Summary
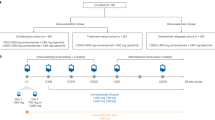
Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) are recommended first-line treatments in EGFR-mutated (EGFRm) non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, acquired resistance (e.g. MET amplification) is frequently observed. Savolitinib (volitinib, HMPL-504, AZD6094) is an oral, potent, and highly selective MET-TKI. In this phase Ib, open-label, multicenter study, we enrolled Chinese patients with EGFRm advanced NSCLC, whose disease progressed following prior EGFR-TKI treatment. In the safety run-in, patients received savolitinib 600 or 800 mg plus gefitinib 250 mg orally once daily, and dose-limiting toxicities were recorded. In the expansion phase, patients with MET amplification received savolitinib plus gefitinib. The primary endpoint was safety/tolerability. Secondary endpoints included antitumor activity. Thirteen patients were enrolled in the safety phase (median age 52 years, 46% female) and 51 enrolled in the expansion phase (median age 61 years, 67% female). No dose-limiting toxicities were reported in either dose group during the safety run-in. Adverse events of grade ≥ 3 in the safety run-in and expansion phases (n = 57) were reported in 21 (37%) patients. The most frequently reported adverse events (all grades) were: vomiting (n = 26, 46%), nausea (n = 23, 40%), increased aspartate aminotransferase (n = 22, 39%). Of four deaths, none were treatment-related. The objective response rates in EGFR T790M-negative, −positive, and -unknown patients were 52% (12/23), 9% (2/23), and 40% (2/5), respectively. Savolitinib 600 mg plus gefitinib 250 mg once daily had an acceptable safety profile and demonstrated promising antitumor activity in EGFRm, MET-amplified advanced NSCLC patients who had disease progression on EGFR-TKIs. NCT02374645, Date of registration: March 2nd 2015.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Planchard D, Popat S, Kerr K et al (2018) Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 29:iv192–iv237
Wu YL, Planchard D, Lu S, Sun H, Yamamoto N, Kim DW, Tan DSW, Yang JCH, Azrif M, Mitsudomi T, Park K, Soo RA, Chang JWC, Alip A, Peters S, Douillard JY (2019) Pan-Asian adapted clinical practice guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a CSCO-ESMO initiative endorsed by JSMO, KSMO, MOS, SSO and TOS. Ann Oncol 30:171–210
Sequist LV, Yang JC, Yamamoto N et al (2013) Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol 31:3327–3334
Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, Palmero R, Garcia-Gomez R, Pallares C, Sanchez JM, Porta R, Cobo M, Garrido P, Longo F, Moran T, Insa A, de Marinis F, Corre R, Bover I, Illiano A, Dansin E, de Castro J, Milella M, Reguart N, Altavilla G, Jimenez U, Provencio M, Moreno MA, Terrasa J, Muñoz-Langa J, Valdivia J, Isla D, Domine M, Molinier O, Mazieres J, Baize N, Garcia-Campelo R, Robinet G, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Lopez-Vivanco G, Gebbia V, Ferrera-Delgado L, Bombaron P, Bernabe R, Bearz A, Artal A, Cortesi E, Rolfo C, Sanchez-Ronco M, Drozdowskyj A, Queralt C, de Aguirre I, Ramirez JL, Sanchez JJ, Molina MA, Taron M, Paz-Ares L, Spanish Lung Cancer Group in collaboration with Groupe Français de Pneumo-Cancérologie and Associazione Italiana Oncologia Toracica (2012) Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 13:239–246
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ichinose Y, Nishiwaki Y, Ohe Y, Yang JJ, Chewaskulyong B, Jiang H, Duffield EL, Watkins CL, Armour AA, Fukuoka M (2009) Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 361:947–957
Oxnard GR, Arcila ME, Sima CS, Riely GJ, Chmielecki J, Kris MG, Pao W, Ladanyi M, Miller VA (2011) Acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant lung cancer: distinct natural history of patients with tumors harboring the T790M mutation. Clin Cancer Res 17:1616–1622
Jenkins S, Chih-Hsin Yang J, Janne PA et al (2017) EGFR mutation analysis for prospective patient selection in two phase II registration studies of osimertinib. J Thorac Oncol 12:1247–1256
Kuiper JL, Heideman DA, Thunnissen E, Paul MA, van Wijk A, Postmus PE, Smit EF (2014) Incidence of T790M mutation in (sequential) rebiopsies in EGFR-mutated NSCLC-patients. Lung Cancer 85:19–24
Wang ZF, Ren SX, Li W, Gao GH (2018) Frequency of the acquired resistant mutation T790 M in non-small cell lung cancer patients with active exon 19Del and exon 21 L858R: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 18:148
Papadimitrakopoulou VA, Wu YL, Han JY et al (2018) LBA51 analysis of resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in patients with EGFR T790M advanced NSCLC from the AURA3 study. Ann Oncol 29:mdy424.064–mdy424.064
Yu HA, Arcila ME, Rekhtman N, Sima CS, Zakowski MF, Pao W, Kris MG, Miller VA, Ladanyi M, Riely GJ (2013) Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin Cancer Res 19:2240–2247
Oxnard GR, Hu Y, Mileham KF, Husain H, Costa DB, Tracy P, Feeney N, Sholl LM, Dahlberg SE, Redig AJ, Kwiatkowski DJ, Rabin MS, Paweletz CP, Thress KS, Jänne PA (2018) Assessment of resistance mechanisms and clinical implications in patients with EGFR T790M-positive lung Cancer and acquired resistance to Osimertinib. JAMA Oncol 4:1527–1534
Piotrowska Z, Isozaki H, Lennerz JK, Gainor JF, Lennes IT, Zhu VW, Marcoux N, Banwait MK, Digumarthy SR, Su W, Yoda S, Riley AK, Nangia V, Lin JJ, Nagy RJ, Lanman RB, Dias-Santagata D, Mino-Kenudson M, Iafrate AJ, Heist RS, Shaw AT, Evans EK, Clifford C, Ou SHI, Wolf B, Hata AN, Sequist LV (2018) Landscape of acquired resistance to osimertinib in EGFR-mutant NSCLC and clinical validation of combined EGFR and RET inhibition with Osimertinib and BLU-667 for acquired RET fusion. Cancer Discov 8:1529–1539
Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D et al (2011) Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci Transl Med 3:75ra26
Ramalingam SS, Cheng Y, Zhou C et al (2018) LBA 50 mechanisms of acquired resistance to first-line osimertinib: preliminary data from the phase III FLAURA study. Ann Oncol 29:LBA50
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO, Lindeman N, Gale CM, Zhao X, Christensen J, Kosaka T, Holmes AJ, Rogers AM, Cappuzzo F, Mok T, Lee C, Johnson BE, Cantley LC, Jänne PA (2007) MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 316:1039–1043
Bean J, Brennan C, Shih JY, Riely G, Viale A, Wang L, Chitale D, Motoi N, Szoke J, Broderick S, Balak M, Chang WC, Yu CJ, Gazdar A, Pass H, Rusch V, Gerald W, Huang SF, Yang PC, Miller V, Ladanyi M, Yang CH, Pao W (2007) MET amplification occurs with or without T790M mutations in EGFR mutant lung tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:20932–20937
Hua Y, Shen L, Gan H et al (2015) Abstract CT305: phase I studies of a selective cMet inhibitor AZD6094 (HMPL504/volitinib) in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Res 75:CT305
Jia H, Dai G, Weng J et al (2014) Discovery of (S)-1-(1-(Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-6-yl)ethyl)-6-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1H-[1,2, 3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazine (volitinib) as a highly potent and selective mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (c-met) inhibitor in clinical development for treatment of cancer. J Med Chem 57:7577–7589
Gavine PR, Ren Y, Han L, Lv J, Fan S, Zhang W, Xu W, Liu YJ, Zhang T, Fu H, Yu Y, Wang H, Xu S, Zhou F, Su X, Yin XL, Xie L, Wang L, Qing W, Jiao L, Su W, Wang QM (2015) Volitinib, a potent and highly selective c-met inhibitor, effectively blocks c-met signaling and growth in c-MET amplified gastric cancer patient-derived tumor xenograft models. Mol Oncol 9:323–333
D'Cruz C, Barry E, Henry R et al (2015) Abstract 761. Changing the paradigm for treating drug resistance in NSCLC: novel combinations of AZD6094, a selective MET inhibitor, and an irreversible, selective (EGFRm/T790M) EGFRTKI, AZD9291. Cancer Res 75:761
Oxnard GR, Ramalingam SS, Ahn M-J et al (2015) Preliminary results of TATTON, a multi-arm phase Ib trial of AZD9291 combined with MEDI4736, AZD6094 or selumetinib in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 33:abstract 2509
Gan HK, Millward M, Hua Y, Qi C, Sai Y, Su W, Wang J, Zhang L, Frigault MM, Morgan S, Yang L, Lickliter JD (2019) First-in-human phase I study of the selective MET inhibitor, savolitinib, in patients with advanced solid tumors: safety, pharmacokinetics, and antitumor activity. Clin Cancer Res 25:4924–4932
Ahn M, Han J, Sequist L, Cho BC, Lee JS, Kim S, Su W, Tsai C, Yang JC, Yu H, Horn L, Lee K, Haddad V, Frigault M, Ahmed G, Yang L, Ghiorghiu D, Oxnard G (2017) TATTON Ph Ib expansion cohort: osimertinib plus savolitinib for pts with EGFR-mutant MET-amplified NSCLC after progression on prior EGFR-TKI. J Thorac Oncol 12:S1768 (OA 09.03)
Choueiri TK, Plimack E, Arkenau HT, Jonasch E, Heng DYC, Powles T, Frigault MM, Clark EA, Handzel AA, Gardner H, Morgan S, Albiges L, Pal SK (2017) Biomarker-based phase II trial of Savolitinib in patients with advanced papillary renal cell Cancer. J Clin Oncol 35:2993–3001
Huang J, Meng L, Yang B, Sun S, Luo Z, Chen H (2020) Safety profile of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a disproportionality analysis of FDA adverse event reporting system. Sci Rep 10:4803
Choueiri TK, Vaishampayan U, Rosenberg JE, Logan TF, Harzstark AL, Bukowski RM, Rini BI, Srinivas S, Stein MN, Adams LM, Ottesen LH, Laubscher KH, Sherman L, McDermott DF, Haas NB, Flaherty KT, Ross R, Eisenberg P, Meltzer PS, Merino MJ, Bottaro DP, Linehan WM, Srinivasan R (2013) Phase II and biomarker study of the dual MET/VEGFR2 inhibitor foretinib in patients with papillary renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 31:181–186
Blackhall F, Cappuzzo F (2016) Crizotinib: from discovery to accelerated development to front-line treatment. Ann Oncol 27(Suppl 3):iii35–iii41
Ruiz-Morales JM, Heng DY (2016) Cabozantinib in the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma: clinical trial evidence and experience. Ther Adv Urol 8:338–347
Patel N, Wu P, Zhang H (2017) Comparison of gefitinib as first- and second-line therapy for advanced lung adenocarcinoma patients with positive exon 21 or 19 del epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. Cancer Manag Res 9:243–248
Chen HJ, Mok TS, Chen ZH, Guo AL, Zhang XC, Su J, Wu YL (2009) Clinicopathologic and molecular features of epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation and c-MET amplification in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant Chinese non-small cell lung cancer. Pathol Oncol Res 15:651–658
Hartmaier RJ, Han J-Y, Cho BC et al (2019) Abstract 4897: detection of MET-mediated EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) resistance in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): biomarker analysis of the TATTON study. Cancer Res 79:4897
Salgia R (2017) MET in lung Cancer: biomarker selection based on scientific rationale. Mol Cancer Ther 16:555–565
Wang Y, Li L, Han R, Jiao L, Zheng J, He Y (2018) Clinical analysis by next-generation sequencing for NSCLC patients with MET amplification resistant to osimertinib. Lung Cancer 118:105–110
Piotrowska Z, Thress KS, Mooradian M et al (2017) MET amplification (amp) as a resistance mechanism to osimertinib. J Clin Oncol 35:abstract 9020
Wu YL, Zhang L, Kim DW, Liu X, Lee DH, Yang JCH, Ahn MJ, Vansteenkiste JF, Su WC, Felip E, Chia V, Glaser S, Pultar P, Zhao S, Peng B, Akimov M, Tan DSW (2018) Phase Ib/II study of capmatinib (INC280) plus gefitinib after failure of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor therapy in patients with EGFR-mutated, MET factor-dysregulated non-small-cell lung Cancer. J Clin Oncol 36:3101–3109
Cheng Y, Zhou J, Lu S et al (2018) 1377O Phase II study of tepotinib + gefitinib (TEP+GEF) in MET-positive (MET+)/epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant (MT) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann Oncol 29:viii493–viii547
Yu H, Ahn M-J, Kim S-W et al (2019) Abstract CT032. TATTON phase Ib expansion cohort: Osimertinib plus savolitinib for patients (pts) with EGFR-mutant, MET-amplified NSCLC after progression on prior first/second-generation epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI). Cancer Res 79(13). https://doi.org/10.1158/1538-7445.AM2019-CT032
Sequist LV, Han J-Y, Ahn M-J, Cho BC, Yu H, Kim SW, Yang JCH, Lee JS, Su WC, Kowalski D, Orlov S, Cantarini M, Verheijen RB, Mellemgaard A, Ottesen L, Frewer P, Ou X, Oxnard G (2020) Osimertinib plus savolitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive, MET-amplified, non-small-cell lung cancer after progression on EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors: interim results from a multicentre, open-label, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol 21:373–386
Oxnard GR, Cantarini M, Frewer P, Hawkins G, Peters J, Howarth P, Ahmed GF, Sahota T, Hartmaier R, Li-Sucholeiki X, Ahn MJ (2019) SAVANNAH: a phase II trial of osimertinib plus savolitinib for patients (pts) with EGFR-mutant, MET-driven (MET+), locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), following disease progression on osimertinib. J Clin Oncol 37:TPS9119
Swaisland HC, Smith RP, Laight A, Kerr DJ, Ranson M, Wilder-Smith CH, Duvauchelle T (2005) Single-dose clinical pharmacokinetic studies of gefitinib. Clin Pharmacokinet 44:1165–1177
Acknowledgments
We thank all the patients who participated in this study and their families, as well as the staff and investigators at all of the study sites. We would also like to thank Julia DeCesare for her contribution in management of the study, Xinying Su for her help in overseeing the central testing of MET, Harry Yang for expert advice on the Human Genetics Resources Administration of China, Song Ren for her help with managing and reporting pharmacokinetic data and Paul Frewer for assistance with statistical analysis. Medical writing support funded by AstraZeneca in accordance with Good Publications Practice (GPP3) guidelines (http://www.ismpp.org/gpp3) was provided by Bernadette Tynan, MSc, on behalf of Ashfield Healthcare communications, Macclesfield, UK, part of UDG Healthcare plc.
Role of the funder/sponsor
AstraZeneca were involved in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication and as such are included in the author list and acknowledgments.
Data sharing statement
Data underlying the findings described in this manuscript may be obtained in accordance with AstraZeneca’s data sharing policy described at https://astrazenecagrouptrials.pharmacm.com/ST/Submission/Disclosure.
Funding
The study (NCT02374645) was funded by AstraZeneca, Cambridge, UK, the manufacturer of savolitinib and gefitinib. Hutchison MediPharma authorized AstraZeneca to conduct this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yi-Long Wu (International co-ordinating investigator) had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Dr. Jin-Ji Yang, Dr. Yong-Qian Shu, Dr. Caicun Zhou, Dr. Melanie M. Frigault, Dr. Coumaran Egile, Dr. Shethah Morgan and Dr. Yi-Long Wu designed the study.
Dr. Jin-Ji Yang, Mr. Jian Fang, Dr. Yong-Qian Shu, Dr. Jian-Hua Chang, Dr. Gong-Yan Chen, Dr. Jian Xing He, Dr. Wei Li, Ms. Xiao-Qing Liu, Dr. Nong Yang, Dr. Caicun Zhou, Dr. Jian An Huang, Dr. Melanie M. Frigault, Dr. Ryan Hartmaier, Dr. Shethah Morgan and Dr. Remy B. Verheijen collected the data.
Dr. Jin-Ji Yang, Dr. Yong-Qian Shu, Dr. Melanie M. Frigault, Dr. Ghada F. Ahmed, Dr. Coumaran Egile, Dr. Shethah Morgan, Dr. Remy B. Verheijen, Dr. Anders Mellemgaard, Ms. Liu Yang and Dr. Yi-Long Wu analyzed and interpreted the study data.
All authors critically reviewed the manuscript and approved the final version for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Melanie M. Frigault, Ryan Hartmaier, Ghada F. Ahmed, Coumaran Egile, Shethah Morgan, Remy B. Verheijen and Anders Mellemgaard are AstraZeneca employees and shareholders. Ryan Hartmaier also owns shares in Foundation Medicine, and has a patent pending for Foundation Medicine. Melanie M. Frigault is also a patent holder for AstraZeneca. Yi-Long Wu has received personal fees from AstraZeneca, Roche, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Sanofi; and grants from AstraZeneca, Roche, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Jin-Ji Yang declares no conflict of interest. Jian Fang declares no conflict of interest. Yong-Qian Shu declares no conflict of interest. Jian-Hua Chang declares no conflict of interest. Jian Xing He declares no conflict of interest. Wei Li declares no conflict of interest. Xiao-Qing Liu declares no conflict of interest. Nong Yang declares no conflict of interest. Caicun Zhou declares no conflict of interest. Jian An Huang declares no conflict of interest. Liu Yang declares no conflict of interest. No other disclosures were reported.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1.73 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, JJ., Fang, J., Shu, YQ. et al. A phase Ib study of the highly selective MET-TKI savolitinib plus gefitinib in patients with EGFR-mutated, MET-amplified advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Invest New Drugs 39, 477–487 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-020-01010-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-020-01010-4