Abstract
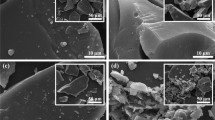
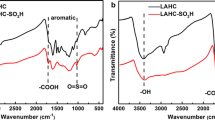
Preparation of lactic acid (LaA) from waste biomass Pueraria cellulose by chemically catalyzed conversion is important for the realization of biomass waste resource utilization. In this study, lignin was used as raw material to prepare lignin-based carbonaceous support (LCSA) by one-step sulfonation and carbonization with chlorosulfonic acid. LCSA–AlxZny, a lignin-based carbon solid acid catalyst, was obtained by modifying the carbonaceous support with inexpensive and readily available Al and Zn chlorides. Through the use of SEM, BET, XRD, FT-IR and NH3–TPD, the catalyst’s physical as well as chemical characteristics were identified. In an aqueous solution, these catalysts were evaluated for the generation of LaA from Pueraria cellulose. LCSA–Al was identified as the optimal catalyst, subsequently, experimental conditions such as reaction time, reaction temperature, and catalyst dosage were studied and optimized. The results showed that at 160 °C, with 50 mg Pueraria cellulose, 50 mg catalyst, and 10 mL deionized water, the conversion rate of Pueraria cellulose was 53.7% and the highest LaA yield was 24.7% after 120 min of reaction. This research provides a new pathway for the preparation of chemicals from cellulose via multi-step tandem catalytic reactions.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Balasubramanian S, Venkatachalam P (2022) Green synthesis of carbon solid acid catalysts using methane sulfonic acid and its application in the conversion of cellulose to platform chemicals. Cellulose 29(3):1509–1526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04419-7
Cai W, Chen Q, Xuan H, Li C, Yu H, Cui L, Yu Z, Zhang S, Qu F (2019) One-pot synthesis of lactic acid from cellulose over a sulfonated Sn-KIT6 catalyst. Korean J Chem Eng 36(4):513–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-019-0236-8
Castillo Martinez FA, Balciunas EM, Salgado JM, Domínguez González JM, Converti A, Oliveira RPDS (2013) Lactic acid properties, applications and production: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 30(1):70–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2012.11.007
Chen SS, Tsang DCW, Tessonnier J (2020) Comparative investigation of homogeneous and heterogeneous Brønsted base catalysts for the isomerization of glucose to fructose in aqueous media. Appl Catal B 261:118126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118126
Chen Z, Zhang S, Yan B, Cai Q, Zhang S (2022) Lignin-based solid acid catalyst for cellulose residue conversion into levulinic acid in biphasic system. Ind Crops Prod 178:114523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.114523
Dapsens PY, Mondelli C, Pérez-Ramírez J (2013) Highly selective lewis acid sites in desilicated MFI zeolites for dihydroxyacetone isomerization to lactic acid. Chemsuschem 6(5):831–839. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201200703
Deng W, Wang P, Wang B, Wang Y, Yan L, Li Y, Zhang Q, Cao Z, Wang Y (2018) Transformation of cellulose and related carbohydrates into lactic acid with bifunctional Al(iii)–Sn(ii) catalysts. Green Chem 20(3):735–744. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7gc02975f
Deng W, Wang Y, Zhang S, Gupta KM, Hülsey MJ, Asakura H, Liu L, Han Y, Karp EM, Beckham GT, Dyson PJ, Jiang J, Tanaka T, Wang Y, Yan N (2018) Catalytic amino acid production from biomass-derived intermediates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(20):5093–5098. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1800272115
Dong W, Ou M, Qu D, Shi X, Guo M, Liu G, Wang S, Wang F, Chen Y (2022) Rare-earth metal yttrium-modified composite metal oxide catalysts for high selectivity synthesis of biomass-derived lactic acid from cellulose. ChemCatChem 14(12):e202200265. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.202200265
Dusselier M, Van Wouwe P, Dewaele A, Makshina E, Sels BF (2013) Lactic acid as a platform chemical in the biobased economy: the role of chemocatalysis. Energy Environ Sci 6(5):1415–1442. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ee00069a
Esposito D, Antonietti M (2013) Chemical conversion of sugars to lactic acid by alkaline hydrothermal processes. Chemsuschem 6(6):989–992. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201300092
Fareez IM, Ibrahim NA, Wan Yaacob WMH, Mamat Razali NA, Jasni AH, Abdul Aziz F (2018) Characteristics of cellulose extracted from Josapine pineapple leaf fibre after alkali treatment followed by extensive bleaching. Cellulose 25(8):4407–4421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1878-0
Feliczak-Guzik A, Sprynskyy M, Nowak I, Buszewski B (2018) Catalytic isomerization of dihydroxyacetone to lactic acid and alkyl lactates over hierarchical zeolites containing tin. Catalysts 8(1):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8010031
Gan L, Zhu J, Lv L (2017) Cellulose hydrolysis catalyzed by highly acidic lignin-derived carbonaceous catalyst synthesized via hydrothermal carbonization. Cellulose 24(12):5327–5339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1515-3
Gezae Daful A, Görgens JF (2017) Techno-economic analysis and environmental impact assessment of lignocellulosic lactic acid production. Chem Eng Sci 162:53–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2016.12.054
Guo L, Li J, Yuan Y, Gui Y, Zou F, Lu L, Cui B (2021) Structural and functional modification of kudzu starch using alpha-amylase and transglucosidase. Int J Biol Macromol 169:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.099
Hossain MA, Mills KN, Molley AM, Rahaman MS, Tulaphol S, Lalvani SB, Dong J, Sunkara MK, Sathitsuksanoh N (2021) Catalytic isomerization of dihydroxyacetone to lactic acid by heat treated zeolites. Appl Catal A Gen 611:117979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2020.117979
Huang S, Yang K, Liu X, Pan H, Zhang H, Yang S (2017) MIL-100(Fe)-catalyzed efficient conversion of hexoses to lactic acid. Rsc Adv 7(10):5621–5627. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra26469g
Kian LK, Jawaid M, Ariffin H, Alothman OY (2017) Isolation and characterization of microcrystalline cellulose from roselle fibers. Int J Biol Macromol 103:931–940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.135
Kupila R, Lappalainen K, Hu T, Romar H, Lassi U (2021) Lignin-based activated carbon-supported metal oxide catalysts in lactic acid production from glucose. Appl Catal A Gen 612:118011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2021.118011
Kusuma HD, Rochmadi, Prasetyo I, Ariyanto T (2021) Mesoporous manganese oxide/lignin-derived carbon for high performance of supercapacitor electrodes. Molecules 26(23):7104. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26237104
Lei X, Wang F, Liu C, Yang R, Dong W (2014) One-pot catalytic conversion of carbohydrate biomass to lactic acid using an ErCl3 catalyst. Appl Catal A Gen 482:78–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2014.05.029
Li Y, Shen S, Wang C, Peng X, Yuan S (2018) The effect of difference in chemical composition between cellulose and lignin on carbon based solid acids applied for cellulose hydrolysis. Cellulose 25(3):1851–1863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1693-7
Li S, Deng W, Li Y, Zhang Q, Wang Y (2019) Catalytic conversion of cellulose-based biomass and glycerol to lactic acid. J Energy Chem 32:138–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2018.07.012
Lu Z, Demianets I, Hamze R, Terrile NJ, Williams TJ (2016) A prolific catalyst for selective conversion of neat glycerol to lactic acid. ACS Catal 6(3):2014–2017. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.5b02732
Marianou AA, Michailof CM, Pineda A, Iliopoulou EF, Triantafyllidis KS, Lappas AA (2016) Glucose to fructose isomerization in aqueous media over homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts. ChemCatChem 8(6):1100–1110. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201501203
Marianou AA, Michailof CC, Ipsakis D, Triantafyllidis K, Lappas AA (2019) Cellulose conversion into lactic acid over supported HPA catalysts. Green Chem 21(22):6161–6178. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9gc02622c
Palacio R, Torres S, Lopez D, Hernandez D (2018) Selective glycerol conversion to lactic acid on Co3O4/CeO2 catalysts. Catal Today 302:196–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2017.05.053
Peng D, Guo J, He J, Zhou X, Song K (2022) Separation of cellulose from Pueraria Edulis Pampan. Residue. Chem Ind Prod 42(1):79–86. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0253-2417.2022.01.011
Pérez-Mayoral E, Calvino-Casilda V, Soriano E (2016) Metal-supported carbon-based materials: opportunities and challenges in the synthesis of valuable products. Catal Sci Technol 6(5):1265–1291. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cy01437a
Qureshi AS, Zhang J, da Costa Sousa L, Bao J (2017) Antibacterial peptide secreted by Pediococcus acidilactici enables efficient cellulosic open l-Lactic acid fermentation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(10):9254–9262. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b02212
Rahaman MS, Tulaphol S, Mills K, Molley A, Hossain MA, Lalvani S, Maihom T, Crocker M, Sathitsuksanoh N (2022) Aluminum-based metal‐organic framework as water‐tolerant lewis acid catalyst for selective dihydroxyacetone isomerization to lactic acid. ChemCatChem 14(4):e202101756. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.202101756
Sain M, Panthapulakkal S (2006) Bioprocess preparation of wheat straw fibers and their characterization. Ind Crops Prod 23(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2005.01.006
Sangsiri P, Laosiripojana N, Daorattanachai P (2022) Synthesis of sulfonated carbon-based catalysts from organosolv lignin and methanesulfonic acid. Renew Energy 193:113–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.05.012
Serrano-Ruiz JC, Luque R, Sepúlveda-Escribano A (2011) Transformations of biomass-derived platform molecules: from high added-value chemicals to fuelsvia aqueous-phase processing. Chem Soc Rev 40(11):5266–5281. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cs15131b
Shen Z, Kong L, Zhang W, Gu M, Xia M, Zhou X, Zhang Y (2019) Surface amino-functionalization of Sn-Beta zeolite catalyst for lactic acid production from glucose. Rsc Adv 9(33):18989–18995. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra01264h
Suganuma S, Nakajima K, Kitano M, Kato H, Tamura A, Kondo H, Yanagawa S, Hayashi S, Hara M (2011) SO3H-bearing mesoporous carbon with highly selective catalysis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 143(2–3):443–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2011.03.028
Sun XF, Xu F, Sun RC, Fowler P, Baird MS (2005) Characteristics of degraded cellulose obtained from steam-exploded wheat straw. Carbohydr Res 340(1):97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2004.10.022
Tang Z, Deng W, Wang Y, Zhu E, Wan X, Zhang Q, Wang Y (2014) Transformation of cellulose and its derived carbohydrates into formic and lactic acids catalyzed by vanadyl cations. Chemsuschem 7(6):1557–1567. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201400150
Tanpichai S, Witayakran S, Srimarut Y, Woraprayote W, Malila Y (2019) Porosity, density and mechanical properties of the paper of steam exploded bamboo microfibers controlled by nanofibrillated cellulose. J Mater Res Technol 8(4):3612–3622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.05.024
Tarchoun AF, Trache D, Klapötke TM, Derradji M, Bessa W (2019) Ecofriendly isolation and characterization of microcrystalline cellulose from giant reed using various acidic media. Cellulose 26(13–14):7635–7651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02672-x
Tong D, Chen X, Dong Y, Fang Z, Zhang H, Zhou C, Yu W (2022) Copper dispersed natural kaolinite as high-performance catalysts for the hydrolysis of cellulose in water. Biomass Convers Biorefinery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02764-y
Wang F, Liu C, Dong W (2013) Highly efficient production of lactic acid from cellulose using lanthanide triflate catalysts. Green Chem 15(8):2091–2095. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3gc40836a
Wang Y, Deng W, Wang B, Zhang Q, Wan X, Tang Z, Wang Y, Zhu C, Cao Z, Wang G, Wan H (2013) Chemical synthesis of lactic acid from cellulose catalysed by lead(II) ions in water. Nat Commun 4:2141. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3141
Wang Z, Mo C, Xu S, Chen S, Deng T, Zhu W, Wang H (2021) Ca(OH)2 induced a controlled-release catalytic system for the efficient conversion of high-concentration glucose to lactic acid. Mol Catal 502:111406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2021.111406
Wattanapaphawong P, Reubroycharoen P, Yamaguchi A (2017) Conversion of cellulose into lactic acid using zirconium oxide catalysts. RSC Adv 7(30):18561–18568. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra28568f
Wei C, Liu G, Xie Y, Sun Z, Liu C, Song F, Cui H (2022) Cellulose dissolution and conversion into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in mixed molten salt hydrate. Cellulose 30(2):801–813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04967-y
Wu T, Li N, Pan X, Chen S (2020) Homogenous hydrolysis of cellulose to glucose in an inorganic ionic liquid catalyzed by zeolites. Cellulose 27(16):9201–9215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03411-3
Xiao Y, Liao S, Xu S, Li J, Lu Z, Hu C (2022) Selective transformation of typical sugars to lactic acid catalyzed by dealuminated ZSM-5 supported erbium. Renew Energy 187:551–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.01.100
Xu J, Zhang H, Zhao Y, Yu B, Chen S, Li Y, Hao L, Liu Z (2013) Selective oxidation of glycerol to lactic acid under acidic conditions using AuPd/TiO2 catalyst. Green Chem 15(6):1520–1525. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3gc40314a
Xu H, Ye X, Shi X, Zhong H, He D, Jin B, Jin F (2022) ZnO as a simple and facile catalyst for acid-base coordination transformation of biomass-based monosaccharides into lactic acid. Mol Catal 522:112241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2022.112241
Yang X, Yang L, Fan W, Lin H (2016) Effect of redox properties of LaCoO3 perovskite catalyst on production of lactic acid from cellulosic biomass. Catal Today 269:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2015.12.003
Yang H, Zhou Y, Tong D, Yang M, Fang K, Zhou C, Yu W (2020) Catalytic conversion of cellulose to reducing sugars over clay-based solid acid catalyst supported nanosized SO42–-ZrO2. Appl Clay Sci 185:105376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2019.105376
Ye J, Chen C, Zheng Y, Zhou D, Liu Y, Chen D, Ni L, Xu G, Wang F (2021) Efficient conversion of cellulose to lactic acid over yttrium modified siliceous Beta zeolites. Appl Catal A-gen 619:118133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2021.118133
Yue X, He J, Xu Y, Yang M, Xu Y (2019) A novel method for preparing microcrystalline cellulose from bleached chemical pulp using transition metal ions enhanced high temperature liquid water process. Carbohydr Polym 208:115–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.12.072
Zhang S, Jin F, Hu J, Huo Z (2011) Improvement of lactic acid production from cellulose with the addition of Zn/Ni/C under alkaline hydrothermal conditions. Bioresour Technol 102(2):1998–2003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.049
Zhang H, Liu W, Cao D, Cheng D (2022) Carbon-based material-supported single-atom catalysts for energy conversion. iScience 25(6):104367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2022.104367
Zhao B, Yue X, Li H, Li J, Liu C-L, Xu C, Dong W-S (2018) Lanthanum-modified phosphomolybdic acid as an efficient catalyst for the conversion of fructose to lactic acid. React Kinet Mech Catal 125(1):55–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-018-1416-y
Zhao X, Zhou Z, Luo H, Zhang Y, Liu W, Miao G, Zhu L, Kong L, Li S, Sun Y (2021) γ-Valerolactone-introduced controlled-isomerization of glucose for lactic acid production over an Sn-Beta catalyst. Green Chem 23(7):2634–2639. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1gc00378j
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22268019), and the Natural Science Innovation Project of Jishou University (JGY2023061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HK is the first author of this study. KS is the corresponding author of this study, and he is supervisor of this project. HK and KS contributed to the study conception and design. JG and XG prepared Figures. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by HK, KS, JH and XZ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by HK and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, H., Guo, J., Gai, Xt. et al. Lignin-derived carbon-based solid acid catalyst for the conversion of Pueraria cellulose to lactic acid. Cellulose 31, 777–791 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05684-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05684-w