Abstract
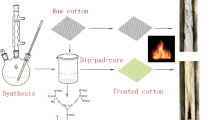
A novel phosphorus-containing cotton flame retardant 2, 6-dimethoxy polysaccharose phosphonic acid ester ammonium phosphonate (DOPSPAP) was synthesized and its chemical structure was confirmed by nuclear magnetic resonance (1H, 13C and 31P NMR) and Fourier infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The damage length of the cotton fabric treated with 25wt% DOPSPAP was only 4.2 cm in the vertical flame test (VFT), and the char residue was observed to maintain the intact fiber structure by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The limiting oxygen index (LOI) of 25wt% DOPSPAP treated cotton fabric was as high as 44.5%, and the LOI was still 34.5% after 50 LCs according to AATCC 61–2013 3A standard. SEM observed the presence of DOPSPAP flame retardant on the surface of cotton fiber. Durability, FT-IR and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) confirmed the grafting of DOPSPAP on cotton fibers through P(= O)-O-C covalent bonds. The cone calorimetric results showed that DOPSPAP effectively inhibited the heat release during combustion of cotton fabrics. The thermogravimetric (TG) and TG-FTIR results suggested DOPSPAP changed the decomposition pathway of cotton fibers and promoted their dehydration into char. The bending length and tensile strength of DOPSPAP-treated cotton fabrics are well maintained. Compared with 2, 6-dimethoxy polysaccharide ammonium phosphonate (DOPSAP), DOPSPAP-treated cotton fabric showed better flame retardant durability and tensile strength. The EDS results showed that the metal ion content of DOPSPAP-treated cotton was significantly lower than that of DOPSAP-treated cotton after 50 LCs. These results indicate that the simultaneous introduction of phosphonic acid ester and ammonium phosphonate groups into flame retardants can not only improve the durability of flame retardants, but also reduce the loss of strength.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Ali W, Zilke O, Danielsiek D et al (2023) Flame-retardant finishing of cotton fabrics using DOPO functionalized alkoxy- and amido alkoxysilane. Cellulose 30:2627–2652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-05033-3
Annalisa C, Francesca B, Giulio M et al (2016) DNA-chitosan cross-linking and photografting to cotton fabrics to improve washing fastness of the fire-resistant finishing. Cellulose 23:3963–3984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1067-y
Ding D, Liu Y, Lu Y et al (2022) Highly effective and durable P-N synergistic flame retardant containing ammonium phosphate and phosphonate for cotton fabrics. Polym Degrad Stab 200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2022.109964
Durrani H, Sharma V, Bamboria D et al (2020) Exploration of flame retardant efficacy of cellulosic fabric using in-situ synthesized zinc borate particles. Cellulose 27:9061–9073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03383-4
Frederiksen M, Vorkamp K, Thomsen M, Knudsen LE (2009) Human internal and external exposure to PBDEs - A review of levels and sources. Int J Hyg Environ Health 212:109–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2008.04.005
Gao YJ, Jin WJ, Hu BQ et al (2023) Preparation of a Reactive Phosphorus/nitrogen-Based Intumescent Flame Retardant Coating for Cotton Fabrics. Journal of Natural Fibers 20. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2022.2153195
Hou F, Zhu M, Liu Y, et al (2022) A self-assembled bio-based coating with phytic acid and DL-arginine used for a flame-retardant and antibacterial cellulose fabric. Prog Org Coat 173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2022.107179
Hu Z, Ma Y, Chen H et al (2023) Efficient, durable, and breathable flame retardant cotton fabric via a feasible surface finishing. Appl Surf Sci 615:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.156314
Javed A, Wiener J, Saskova J, Müllerová J (2022) Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) and N-Methylol Dimethyl Phosphonopropion Amide (MDPA) System for Flame Retardant Cotton Fabrics. Polymers (Basel) 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163414
Jin X, Cui S, Sun S et al (2021) The preparation and characterization of polylactic acid composites with chitin-based intumescent flame retardants. Polymers (Basel) 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13203513
Li P, Wang B, Xu YJ et al (2019) Ecofriendly Flame-Retardant Cotton Fabrics: Preparation, Flame Retardancy, Thermal Degradation Properties, and Mechanism. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:19246–19256. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b05523
Li N, Kang G, Liu H et al (2022a) Fabrication of eco-friendly and efficient flame retardant modified cellulose with antibacterial property. J Colloid Interface Sci 618:462–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.03.078
Li S, Yu L, Xiong J et al (2022b) Facile Fabrication of Superhydrophobic and Flame-Retardant Coatings on Cotton Fabrics. Polymers (Basel) 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235314
Lu Y, Zhao P, Chen Y et al (2022) A bio-based macromolecular phosphorus-containing active cotton flame retardant synthesized from starch. Carbohydr Polym 298:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120076
Lu Y, Ding D, Liu Y et al (2023a) A high durable polysaccharide flame retardant based on phosphorus element for cotton fabrics. Polym Degrad Stab 210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2023.110313
Lu Y, Lu Y, Yang Y et al (2023b) Synthesis and application of a novel high durable cotton flame retardant rich in P[sbnd]N covalent bonds and ammonium phosphate groups. Chemical Engineering Journal 454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.140422
Morgan AB (2019) The Future of Flame Retardant Polymers-Unmet Needs and Likely New Approaches. Polym Rev 59:25–54. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583724.2018.1454948
Ortelli S, Malucelli G, Blosi M et al (2019) NanoTiO 2 @DNA complex: a novel eco, durable, fire retardant design strategy for cotton textiles. J Colloid Interface Sci 546:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.03.055
Özer MS, Gaan S (2022) Recent developments in phosphorus based flame retardant coatings for textiles: Synthesis, applications and performance. Prog Org Coat 171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2022.107027
Pethsangave DA, Khose RV, Wadekar PH, Some S (2019) Novel Approach toward the Synthesis of a Phosphorus-Functionalized Polymer-Based Graphene Composite as an Efficient Flame Retardant. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:11745–11753. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b01975
Price ’n D, Horrucks AR, Akalin’ M, Faroq AA (1997) Influence of flame retardants on the mechanism of pyrolysis of cotton (celluIose) fabrics in air. J Anal Appl Pyrol 40:511–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-2370(97)00043-0
Rosace G, Castellano A, Trovato V et al (2018) Thermal and flame retardant behaviour of cotton fabrics treated with a novel nitrogen-containing carboxyl-functionalized organophosphorus system. Carbohydr Polym 196:348–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.05.012
Safi K, Kant K, Bramhecha I et al (2020) Multifunctional modification of cotton using layer-by-layer finishing with chitosan, sodium lignin sulphonate and boric acid. Int J Biol Macromol 158:903–910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.066
Shao ZB, Deng C, Tan Y et al (2014) An efficient mono-component polymeric intumescent flame retardant for polypropylene: Preparation and application. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:7363–7370. https://doi.org/10.1021/am500789q
Shen R, Fan T, Quan Y et al (2022) Thermal stability and flammability of cotton fabric with TiO2 coatings based on biomineralization. Mater Chem Phys 282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.125986
Song F, Zhao Q, Zhu T et al (2022) Biobased coating derived from fish scale protein and phytic acid for flame-retardant cotton fabrics. Mater Des 221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2022.110925
Sun J, Shi L, Song T, Sun C (2021) Flame resistance of cotton fabric finishing with N-hydroxymethylacrylamide spirophosphate. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4:1155–1165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00348-4
Taherkhani A, Hasanzadeh M (2018) Durable flame retardant finishing of cotton fabrics with poly(amidoamine) dendrimer using citric acid. Mater Chem Phys 219:425–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.08.058
Tu J, Mao T, Xie S et al (2022) Environmentally benign flame-retardant cotton fabric with superior anti-wrinkle performance and restorable flame retardancy. Ind Crops Prod 189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115856
Tu J, Xie S, Zhao Q et al (2023) Reactive P/S/N-containing synergistic flame retardant towards eco-friendly durable flame-retardant cotton fabric: Flame-retardant property, durability and mechanism. Polym Test 118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2022.107918
Ur Rehman Z, Huh SH, Ullah Z et al (2021) LBL generated fire retardant nanocomposites on cotton fabric using cationized starch-clay-nanoparticles matrix. Carbohydr Polym 274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118626
van der Veen I, de Boer J (2012) Phosphorus flame retardants: Properties, production, environmental occurrence, toxicity and analysis. Chemosphere 88:1119–1153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.067
Vishwakarma A, Reddy VJ, Kandola BK et al (2021) Egg white protein-hypophosphorous acid-based fire retardant single bilayer coating assembly for cotton fabrics. Cellulose 28:10689–10705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04208-8
Wang B, Xu YJ, Li P et al (2020a) Flame-retardant polyester/cotton blend with phosphorus/nitrogen/silicon-containing nano-coating by layer-by-layer assembly. Appl Surf Sci 509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145323
Wang P, Xiao H, Duan C et al (2020b) Sulfathiazole derivative with phosphaphenanthrene group: Synthesis, characterization and its high flame-retardant activity on epoxy resin. Polym Degrad Stab 173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2020.109078
Wu X, Gou T, Zhao Q et al (2022) High-efficiency durable flame retardant with ammonium phosphate ester and phosphine oxide groups for cotton cellulose biomacromolecule. Int J Biol Macromol 194:945–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.11.149
Xu F, Zhang G, Wang P, Dai F (2022) Durable and high-efficiency casein-derived phosphorus-nitrogen-rich flame retardants for cotton fabrics. Cellulose 29:2681–2697. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04430-y
Zain G, Jordanov I, Bischof S et al (2023) Flame-retardant finishing of cotton fabric by surface-initiated photochemically induced atom transfer radical polymerization. Cellulose 30:2529–2550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04982-z
Zhan Y, Yuan B, Shang S (2022) Synergistic effect of layered melamine-phytate and intumescent flame retardant on enhancing fire safety of polypropylene. J Therm Anal Calorim 147:285–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10228-6
Zhang D, Pei M, Wei K et al (2022) Flame-Retardant Properties and Mechanism of Polylactic Acid-Conjugated Flame-Retardant Composites. Front Chem 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2022.894112
Zhang X, Chen Y, Huang R, et al (2023) Study on the effect of different concentrations of choline glycine ionic liquid-water mixtures on debranched starch butyrylation reaction. Carbohydr Polym 308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120680
Zhao P, Xu F, Chen Y et al (2022) A novel durable flame retardant for cotton fabrics based on diethylenetriamine. Polym Degrad Stab 195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2021.109796
Zhou S, Song L, Wang Z et al (2008) Flame retardation and char formation mechanism of intumescent flame retarded polypropylene composites containing melamine phosphate and pentaerythritol phosphate. Polym Degrad Stab 93:1799–1806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2008.07.012
Acknowledgements
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Funding
The authors did not receive support for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JW: Formal analysis, Investigation, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft. YL: Investigation, Resources, Software, Methodology, Validation. YL: Software, Investigation, Formal Analysis. GZ: Resources, Writing—Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The work is compliant with ethical standards.
Consent for publication
The manuscript was approved for publication by all the authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, J., Lu, Y., Lu, Y. et al. Synthesis of polysaccharide-based macromolecular flame retardants containing ammonium phosphonate and phosphonic acid ester for cotton fabrics. Cellulose 31, 4549–4563 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05860-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05860-6