Abstract
Background
Phospholipase C delta 1 (PLCD1) has been found to be abnormally expressed in various cancers. However, the potential roles of PLCD1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) are still unknown.
Methods
Western blot and qPCR were used to explore PLCD1 expression in various ESCC cells. MTT, colony formation assays, wound-healing assay, and transwell cell invasion assay were used to examine the cell viability in vitro. Western blot, qPCR, and luciferase assays were used to investigate the effects of PLCD1 on Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. The xenograft models in nude mice were established to explore the roles of PLCD1 in vivo.
Results
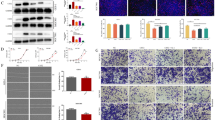
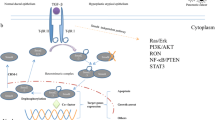
We found that the expression of PLCD1 in ESCC cells was significantly downregulated than that in normal esophageal epithelial cells. In addition, upregulation of PLCD1 decreased the capacity of TE-1 and EC18 cells in proliferation, invasion, and migration. Then, the expression of β-catenin/p-β-catenin, C-myc, cyclin D1, MMP9, and MMP7 was investigated. PLCD1 activity was found to be negatively associated with the expression of β-catenin, C-myc, cyclin D1, MMP9, and MMP7. Finally, the activity of PLCD1 in inhibiting ESCC proliferation in vivo was validated.
Conclusion
The inhibitory effects of PLCD1 on the proliferation, invasion, and migration of TE-1 and EC18 cells might be associated with inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. PLCD1 played a key role in inhibiting ESCC carcinogenesis and progression in patients with ESCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atefeh T, Mohsen M, Alireza M, et al. Biological and clinical relevance of metastasis-associated long coding RNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review. J Cell Physiol. 2019;. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29083.
Bollschweiler E, Plum P, Mönig SP, et al. Current and future treatment options for esophageal cancer in the elderly. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2017;18:1001–1010.
Rustgi AK, El-Serag HBJNEJM. Esophageal carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2499–2509.
Tran GD, Sun XD, Abnet CC, et al. Prospective study of risk factors for esophageal and gastric cancers in the Linxian general population trial cohort in China. Int J Cancer. 2005;113:456–463.
Lattanzio R, Piantelli M, Falasca M. Role of phospholipase C in cell invasion and metastasis. Adv Biol Regul. 2013;53:309–318.
Fukami K. Structure, regulation, and function of phospholipase C isozymes. J Biochem. 2002;131:293–299.
Qing S, Xinrong L, Dejuan Y, et al. Phospholipase Cδ1 suppresses cell migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by modulating KIF3A-mediated ERK1/2/β-catenin/MMP7 signalling. Oncotarget. 2017;8:29056–29066.
Mu H, Wang N, Zhao L, et al. Methylation of PLCD1 and adenovirus-mediated PLCD1 overexpression elicits a gene therapy effect on human breast cancer. Exp Cell Res. 2015;332:179–189.
Hu XT, Zhang FB, Fan YC, et al. Phospholipase C delta 1 is a novel 3p22.3 tumor suppressor involved in cytoskeleton organization, with its epigenetic silencing correlated with high-stage gastric cancer. Oncogene. 2009;28:2466–2475.
Zhu X, Wang J, Li L, et al. GPX3 suppresses tumor migration and invasion via the FAK/AKT pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10:1908–1920.
Bian ZQ, Luo Y, Guo F, et al. Overexpressed ACP5 has prognostic value in colorectal cancer and promotes cell proliferation andtumorigenesis via FAK/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Am J Cancer Res. 2019;9:22–35.
Shang S, Hua F, Hu ZW. The regulation of beta-catenin activity and function in cancer: therapeutic opportunities. Oncotarget. 2017;8:33972–33989.
Lin DC, Wang MR, Koeffler HP. Genomic and epigenomic aberrations in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and implications for patients. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:374–389.
Xiang T, Li L, Fan Y, et al. PLCD1 is a functional tumor suppressor inducing G(2)/M arrest and frequently methylated in breast cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010;10:520–527.
Danielsen SA, Cekaite L, Agesen TH, et al. Phospholipase C isozymes are deregulated in colorectal cancer–insights gained from gene set enrichment analysis of the transcriptome. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e24419.
Huang SP, Liu PY, Kuo CJ, et al. The Gαh-PLCδ1 signaling axis drives metastatic progression in triple-negative breast cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:114.
Song JJ, Liu Q, Li Y, et al. Epigenetic inactivation of PLCD1 in chronic myeloid leukemia. Int J Mol Med. 2012;30:179–184.
Dakeng S, Duangmano S, Jiratchariyakul W, et al. Inhibition of Wnt signaling by cucurbitacin B in breast cancer cells: reduction of Wnt-associated proteins and reduced translocation of galectin-3-mediated β-catenin to the nucleus. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113:49–60.
Chen C, Zhao M, Tian A, et al. Aberrant activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling drives proliferation of bone sarcoma cells. Oncotarget. 2015;6:17570–17583.
MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell. 2009;17:9–26.
Valenta T, Hausmann G, Basler K. The many faces and functions of β-catenin. EMBO J. 2012;31:2714–2736.
Scholzen T, Gerdes J. The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol. 2000;182:311–322.
Rennoll S, Yochum G. Regulation of MYC gene expression by aberrant Wnt/β-catenin signaling in colorectal cancer. World J Biol Chem. 2015;6:290–300.
Weber JD, Raben DM, Phillips PJ, et al. Sustained activation of erace-ularsignal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1) is required for the continued expression of cyclin D1 in G1 phase. Biochem J. 1997;326:61–68.
Qie S, Diehl JA. Cyclin D1, cancer progression, and opportunities in cancer treatment. J Mol Med (Berl). 2016;94:1313–1326.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81960438), Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education Project (Nos. 190792, 190790, 190842, and 190845), and a Grant from Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2018A0303130233).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XH, FM, and YFZ designed experiments. XH and FM carried out experiments. ZJY, LYQ, XRW, and ZLL performed bioinformatics analysis. ZLL, XJZ, and YL conducted statistical analysis. XH and YFZ wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All animal experiments were performed in accordance with the principles and procedures outlined in the Nanfang Medical University Guide for the Care and Use of Animals under the assurance number SCXK (Guangdong) 2008-0002. Approval was obtained from the Nanfang Hospital Animal Ethics Committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, X., Meng, F., Yu, Zj. et al. PLCD1 Suppressed Cellular Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration via Inhibition of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 66, 442–451 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06218-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06218-1