Abstract
Background
Tobacco smoking is a known risk factor for progression of chronic pancreatitis (CP).
Aim
We compare clinical outcomes of CP patients with current or former smoking with those who have never smoked.
Methods
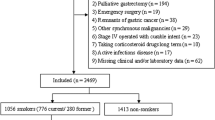
We reviewed all patients with followed at our Pancreas Center from 2016 to 2021, comparing the demographics, clinical features, comorbidities, outcomes, and resource utilization between smokers and non-smokers.
Results
Of 439 CP patients, 283 were smokers (125 current, 158 former). Significantly more smokers were men (58.3% vs 40.4%), with alcoholic CP (45.5% vs 12.1%), chronic abdominal pain (77.7% vs 65.4%), anxiety and depression (22.6% vs 14.1% and 38.9% vs 23.1%), and with more local pancreatic complications [splanchnic vein thrombosis (15.7% vs 5.13%), pseudocyst (42.7% vs 23.7%), biliary obstruction (20.5% vs 5.88%)], exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (65.8% vs 46.2%), hospitalizations (2.59 vs 1.75 visits), and emergency department visits (8.96% vs 3.25%). Opioid and neuromodulator use were significantly higher (59.2% vs 30.3% and 58.4% vs 31.2%). Current smokers had worse outcomes than former smokers. Multivariate analysis controlling for multiple factors identified smoking as an independent predictor of chronic abdominal pain (OR 2.49, CI 1.23–5.04, p = 0.011), opioid (OR 2.36, CI 1.35–4.12, p = 0.002), neuromodulators (OR 2.55, CI 1.46–4.46, p = 0.001), and non-opioid-controlled medications (OR 2.28, CI 1.22–4.30, p = 0.01) use, as well as splanchnic vein thromboses (OR 2.65, CI 1.02–6.91, p = 0.045) and biliary obstruction (OR 4.12, CI 1.60–10.61, p = 0.003).
Conclusion
CP patients who smoke or formerly smoked have greater morbidity and worse outcomes than non-smokers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh VK, Yadav D, Garg PK. Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Pancreatitis: A Review. Jama 2019;322:2422–2434.
Talamini G, Bassi C, Falconi M et al. Alcohol and smoking as risk factors in chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 1999;44:1303–1311. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1026670911955.
Maisonneuve P, Lowenfels AB, Müllhaupt B et al. Cigarette smoking accelerates progression of alcoholic chronic pancreatitis. Gut 2005;54:510–514.
Mavilakandy A, Oyebola T, Boyce R et al. Pilot study examining the impact of a specialist multidisciplinary team clinic for patients with chronic pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2020;20:1661–1666.
Olesen SS, Kuhlmann L, Novovic S et al. Association of multiple patient and disease characteristics with the presence and type of pain in chronic pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;35:326–333.
Talamini G, Bassi C, Falconi M et al. Pain relapses in the first 10 years of chronic pancreatitis. Am J Surg 1996;171:565–569.
Delhaye M, Arvanitakis M, Verset G, Cremer M, Devière J. Long-term clinical outcome after endoscopic pancreatic ductal drainage for patients with painful chronic pancreatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004;2:1096–1106.
Tolstrup JS, Kristiansen L, Becker U, Grønbaek M. Smoking and risk of acute and chronic pancreatitis among women and men: a population-based cohort study [published correction appears in Arch Intern Med. 2010 Sep 13;170(16):1424]. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169:603–609. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinternmed.2008.601.
Lankisch PG, Breuer N, Bruns A, Weber-Dany B, Lowenfels AB, Maisonneuve P. Natural history of acute pancreatitis: a long-term population-based study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:2797–2806. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2009.405.
Catalano MF, Sahai A, Levy M et al. EUS-based criteria for the diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis: the Rosemont classification. Gastrointest Endosc 2009;69:1251–1261.
Wickham H, Averick M, Bryan J, Chang W, McGowan LD, Francois R, Grolemund G et al. Welcome to the tidyverse. Journal of Open Source Software 2019;4:1686. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.01686.
Alexandre M, Pandol SJ, Gorelick FS, Thrower EC. The emerging role of smoking in the development of pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2011;11:469–474. https://doi.org/10.1159/000332196.
Ye X, Lu G, Huai J, Ding J. Impact of smoking on the risk of pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0124075. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124075.
Funding
No financial support was available for this study other than funding of the Pancreas Fellowship to Ishani Shah through the Art Hilsinger/Barbara Janson Fellowship in Pancreatic Disease at BIDMC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LC, RLB, and SGH participated in the manuscript drafting, LC, RLB, and IS participated in the data collection/interpretation, SGH, SDF, WY, AA, and DJK participated in the manuscript supervision/editing, SGS and IS participated in the project design.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest pertaining to this manuscript.
Ethical approval
Our Institutional Review Board (IRB) approved this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liyen Cartelle, A., Bocchino, R.L., Shah, I. et al. Smoking Is Associated with Worse Clinical Outcomes in Chronic Pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci 68, 2667–2673 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-023-07841-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-023-07841-4