Abstract
Background
The mechanism of cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer (GC) is still elusive; several recent evidences proposed that chemoresistant tumor cells acquired aggressive behaviors.
Aims
This study was aimed to investigate the mechanism of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and angiogenesis in chemoresistant GC.
Methods
Bioinformatics analysis and function or mechanism experiments including RT-qPCR, immunofluorescence, Western blot, luciferase reporter assay, Chromatin immunoprecipitation, Chicken chorioallantoic membrane assay and animal experiments were applied to evaluate the role of EGR1-CCL2 feedback loop.
Results
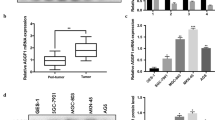
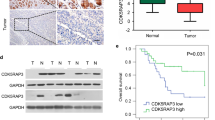
Compared with the parental cell line SGC7901, cisplatin resistant SGC7901R cells underwent EMT and showed increased angiogenic capabilities. Mechanistically, SGC7901R cells showed increased levels of EGR1, which could transcriptionally activate the angiogenic factor CCL2 and EMT regulator ZEB2. Reciprocally, CCL2 activated the CCR2-ERK-ELK1-EGR1 pathway, thus forming a positive feed-forward loop. Moreover, CCL2 in culture medium of SGC7901R cells promoted angiogenesis of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs). EGR1 expression was positively correlated with CCL2 and ZEB2 in clinical GC tissues, and the depletion of ERG1 could also decrease microvessel density and ZEB2 expression in metastatic nodules of nude mice.
Conclusions
EGR1-CCL2 feedback loop might exert critical roles on EMT and angiogenesis of chemoresistant GC.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thrift AP, El-Serag HB. Burden of gastric cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;18:534–542.
J.G.C.A.j.k.k.-m.a. jp, Japanese gastric cancer treatment guidelines 2018, Gastric Cancer, 2020; 1–21.
Kelland L. The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy, Nature reviews. Cancer 2007;7:573–584.
Madden EC, Gorman AM, Logue SE, Samali A. Tumour cell secretome in chemoresistance and tumour recurrence. Trends Cancer 2020;6:489–505.
Dongre A, Weinberg RA. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial–mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2019;20:69–84.
Yeung KT, Yang J. Epithelial–mesenchymal transition in tumor metastasis. Mol Oncol 2017;11:28–39.
van Staalduinen J, Baker D, Ten Dijke P, van Dam H. Epithelial–mesenchymal-transition-inducing transcription factors: New targets for tackling chemoresistance in cancer? Oncogene 2018;37:6195–6211.
Zhang B, Ling T, Zhaxi P, Cao Y, Qian L, Zhao D, Kang W, Zhang W, Wang L, Xu G. Proton pump inhibitor pantoprazole inhibits gastric cancer metastasis via suppression of telomerase reverse transcriptase gene expression. Cancer Lett 2019;452:23–30.
Dong J, Wang R, Ren G, Li X, Wang J, Sun Y, Liang J, Nie Y, Wu K, Feng B. HMGA2–FOXL2 axis regulates metastases and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of chemoresistant gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2017;23:3461–3473.
Liu H-T, Liu S, Liu L, Ma R-R, Gao P. EGR1-mediated transcription of lncRNA-HNF1A-AS1 promotes cell-cycle progression in gastric cancer. Cancer Res 2018;78:5877–5890.
Tang T, Zhu Q, Li X, Zhu G, Deng S, Wang Y, Ni L, Chen X, Zhang Y, Xia T. Protease Nexin I is a feedback regulator of EGF/PKC/MAPK/EGR1 signaling in breast cancer cells metastasis and stemness. Cell Death Disease 2019;10:1–17.
Jing Z, Ye X, Ma X, Hu X, Yang W, Shi J, Chen G, Gong L. SNGH16 regulates cell autophagy to promote Sorafenib Resistance through suppressing miR-23b-3p via sponging EGR1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med 2020;9:4324–4338.
Zhang W, Tong H, Zhang Z, Shao S, Liu D, Li S, Yan Y. Transcription factor EGR1 promotes differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by regulating MyoG gene expression. J Cell Physiol 2018;233:350–362.
Meng X, Brodsky MH, Wolfe SA. A bacterial one-hybrid system for determining the DNA-binding specificity of transcription factors. Nat Biotechnol 2005;23:988–994.
Ferraro B, Bepler G, Sharma S, Cantor A, Haura EB. EGR1 predicts PTEN and survival in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 2005;23:1921–1926.
Kim J, Kang HS, Lee YJ, Lee HJ, Yun J, Shin JH, Lee CW, Kwon BM, Hong SH. EGR1-dependent PTEN upregulation by 2-benzoyloxycinnamaldehyde attenuates cell invasion and EMT in colon cancer. Cancer Lett 2014;349:35–44.
Yang Y, Wu F, Zhang J, Sun R, Li F, Li Y, Chang SE, Wang L, Wang X, Liu L. EGR1 interacts with DNMT3L to inhibit the transcription of miR-195 and plays an anti-apoptotic role in the development of gastric cancer. J Cell Mol Med 2019;23:7372–7381.
Ma Z, Gao X, Shuai Y, Wu X, Yan Y, Xing X, Ji J. EGR1‐mediated linc01503 promotes cell cycle progression and tumorigenesis in gastric cancer, Cell Prolif, 2020; e12922.
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2005;102:15545–15550.
Puisieux A, Brabletz T, Caramel J. Oncogenic roles of EMT-inducing transcription factors. Nat Cell Biol 2014;16:488–494.
Tang C, Sun R, Wen G, Zhong C, Yang J, Zhu J, Cong Z, Luo X, Ma C. Bromocriptine and cabergoline induce cell death in prolactinoma cells via the ERK/EGR1 and AKT/mTOR pathway respectively. Cell Death Disease 2019;10:1–14.
Shi J, Li F, Yao X, Mou T, Xu Z, Han Z, Chen S, Li W, Yu J, Qi X. The HER4-YAP1 axis promotes trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive gastric cancer by inducing epithelial and mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 2018;37:3022–3038.
Kinehara M, Kawamura S, Mimura S, Suga M, Hamada A, Wakabayashi M, Nikawa H, Furue MK. Protein kinase C-induced early growth response protein-1 binding to SNAIL promoter in epithelial–mesenchymal transition of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 2014;23:2180–2189.
Lamouille S, Xu J, Derynck R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2014;15:178–196.
De Palma M, Biziato D, Petrova TV. Microenvironmental regulation of tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 2017;17:457.
He M, Yu W, Chang C, Miyamoto H, Liu X, Jiang K, Yeh S. Estrogen receptor α promotes lung cancer cell invasion via increase of and cross-talk with infiltrated macrophages through the CCL2/CCR2/MMP9 and CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling pathways. Mol Oncol 2020;14:1779–1799.
Yao M, Fang W, Smart C, Hu Q, Huang S, Alvarez N, Fields P, Cheng N. CCR2 chemokine receptors enhance growth and cell-cycle progression of breast cancer cells through SRC and PKC activation. Mol Cancer Res 2019;17:604–617.
Xu W, Wei Q, Han M, Zhou B, Wang H, Zhang J, Wang Q, Sun J, Feng L, Wang S. CCL2-SQSTM1 positive feedback loop suppresses autophagy to promote chemoresistance in gastric cancer. Int J Biol Sci 2018;14:1054.
Whiteside T. The tumor microenvironment and its role in promoting tumor growth. Oncogene 2008;27:5904–5912.
Balkwill FR, Capasso M, Hagemann T. The tumor microenvironment at a glance, The Company of Biologists Ltd, 2012.
Gerarduzzi C, Hartmann U, Leask A, Drobetsky E. The matrix revolution: matricellular proteins and restructuring of the cancer microenvironment. Cancer Res 2020;80:2705–2717.
Hinshaw DC, Shevde LA. The tumor microenvironment innately modulates cancer progression. Cancer Res 2019;79:4557–4566.
Wang Y-H, Dong Y-Y, Wang W-M, Xie X-Y, Wang Z-M, Chen R-X, Chen J, Gao D-M, Cui J-F, Ren Z-G. Vascular endothelial cells facilitated HCC invasion and metastasis through the Akt and NF-κB pathways induced by paracrine cytokines. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2013;32:1–11.
Funding
This work was supported by the Youth Fund Program of The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, J., Gao, Y., Lin, S. et al. EGR1-CCL2 Feedback Loop Maintains Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Cisplatin-Resistant Gastric Cancer Cells and Promotes Tumor Angiogenesis. Dig Dis Sci 67, 3702–3713 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-021-07250-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-021-07250-5