Review,16(2), 31–38.
Vlahos, P., Schensul, S. L., Nanayakkara, N., Chandrajith, R., Haider, L., Anand, S., et al. (2019). Kidney progression project (KiPP): Protocol for a longitudinal cohort study of progression in chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology in Sri Lanka. Global Public Health,14(2), 214–226.
Warnakulasuriya, K. A. A. S., Balasuriya, S., Perera, P. A. J., & Peiris, L. C. L. (1992). Determining optimal levels of fluoride in drinking water for hot, dry climates—A case study in Sri Lanka. Community Dentistry and Oral Epidemiology,20(6), 364–367.
Wesseling, C., Crowe, J., Hogstedt, C., Jakobsson, K., Lucas, R., & Wegman, D. H. (2013). The epidemic of chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology in Mesoamerica: A call for interdisciplinary research and action. American Journal of Public Health,103(11), 1927–1930.
Whitford, G. M. (1999). Fluoride metabolism and excretion in children. Journal of Public Health Dentistry,59(4), 224–228.
Wickramarathna, S., Balasooriya, S., Diyabalanage, S., & Chandrajith, R. (2017). Tracing environmental aetiological factors of chronic kidney diseases in the dry zone of Sri Lanka—A hydrogeochemical and isotope approach. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology,44, 298–306.
Xiong, X. Z., Liu, J. L., He, W. H., Xia, T., He, P., Chen, X. M., et al. (2007). Dose–effect relationship between drinking water fluoride levels and damage to liver and kidney functions in children. Environmental Research,103(1), 112–116.
Zohoori, F. V., Innerd, A., Azevedo, L. B., Whitford, G. M., & Maguire, A. (2015). Effect of exercise on fluoride metabolism in adult humans: A pilot study. Nature Scientific Reports,5, 16905.
Zuo, H., Chen, L., Kong, M., Qiu, L., Lü, P., Wu, P., et al. (2018). Toxic effects of fluoride on organisms. Life Sciences,198, 18–24.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Research Council (NRC) Target Orient research grant (TO 14-05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statements
The study was carried out with the approval of the Ethical Review Board of the Faculty of Medicine, University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka. Written consents were obtained from all subjects before collecting samples.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernando, W.B.N.T., Nanayakkara, N., Gunarathne, L. et al. Serum and urine fluoride levels in populations of high environmental fluoride exposure with endemic CKDu: a case–control study from Sri Lanka. Environ Geochem Health 42, 1497–1504 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00444-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00444-x