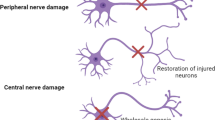
Abstract
Central Post-Stroke Pain (CPSP) is a primary sequelae of stroke that can develop in the body part corresponding to the cerebrovascular lesion after stroke, most typically after ischemic stroke but also after hemorrhagic stroke. The pathogenesis of CPSP is currently unknown, and research into its mechanism is ongoing. To summarize current research on the CPSP mechanism and provide guidance for future studies. Use “central post-stroke pain,” “stroke AND thalamic pain,” “stroke AND neuropathic pain,” “post-stroke thalamic pain” as the search term. The search was conducted in the PubMed and China National Knowledge Infrastructure databases, summarizing and classifying the retrieved mechanism studies. The mechanistic studies on CPSP are extensive, and we categorized the included mechanistic studies and summarized them in terms of relevant pathway studies, relevant signals and receptors, relevant neural tissues, and described endoplasmic reticulum stress and other relevant studies, as well as summarized the mechanisms of acupuncture treatment. Studies have shown that the pathogenesis of CPSP involves the entire spinal-thalamo-cortical pathway and that multiple substances in the nervous system are involved in the formation and development of CPSP. Among them, the relevant receptors and signals are the hotspot of research, and the discovery and exploration of different receptors and signals have provided a wide range of therapeutic ideas for CPSP. As a very effective treatment, acupuncture is less studied regarding the analgesic mechanism of CPSP, and further experimental studies are still needed.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data availability is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study
Abbreviations
- ACC:
-
Anterior cingulate cortex
- ACCGABA→Glu :
-
Anterior cingulate cortex GABA-containing neurons to glutamatergic neurons
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- BCAO:
-
Bilateral carotid artery occlusion
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- CFA:
-
Complete Freund’s adjuvant
- CPSP:
-
Central post-stroke pain
- CXCR4:
-
C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4
- DHA:
-
Docosahexaenoic acid
- EA:
-
Electroacupuncture
- EETs:
-
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids
- EPA:
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- GABA:
-
Gamma-aminobutyric acid
- GABAaR:
-
Gamma-aminobutyric acid a receptor
- GRP40:
-
Free fatty acid receptor 1 (FFA1)
- HCN:
-
Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated
- HIF-1α:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α
- I/R:
-
Ischemia/reperfusion
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- ITAB:
-
Intra-thalamic autologous blood
- ITC:
-
Intra-thalamic collagenase
- LPA:
-
Lysophosphatidic acid receptors
- MD:
-
Medial dorsal thalamus
- MED1:
-
Mediator complex subunit 1
- MT:
-
Medial thalamus
- NLRP3:
-
NLR pyrin domain-containing 3
- NOS:
-
Nitric oxide synthase
- PEALut:
-
N-palmitoylethanolamide and luteolin
- PFC:
-
Prefrontal cortex
- PFGlu :
-
Parafascicular thalamic nucleus
- PIT:
-
Photochemically induced thrombosis
- POGlu :
-
Posterior thalamic nucleus
- PUFA:
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acid
- PWT:
-
Paw retraction threshold
- S1Glu :
-
Primary somatosensory cortex glutamatergic neurons
- SDF1:
-
Stromal cell-derived factor 1
- sEH:
-
Soluble epoxide hydrolase
- STT:
-
Spinal thalamic tract
- TH:
-
Thalamic hemorrhage
- THS:
-
Thalamic hemorrhagic stroke
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- TrkB:
-
Tropomyosin receptor kinase B
- TRN:
-
Thalamic reticular nucleus
- TSPO:
-
Translocator protein
- UPR:
-
Unfolded protein response
- VB:
-
Ventrobasal thalamus
- VPL:
-
Ventral posterolateral
- VPM:
-
Ventral posteromedial
References
Andersen G, Vestergaard K, Ingeman-Nielsen M, Jensen TS (1995) Incidence of central post-stroke pain. Pain 61:187–193
Betancur DFA, Tarragó MDGL, Torres ILDS, Fregni F, Caumo W (2021) Central post-stroke pain: an integrative review of somatotopic damage, clinical symptoms, and neurophysiological measures. Front Neurol 12:678198
Boakye PA, Tang SJ, Smith PA (2021) Mediators of neuropathic pain; focus on spinal microglia, CSF-1, BDNF, CCL21, TNF-α, Wnt ligands, and interleukin 1β. Front Pain Res (lausanne) 2:698157
Boccella S, Guida F, De Logu F, De Gregorio D, Mazzitelli M, Belardo C, Iannotta M, Serra N, Nassini R, de Novellis V, Geppetti P, Maione S, Luongo L (2019) Ketones and pain: unexplored role of hydroxyl carboxylic acid receptor type 2 in the pathophysiology of neuropathic pain. Faseb J 33:1062–1073
Chanaday NL, Nosyreva E, Shin OH, Zhang H, Aklan I, Atasoy D, Bezprozvanny I, Kavalali ET (2021) Presynaptic store-operated Ca(2+) entry drives excitatory spontaneous neurotransmission and augments endoplasmic reticulum stress. Neuron 109:1314–32.e5
Danilov A, Kurganova J (2016) Melatonin in chronic pain syndromes. Pain Ther 5:1–17
Davidson S, Zhang X, Khasabov SG, Moser HR, Honda CN, Simone DA, Giesler GJ Jr (2012) Pruriceptive spinothalamic tract neurons: physiological properties and projection targets in the primate. J Neurophysiol 108:1711–1723
Delpont B, Blanc C, Osseby GV, Hervieu-Bègue M, Giroud M, Béjot Y (2018) Pain after stroke: a review. Rev Neurol (paris) 174:671–674
Ding W, You Z, Shen S, Chen L, Zhu S, Mao J (2016) Inhibition of HCN channel activity in the thalamus attenuates chronic pain in rats. Neurosci Lett 631:97–103
Dong P, Wang H, Shen XF, Jiang P, Zhu XT, Li Y, Gao JH, Lin S, Huang Y, He XB, Xu FQ, Duan S, Lian H, Wang H, Chen J, Li XM (2019) A novel cortico-intrathalamic circuit for flight behavior. Nat Neurosci 22:941–949
Du L, Wang SJ, Cui J, He WJ, Ruan HZ (2013) The role of HCN channels within the periaqueductal gray in neuropathic pain. Brain Res 1500:36–44
Eady TN, Khoutorova L, Obenaus A, Mohd-Yusof A, Bazan NG, Belayev L (2014) Docosahexaenoic acid complexed to albumin provides neuroprotection after experimental stroke in aged rats. Neurobiol Dis 62:1–7
Englezou PC, Rothwell SW, Ainscough JS, Brough D, Landsiedel R, Verkhratsky A, Kimber I, Dearman RJ (2015) P2X7R activation drives distinct IL-1 responses in dendritic cells compared to macrophages. Cytokine 74:293–304
Feigin VL, Brainin M, Norrving B, Martins S, Sacco RL, Hacke W, Fisher M, Pandian J, Lindsay P (2022) World stroke organization (WSO): global stroke fact sheet 2022. Int J Stroke 17:18–29
Figueroa JD, Cordero K, Serrano-Illan M, Almeyda A, Baldeosingh K, Almaguel FG, De Leon M (2013) Metabolomics uncovers dietary omega-3 fatty acid-derived metabolites implicated in anti-nociceptive responses after experimental spinal cord injury. Neuroscience 255:1–18
Flaster M, Meresh E, Rao M, Biller J (2013) Central poststroke pain: current diagnosis and treatment. Top Stroke Rehabil 20:116–123
Freeman R, Baron R, Bouhassira D, Cabrera J, Emir B (2014) Sensory profiles of patients with neuropathic pain based on the neuropathic pain symptoms and signs. Pain 155:367–376
GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021 Oct;20(10):795-820. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00252-0. PMID: 34487721; PMCID: PMC8443449.
Guédon A, Thiebaut JB, Benichi S, Mikol J, Moxham B, Plaisant O (2019) Dejerine-Roussy syndrome: historical cases. Neurology 93:624–629
Guida F, De Gregorio D, Palazzo E, Ricciardi F, Boccella S, Belardo C, Iannotta M, Infantino R, Formato F, Marabese I, Luongo L, de Novellis V, Maione S (2020) Behavioral, biochemical and electrophysiological changes in spared nerve injury model of neuropathic pain. Int J Mol Sci 21:3396
Halder SK, Yano R, Chun J, Ueda H (2013) Involvement of LPA1 receptor signaling in cerebral ischemia-induced neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 235:10–15
Haneklaus M, Gerlic M, Kurowska-Stolarska M, Rainey AA, Pich D, McInnes IB, Hammerschmidt W, O’Neill LA, Masters SL (2012) Cutting edge: miR-223 and EBV miR-BART15 regulate the NLRP3 inflammasome and IL-1β production. J Immunol 189:3795–3799
Hansen AP, Marcussen NS, Klit H, Andersen G, Finnerup NB, Jensen TS (2012) Pain following stroke: a prospective study. Eur J Pain 16:1128–1136
Harada S, Haruna Y, Aizawa F, Matsuura W, Nakamoto K, Yamashita T, Kasuya F, Tokuyama S (2014) Involvement of GPR40, a long-chain free fatty acid receptor, in the production of central post-stroke pain after global cerebral ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol 744:115–123
Hiraga SI, Itokazu T, Hoshiko M, Takaya H, Nishibe M, Yamashita T (2020) Microglial depletion under thalamic hemorrhage ameliorates mechanical allodynia and suppresses aberrant axonal sprouting. JCI Insight. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.131801
Huang T, Xiao Y, Zhang Y, Wang C, Chen X, Li Y, Ge Y, Gao J (2022) miR-223 ameliorates thalamus hemorrhage-induced central poststroke pain via targeting NLRP3 in a mouse model. Exp Ther Med 23:353
Infantino R, Schiano C, Luongo L, Paino S, Mansueto G, Boccella S, Guida F, Ricciardi F, Iannotta M, Belardo C, Marabese I, Pieretti G, Serra N, Napoli C, Maione S (2022) MED1/BDNF/TrkB pathway is involved in thalamic hemorrhage-induced pain and depression by regulating microglia. Neurobiol Dis 164:105611
Inoue K (2019) Role of the P2X4 receptor in neuropathic pain. Curr Opin Pharmacol 47:33–39
Ismael S, Zhao L, Nasoohi S, Ishrat T (2018) Inhibition of the NLRP3-inflammasome as a potential approach for neuroprotection after stroke. Sci Rep 8:5971
Jensen TS, Finnerup NB (2014) Allodynia and hyperalgesia in neuropathic pain: clinical manifestations and mechanisms. Lancet Neurol 13:924–935
Ji LL, Guo MW, Ren XJ, Ge DY, Li GM, Tu Y (2017) Effects of electroacupuncture intervention on expression of cyclooxygenase 2 and microglia in spinal cord in rat model of neuropathic pain. Chin J Integr Med 23:786–792
Kaur T, Shih HC, Huang ACW, Shyu BC (2022) Modulation of melatonin to the thalamic lesion-induced pain and comorbid sleep disturbance in the animal model of the central post-stroke hemorrhage. Mol Pain 18:17448069221127180
Klit H, Finnerup NB, Jensen TS (2009) Central post-stroke pain: clinical characteristics, pathophysiology, and management. Lancet Neurol 8:857–868
Kuan YH, Shih HC, Tang SC, Jeng JS, Shyu BC (2015) Targeting P(2)X(7) receptor for the treatment of central post-stroke pain in a rodent model. Neurobiol Dis 78:134–145
Kuan YH, Shih HC, Shyu BC (2018) Involvement of P(2)X(7) receptors and BDNF in the pathogenesis of central poststroke pain. Adv Exp Med Biol 1099:211–227
Kumar B, Kalita J, Kumar G, Misra UK (2009) Central poststroke pain: a review of pathophysiology and treatment. Anesth Analg 108:1645–1657
Layhadi JA, Fountain SJ (2017) P2X4 receptor-dependent Ca(2+) influx in model human monocytes and macrophages. Int J Mol Sci 18:2261
Li Y, Tian H, An L, Shi X (2017) Resuscitation acupuncture for thalamic pain:a randomized controlled trial. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu 37:14–18
Li SJ, Zhang YF, Ma SH, Yi Y, Yu HY, Pei L, Feng D (2018) The role of NLRP3 inflammasome in stroke and central poststroke pain. Medicine (baltimore) 97:e11861
Liang T, Chen XF, Yang Y, Yang F, Yu Y, Yang F, Wang XL, Wang JL, Sun W, Chen J (2022) Secondary damage and neuroinflammation in the spinal dorsal horn mediate post-thalamic hemorrhagic stroke pain hypersensitivity: SDF1-CXCR4 signaling mediation. Front Mol Neurosci 15:911476
Liu W, Shang G, Yang S, Huang J, Xue X, Lin Y, Zheng Y, Wang X, Wang L, Lin R, Tao J, Chen L (2016) Electroacupuncture protects against ischemic stroke by reducing autophagosome formation and inhibiting autophagy through the mTORC1-ULK1 complex-Beclin1 pathway. Int J Mol Med 37:309–318
Liu T, Li T, Chen X, Li Z, Feng M, Yao W, Wan L, Zhang C, Zhang Y (2021) EETs/sEHi alleviates nociception by blocking the crosslink between endoplasmic reticulum stress and neuroinflammation in a central poststroke pain model. J Neuroinflammation 18:211
Liu PF, Wang Y, Xu L, Xiang AF, Liu MZ, Zhu YB, Jia X, Zhang R, Li JB, Zhang L, Mu D (2022) Modulation of itch and pain signals processing in ventrobasal thalamus by thalamic reticular nucleus. iScience 25:103625
Lloyd-Evans E, Waller-Evans H (2020) Biosynthesis and signalling functions of central and peripheral nervous system neurosteroids in health and disease. Essays Biochem 64:591–606
Lu HF, Xu CY, Zhang L, Gan L, Chen C, Yan MY, Guo XN, Fang Q, Xu GY, Zhang YB, Ni JQ, Zhao HR (2018) A new central post-stroke pain rat model: autologous blood injected thalamic hemorrhage involved increased expression of P2X4 receptor. Neurosci Lett 687:124–130
Lu J, Guo X, Yan M, Yuan X, Chen S, Wang Y, Zhu J, Huang S, Shen H, Li H, Xue Q, Fang Q, Ni J, Gan L, Zhao H, Lu H, Chen G (2021) P2X4R contributes to central disinhibition Via TNF-α/TNFR1/GABAaR pathway in post-stroke pain rats. J Pain 22:968–980
Maier PJ, Zemoura K, Acuña MA, Yévenes GE, Zeilhofer HU, Benke D (2014) Ischemia-like oxygen and glucose deprivation mediates down-regulation of cell surface γ-aminobutyric acidB receptors via the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-induced transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP)-homologous protein (CHOP). J Biol Chem 289:12896–12907
Matsuura W, Harada S, Liu K, Nishibori M, Tokuyama S (2018) Evidence of a role for spinal HMGB1 in ischemic stress-induced mechanical allodynia in mice. Brain Res 1687:1–10
Matsuura W, Nakamoto K, Tokuyama S (2019) The involvement of DDAH1 in the activation of spinal NOS signaling in early stage of mechanical allodynia induced by exposure to ischemic stress in mice. Biol Pharm Bull 42:1569–1574
Mishima K (2012) Melatonin as a regulator of human sleep and circadian systems. Nihon Rinsho 70:1139–1144
Monif M, Reid CA, Powell KL, Drummond KJ, O’Brien TJ, Williams DA (2016) Interleukin-1β has trophic effects in microglia and its release is mediated by P2X7R pore. J Neuroinflammation 13:173
Naess H, Lunde L, Brogger J (2012) The effects of fatigue, pain, and depression on quality of life in ischemic stroke patients: the Bergen Stroke Study. Vasc Health Risk Manag 8:407–413
Nagpal N, Sharma S, Maji S, Durante G, Ferracin M, Thakur JK, Kulshreshtha R (2018) Essential role of MED1 in the transcriptional regulation of ER-dependent oncogenic miRNAs in breast cancer. Sci Rep 8:11805
Nah J, Yuan J, Jung YK (2015) Autophagy in neurodegenerative diseases: from mechanism to therapeutic approach. Mol Cells 38:381–389
Oh H, Seo W (2015) A comprehensive review of central post-stroke pain. Pain Manag Nurs 16:804–818
Pillarisetti S, Khanna I (2015) A multimodal disease modifying approach to treat neuropathic pain–inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH). Drug Discov Today 20:1382–1390
Pribiag H, Stellwagen D (2013) TNF-α downregulates inhibitory neurotransmission through protein phosphatase 1-dependent trafficking of GABA(A) receptors. J Neurosci 33:15879–15893
Saab CY (2012) Pain-related changes in the brain: diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Trends Neurosci 35:629–637
Shih HC, Kuan YH, Shyu BC (2017) Targeting brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the medial thalamus for the treatment of central poststroke pain in a rodent model. Pain 158:1302–1313
Shukla GC, Singh J, Barik S (2011) MicroRNAs: processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol 3:83–92
Sokal P, Harat M, Zieliński P, Furtak J, Paczkowski D, Rusinek M (2015) Motor cortex stimulation in patients with chronic central pain. Adv Clin Exp Med 24:289–296
Sprenkle NT, Sims SG, Sánchez CL, Meares GP (2017) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation in the central nervous system. Mol Neurodegener 12:42
Sutterwala FS, Haasken S, Cassel SL (2014) Mechanism of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Ann NY Acad Sci 1319:82–95
Takami K, Fujita-Hamabe W, Harada S, Tokuyama S (2011) Aβ and Aδ but not C-fibres are involved in stroke related pain and allodynia: an experimental study in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol 63:452–456
Tamiya S, Yoshida Y, Harada S, Nakamoto K, Tokuyama S (2013) Establishment of a central post-stroke pain model using global cerebral ischaemic mice. J Pharm Pharmacol 65:615–620
Tan CC, Yu JT, Tan MS, Jiang T, Zhu XC, Tan L (2014) Autophagy in aging and neurodegenerative diseases: implications for pathogenesis and therapy. Neurobiol Aging 35:941–957
Tian GH, Tao SS, Chen MT, Li YS, Li YP, Shang HC, Tang XY, Chen JX, Tang HB (2016) Electroacupuncture treatment alleviates central poststroke pain by inhibiting brain neuronal apoptosis and aberrant astrocyte activation. Neural Plast 2016:1437148
Treede RD, Jensen TS, Campbell JN, Cruccu G, Dostrovsky JO, Griffin JW, Hansson P, Hughes R, Nurmikko T, Serra J (2008) Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 70:1630–1635
Ueda H, Neyama H (2017) LPA1 receptor involvement in fibromyalgia-like pain induced by intermittent psychological stress, empathy. Neurobiol Pain 1:16–25
Ueda H, Neyama H, Sasaki K, Miyama C, Iwamoto R (2019) Lysophosphatidic acid LPA(1) and LPA(3) receptors play roles in the maintenance of late tissue plasminogen activator-induced central poststroke pain in mice. Neurobiol Pain 5:100020
Vartiainen N, Perchet C, Magnin M, Creac’h C, Convers P, Nighoghossian N, Mauguière F, Peyron R, Garcia-Larrea L (2016) Thalamic pain: anatomical and physiological indices of prediction. Brain 139:708–722
Waldvogel HJ, Munkle M, van Roon-Mom W, Mohler H, Faull RLM (2017) The immunohistochemical distribution of the GABA(A) receptor α(1), α(2), α(3), β(2/3) and γ(2) subunits in the human thalamus. J Chem Neuroanat 82:39–55
Westerlind E, Singh R, Persson HC, Sunnerhagen KS (2020) Experienced pain after stroke: a cross-sectional 5-year follow-up study. BMC Neurol 20:4
Xu XM, Luo H, Rong BB, Zheng XM, Wang FT, Zhang SJ, Li ZX (2020) Nonpharmacological therapies for central poststroke pain: a systematic review. Medicine (baltimore) 99:e22611
Yang F, Luo WJ, Sun W, Wang Y, Wang JL, Yang F, Li CL, Wei N, Wang XL, Guan SM, Chen J (2017a) SDF1-CXCR4 Signaling maintains central post-stroke pain through mediation of glial-neuronal interactions. Front Mol Neurosci 10:226
Yang F, Sun W, Luo WJ, Yang Y, Yang F, Wang XL, Chen J (2017b) SDF1-CXCR4 signaling contributes to the transition from acute to chronic pain state. Mol Neurobiol 54:2763–2775
Yang J, Li X, Li C, He K, Wu Y, Lin H, Xie X, Zhang F, Hao H, Tian G (2022) Comparative efficacy and safety of acupuncture and Western medicine for poststroke thalamic pain. Anat Rec (hoboken). https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.24902
Zhang R, Lao L, Ren K, Berman BM (2014) Mechanisms of acupuncture-electroacupuncture on persistent pain. Anesthesiology 120:482–503
Zhang M, Liu J, Zhou MM, Wu H, Hou Y, Li YF, Yin Y, Zheng L, Liu FY, Yi M, Wan Y (2016) Elevated Neurosteroids in the lateral thalamus relieve neuropathic pain in rats with spared nerve injury. Neurosci Bull 32:311–322
Zhang C, Chen RX, Zhang Y, Wang J, Liu FY, Cai J, Liao FF, Xu FQ, Yi M, Wan Y (2017) Reduced GABAergic transmission in the ventrobasal thalamus contributes to thermal hyperalgesia in chronic inflammatory pain. Sci Rep 7:41439
Zheng M, Matsuo T, Miyamoto A, Hoshino O (2014) Tonically balancing intracortical excitation and inhibition by GABAergic gliotransmission. Neural Comput 26:1690–1716
Zheng L, Li XY, Huang FZ, Zhang XT, Tang HB, Li YS, Zhang WK, Li XJ, Tian GH (2020) Effect of electroacupuncture on relieving central post-stroke pain by inhibiting autophagy in the hippocampus. Brain Res 1733:146680
Zhu X, Tang HD, Dong WY, Kang F, Liu A, Mao Y, Xie W, Zhang X, Cao P, Zhou W, Wang H, Farzinpour Z, Tao W, Song X, Zhang Y, Xue T, Jin Y, Li J, Zhang Z (2021) Distinct thalamocortical circuits underlie allodynia induced by tissue injury and by depression-like states. Nat Neurosci 24:542–553
Zorumski CF, Paul SM, Izumi Y, Covey DF, Mennerick S (2013) Neurosteroids, stress and depression: potential therapeutic opportunities. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37:109–122
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YC: collected and summarized the literatures and wrote the first draft of this review. JH and YC: were involved in the collection and arrangement of the literatures. BW: reviewed and revised the paper. All authors contributed to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Y., Wu, B., Huang, J. et al. Research Progress on the Mechanisms of Central Post-Stroke Pain: A Review. Cell Mol Neurobiol 43, 3083–3098 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-023-01360-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-023-01360-6