Abstract
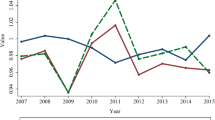
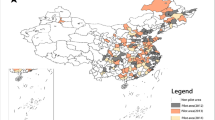
The demand for political promotion brings significant economic growth pressure (EGP) on local officials, which brings considerable economic and environmental impacts and thus theoretically has a significant effect on green total factor productivity (GTFP). However, few studies have explored the theoretical relationship between EGP and GTFP. To fill this gap, this paper based on Chinese prefecture-level cities indicates an inverted U-shaped relationship between EGP and GTFP. Moreover, EGP leads to non-monotonic changes in GTFP through its influence on technological innovation and industrial structure upgrading. The heterogeneity analysis shows that the significant inverted U-shaped relationship between EGP and GTFP exists only in western and northeastern China. Longitudinally, this relationship exists only in the most recent period between 2015 and 2019. The article provides the first evidence of the relationship between EGP and GTFP and offers theoretical and practical insights as well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai H, Hu S, Li K, Shao S (2020) Environmental regulation, total factor productivity, and enterprise duration: evidence from China. Bus Strateg Environ 29(6):2284–2296
Cai L, Wang P (2022) Digital economy and urban green total factor productivity: influencing mechanism and empirical evidence. Stat Decis. https://doi.org/10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2022.09.002
Campos NF, Coricelli F, Frigerio M (2022) The political U: new evidence on democracy and income. IZA discussion paper No. 15598
Cao X, Deng M, Li H (2021) How does e-commerce city pilot improve green total factor productivity? Evidence from 230 cities in China. J Environ Manag 289:112520
Chen Z, Kahn ME, Liu Y, Wang Z (2018) The consequences of spatially differentiated water pollution regulation in China. J Environ Econ Manag 88:468–485
Chen J, Gao M, Cheng S, Hou W, Song M, Liu X et al (2020) County-level CO2 emissions in China. Figshare Dataset. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.12887213.v3
Deryugina T, Heutel G, Miller NH, Molitor D, Reif J (2019) The mortality and medical costs of air pollution: evidence from changes in wind direction. Am Econ Rev 109(12):4178–4219
Du K, Cheng Y, Yao X (2021) Environmental regulation, green technology innovation, and industrial structure upgrading: the road to the green transformation of Chinese cities. Energy Economics 98:105247
Fang C, Cheng J, Zhu Y, Chen J, Peng X (2021a) Green total factor productivity of extractive industries in China: an explanation from technology heterogeneity. Resour Policy 70:101933
Fang L, Hu R, Mao H, Chen S (2021b) How crop insurance influences agricultural green total factor productivity: evidence from Chinese farmers. J Clean Prod 321:128977
Feng C, Huang JB, Wang M (2018) Analysis of green total-factor productivity in China’s regional metal industry: a meta-frontier approach. Resour Policy 58:219–229
Feng Y, Wang X, Liang Z, Hu S, Xie Y, Wu G (2021) Effects of emission trading system on green total factor productivity in China: empirical evidence from a quasi-natural experiment. J Clean Prod 294:126262
Hou S, Song L (2021) Market integration and regional green total factor productivity: evidence from China’s province-level data. Sustainability 13(2):472
Huang Z, Phillips GM, Yang J, Zhang Y (2020) Education and innovation: the long shadow of the cultural revolution (No. w27107). Working paper, https://doi.org/10.3386/w27107
Jiang H, Jiang P, Wang D, Wu J (2021a) Can smart city construction facilitate green total factor productivity? A quasi-natural experiment based on China’s pilot smart city. Sustain Cities Soc 69:102809
Jiang Y, Wang H, Liu Z (2021b) The impact of the free trade zone on green total factor productivity-Evidence from the Shanghai pilot free trade zone. Energy Policy 148:112000
Jin G, Shen K, Li J (2020) Interjurisdiction political competition and green total factor productivity in China: an inverted-U relationship. China Econ Rev 61:101224
Lee CC, Lee CC (2022) How does green finance affect green total factor productivity? Evid China Energy Econ 107:105863
Lee CC, Zeng M, Wang C (2022) Environmental regulation, innovation capability, and green total factor productivity: new evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(26):39384–39399
Leonida L, Patti DMA, Marini A, Navarra P (2015) Political competition and economic growth: a test of two tales. Econ Lett 135:96–99
Li Y, Chen Y (2021) Development of an SBM-ML model for the measurement of green total factor productivity: The case of Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 145:111131
Li T, Liao G (2020) The heterogeneous impact of financial development on green total factor productivity. Front Energy Res 8:29
Li K, Lin B (2017) Economic growth model, structural transformation, and green productivity in China. Appl Energy 187:489–500
Li B, Wu S (2017) Effects of local and civil environmental regulation on green total factor productivity in China: a spatial Durbin econometric analysis. J Clean Prod 153:342–353
Li T, Han D, Ding Y, Shi Z (2020) How does the development of the internet affect green total factor productivity? Evidence from China. IEEE Access 8:216477–216490
Li MM, Wang HJ, Yan K (2021a) Economic growth targets and crowding-out effect of R&D: An empirical study based on multi-objective assessment theory. Nankai Business Rev 24(1):17–26
Li Y, Wu Y, Chen Y, Huang Q (2021b) The influence of foreign direct investment and trade opening on green total factor productivity in the equipment manufacturing industry. Appl Econ 53(57):6641–6654
Li C, Qi Y, Liu S, Wang X (2022) Do carbon ETS pilots improve cities’ green total factor productivity? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Energy Economics 108:105931
Lin B, Chen Z (2018) Does factor market distortion inhibit the green total factor productivity in China? J Clean Prod 197:25–33
Lin B, Xu M (2019) Exploring the green total factor productivity of China’s metallurgical industry under carbon tax: a perspective on factor substitution. J Clean Prod 233:1322–1333
Liu Y, Dong F (2021) How technological innovation impacts urban green economy efficiency in emerging economies: a case study of 278 Chinese cities. Resour Conserv Recycl 169:105534
Liu Z, Xin L (2019) Has China’s belt and road initiative promoted its green total factor productivity?-Evidence from primary provinces along the route. Energy Policy 129:360–369
Liu Y, Yang Y, Li H, Zhong K (2022) Digital economy development, industrial structure upgrading and green total factor productivity: empirical evidence from China’s cities. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(4):2414
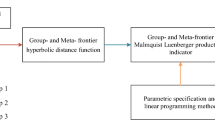
Oh DH, Heshmati A (2010) A sequential Malmquist-Luenberger productivity index: environmentally sensitive productivity growth considering the progressive nature of technology. Energy Econ 32(6):1345–1355
Ramanathan R, Poomkaew B, Nath P (2014) The impact of organizational pressures on environmental performance of firms. Business Ethics Eur Rev 23(2):169–182
Song M, Du J, Tan KH (2018) Impact of fiscal decentralization on green total factor productivity. Int J Prod Econ 205:359–367
Song K, Bian Y, Zhu C, Nan Y (2020) Impacts of dual decentralization on green total factor productivity: evidence from China’s economic transition. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(12):14070–14084
Su F, Tao R, Xi L, Li M (2012) Local officials’ incentives and China’s economic growth: tournament thesis reexamined and alternative explanatory framework. Chin World Econ 20(4):1–18
Sun J, Tang D, Kong H, Boamah V (2022a) Impact of industrial structure upgrading on green total factor productivity in the Yangtze River economic belt. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(6):3718
Sun Y, Tang Y, Li G (2022b) Economic growth targets and green total factor productivity: evidence from China. J Environ Planning Manag. https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2022.2061335
Tang P, Jiang Q, Mi L (2021a) One-vote veto: the threshold effect of environmental pollution in China’s economic promotion tournament. Ecol Econ 185:107069
Tang XM, Huang HW, Tan YX, Li FD (2021b) The pressure of economic growth and the economic cost of environmental protection-Empirical analysis based on “two control areas” in China. Indus Econ Rev 4:89–102. https://doi.org/10.19313/j.cnki.cn10-1223/f.2021.04.005
Wang KL, Pang SQ, Ding LL, Miao Z (2020) Combining the biennial Malmquist-Luenberger index and panel quantile regression to analyze the green total factor productivity of the industrial sector in China. Sci Total Environ 739:140280
Wang H, Cui H, Zhao Q (2021a) Effect of green technology innovation on green total factor productivity in China: evidence from spatial Durbin model analysis. J Clean Prod 288:125624
Wang M, Pang S, Hmani I, Hmani I, Li C, He Z (2021b) Towards sustainable development: How does technological innovation drive the increase in green total factor productivity? Sustain Dev 29(1):217–227
Wang M, Xu M, Ma S (2021c) The effect of the spatial heterogeneity of human capital structure on regional green total factor productivity. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 59:427–441
Wang XB, Liu SL, Huang LX (2021d) Economic growth pressure and regional innovation-Evidence from the setting of economic growth targets. China Econ Quart 21(04):1147–1166. https://doi.org/10.13821/j.cnki.ceq.2021.04.02
Wu H, Yang J, Yang Q (2021) The pressure of economic growth and the issuance of urban investment bonds: based on panel data from 2005 to 2011 in China. J Asian Econ 76:101341
Xie F, Zhang B, Wang N (2021) Non-linear relationship between energy consumption transition and green total factor productivity: a perspective on different technology paths. Sustain Prod Consum 28:91–104
Xu Y, Dong B, Chen Z (2022) Can foreign trade and technological innovation affect green development: evidence from countries along the Belt and Road. Econ Chang Restruct 55(2):1063–1090
Yang X, Jia Z, Yang Z (2021a) How does technological progress impact transportation green total factor productivity: a spatial econometric perspective. Energy Rep 7:3935–3950
Yang X, Wang W, Wu H, Wang J, Ran Q, Ren S (2021b) The impact of the new energy demonstration city policy on the green total factor productivity of resource-based cities: Empirical evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. J Environ Plann Manag. https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2021.1988529
Yang Y, Wei X, Wei J, Gao X (2022) Industrial structure upgrading, green total factor productivity and carbon emissions. Sustainability 14(2):1009
Yi Z, Wu L (2022) Analysis of the impact mechanism of environmental regulations on corporate environmental proactivity—based on the perspective of political connections. Bus Ethics Environ Respons 31(2):323–345
Yu D, Li X, Yu J, Li H (2021) The impact of the spatial agglomeration of foreign direct investment on green total factor productivity of Chinese cities. J Environ Manag 290:112666
Zhang JK (2022) Tourism, urbanization, and urban income inequality in China. Tour Econ. https://doi.org/10.1177/13548166221108121
Zhang Y, Wu Z (2021) Intelligence and green total factor productivity based on China’s province-level manufacturing data. Sustainability 13(9):4989
Zhang J, Zhang Y (2022) Does tourism contribute to the nighttime economy? Evidence from China. Curr Issues Tourism. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2022.2053073
Zhang J, Lu G, Skitmore M, Ballesteros-Pérez P (2021) A critical review of the current research mainstreams and the influencing factors of green total factor productivity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(27):35392–35405
Zhang Y, Xu S, Zhang J (2022a) How economic growth pressure impact carbon emissions: evidence for China. Econ Res Ekonomska Istraživanja. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2022.2159473
Zhang Y, Zhou R, Chen N (2022b) An empirical study on coordinated development of energy consumption structure and green total factor productivity under spatial interaction. Econ Res Ekonomska Istraživanja. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2022.2084436
Zhao W, Xu Y (2022) Public expenditure and green total factor productivity: evidence from Chinese prefecture-level cities. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(9):5755
Zhao C, Dong K, Taghizadeh-Hesary F (2023) Can smart transportation enhance green development efficiency? Econ Chang Restruct 56:825–857
Zhong M, Wang P, Ji M, Zeng XH, Wei HX (2021) Promote or inhibit: economic goal pressure and residents’ health. Front Public Health 9:725957
Zhong S, Li J, Zhang D (2022) Measurement of green total factor productivity on Chinese pig breeding: from the perspective of regional differences. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(18):27479–27495
Zhou L (2007) Governing China’s local officials: an analysis of promotion tournament model. Econ Res J 7:36–50 (In Chinese)
Zhou Y, Xu Y, Liu C, Fang Z, Fu X, He M (2019) The threshold effect of China’s financial development on green total factor productivity. Sustainability 11(14):3776
Zhu J, Lin B (2022) Economic growth pressure and energy efficiency improvement: empirical evidence from Chinese cities. Appl Energy 307:118275
Zhu X, Chen Y, Feng C (2018) Green total factor productivity of China’s mining and quarrying industry: a global data envelopment analysis. Resour Policy 57:1–9
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 71764027.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Zhang, Y. Examining the effects of economic growth pressure on green total factor productivity: evidence from China. Econ Change Restruct 56, 4309–4337 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10644-023-09555-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10644-023-09555-z