Abstract
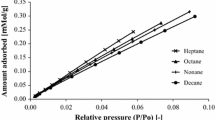
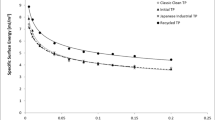
Cellulose is one of the most abundant and sustainable biopolymers on earth. Various types of cellulosic materials such as natural fibres, regenerated cellulose fibres, cellulose derivatives and nanocellulose have increasingly been utilised in developing fibre-reinforced polymeric composites. Analysis of surface physicochemical properties of cellulose-based fillers is essential to maximise fibre-matrix interfacial adhesion to obtain excellent mechanical performance. Among different techniques which can be used to investigate the surface science of cellulose-based materials, inverse gas chromatography (IGC) has been proven as a successful technique for characterising the surface activity, evaluating the efficiency of surface modification methods, and predicting the behaviour of final products. IGC is a versatile approach to evaluate surface energy, acidic-basic characteristics, and surface heterogeneity. These key parameters are used in (i) evaluating the efficiency of different surface treatments for adding new functional groups, (ii) determining the compatibility of cellulosic materials with various polymer matrices to ensure optimal fibre-matrix interaction, and (iii) predicting the performance of cellulose-reinforced composites in actual applications. This article provides a concise review on recent progress in using IGC method for surface analysis of different forms of cellulosic materials in the context of fibre-reinforced composites. For future perspective, the IGC technique can be extensively applied in studying cellulosic materials with high application potential in a variety of fields. This review paper will shed light on understanding the surface characteristics of cellulose-based composites and pave the way for their real-world applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abdel-Halim E (2012) Physiochemical properties of differently pretreated cellulosic fibers. Carbohydr Polym 88(4):1201–1207
Abdelmouleh M, Boufi S, Belgacem M, Duarte A, Salah AB, Gandini A (2004) Modification of cellulosic fibres with functionalised silanes: development of surface properties. Int J Adhes Adhes 24(1):43–54
Alonso E, Faria M, Ferreira A, Cordeiro N (2018) Influence of the matrix and polymerization methods on the synthesis of BC/PANi nanocomposites: an IGC study. Cellulose 25(4):2343–2354
Alonso E, Faria M, Mohammadkazemi F, Resnik M, Ferreira A, Cordeiro N (2018) Conductive bacterial cellulose-polyaniline blends: influence of the matrix and synthesis conditions. Carbohydr Polym 183:254–262
Bahners T, Kelch M, Gebert B, Osorio Barajas XL, Schmidt TC, Gutmann JS, Müssig J (2018) Improvement of fibre-matrix adhesion in cellulose/polyolefin composite materials by means of photo-chemical fibre surface modification. Cellulose 25(4):2451–2471
Barrera CS, Cornish K (2019) Characterization of agricultural and food processing residues for potential rubber filler applications. J Compos Sci 3(4):102
Basivi PK, Pasupuleti VR, Hamieh T (2022) Surface thermodynamic properties of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose by inverse gas chromatography. Chem Eng J Adv 9:100207
Bilgiç C (2018) Determination of the surface properties of kaolinite by inverse gas chromatography. Water Sci Technol 2017(2):319–328
Cantergiani E, Benczédi D (2002) Use of inverse gas chromatography to characterize cotton fabrics and their interactions with fragrance molecules at controlled relative humidity. J Chromatogr A 969(1–2):103–110
Castro C, Cordeiro N, Faria M, Zuluaga R, Putaux JL, Filpponen I, Velez L, Rojas OJ, Gañán P (2015) In-situ glyoxalization during biosynthesis of bacterial cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 126:32–39
Cava D, Gavara R, Lagarón J, Voelkel A (2007) Surface characterization of poly (lactic acid) and polycaprolactone by inverse gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1148(1):86–91
Cherian BM, Pothan LA, Nguyen-Chung T, Mennig G, Kottaisamy M, Thomas S (2008) A novel method for the synthesis of cellulose nanofibril whiskers from banana fibers and characterization. J Agric Food Chem 56(14):5617–5627
Cordeiro N, Gouveia C, John MJ (2011) Investigation of surface properties of physico-chemically modified natural fibres using inverse gas chromatography. Ind Crop Prod 33(1):108–115
Cordeiro N, Mendonça C, Pothan L, Varma A (2012) Monitoring surface properties evolution of thermochemically modified cellulose nanofibres from banana pseudo-stem. Carbohydr Polym 88(1):125–131
Cordeiro N, Faria M, Abraham E, Pothan LA (2013) Assessment of the changes in the cellulosic surface of micro and nano banana fibres due to saponin treatment. Carbohydr Polym 98(1):1065–1071
Csiszár E, Fekete E (2010) Characterization of the surface properties of differently scoured cotton by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution. Text Res J 80(13):1307–1316
da Silva CG, de Oliveira F, Frollini E (2019) Sugarcane bagasse fibers treated and untreated: performance as reinforcement in phenolic-type matrices based on lignosulfonates. Waste Biomass Valor 10(11):3515–3524
Dorris GM, Gray DG (1980) Adsorption of n-alkanes at zero surface coverage on cellulose paper and wood fibers. J Colloid Interface Sci 77(2):353–362
Edgar KJ, Buchanan CM, Debenham JS, Rundquist PA, Seiler BD, Shelton MC, Tindall D (2001) Advances in cellulose ester performance and application. Prog Polym Sci 26(9):1605–1688
Faria M, Vilela C, Silvestre AJ, Deepa B, Resnik M, Freire CS, Cordeiro N (2019) Physicochemical surface properties of bacterial cellulose/polymethacrylate nanocomposites: an approach by inverse gas chromatography. Carbohydr Polym 206:86–93
Faria M, Cunha C, Gomes M, Mendonça I, Kaufmann M, Ferreira A, Cordeiro N (2022) Bacterial cellulose biopolymers: the sustainable solution to water-polluting microplastics. Water Res 222:118952
Faria M, Mohammadkazemi F, Aguiar R, Cordeiro N (2022) Agro-industrial byproducts as modification enhancers of the bacterial cellulose biofilm surface properties: an inverse chromatography approach. Ind Crops Prod 177:114447
Fekete E, Csiszár E (2017) Characterization of the surface properties of cellulosic fibers in fibrous and ground forms by IGC and contact angle measurements. Fibers Polym 18(7):1255–1262
Gamble JF, Leane M, Olusanmi D, Tobyn M, Šupuk E, Khoo J, Naderi M (2012) Surface energy analysis as a tool to probe the surface energy characteristics of micronized materials—a comparison with inverse gas chromatography. Int J Pharm 422(1–2):238–244
Gamelas JA (2013) The surface properties of cellulose and lignocellulosic materials assessed by inverse gas chromatography: a review. Cellulose 20(6):2675–2693
Gamelas JA, Pedrosa J, Lourenço AF, Ferreira PJ (2015) Surface properties of distinct nanofibrillated celluloses assessed by inverse gas chromatography. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 469:36–41
Gamelas J, Salvador A, Hidalgo J, Ferreira P, Tejado A (2017) Unique combination of surface energy and Lewis acid-base characteristics of superhydrophobic cellulose fibers. Langmuir 33(4):927–935
Jacob PN, Berg JC (1994) Acid-base surface energy characterization of microcrystalline cellulose and two wood pulp fiber types using inverse gas chromatography. Langmuir 10(9):3086–3093
John MJ, Anandjiwala RD (2008) Recent developments in chemical modification and characterization of natural fiber-reinforced composites. Polym Compos 29(2):187–207
Joly C, Gauthier R, Escoubes M (1996) Partial masking of cellulosic fiber hydrophilicity for composite applications. water sorption by chemically modified fibers. J Appl Polym Sci 61(1):57–69
Kabir M, Wang H, Lau K, Cardona F (2012) Chemical treatments on plant-based natural fibre reinforced polymer composites: an overview. Compos Part B Eng 43(7):2883–2892
Kazayawoko M, Balatinecz JJ, Romansky M (1997) Thermodynamics of adsorption of n-alkanes on maleated wood fibers by inverse gas chromatography. J Colloid Interface Sci 190(2):408–415
Kondor A, Quellet C, Dallos A (2015) Surface characterization of standard cotton fibres and determination of adsorption isotherms of fragrances by IGC. Surf Interface Anal 47(11):1040–1050
Lapčík L, Otyepka M, Otyepková E, Lapčíková B, Gabriel R, Gavenda A, Prudilová B (2016) Surface heterogeneity: information from inverse gas chromatography and application to model pharmaceutical substances. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 24:64–71
Legras A, Kondor A, Heitzmann M, Truss R (2015) Inverse gas chromatography for natural fibre characterisation: identification of the critical parameters to determine the brunauer-emmett-teller specific surface area. J Chromatogr A 1425:273–279
Legras A, Kondor A, Alcock M, Heitzmann M, Truss R (2017) Inverse gas chromatography for natural fibre characterisation: dispersive and acid-base distribution profiles of the surface energy. Cellulose 24(11):4691–4700
Li YY, Wang B, Ma MG, Wang B (2018) Review of recent development on preparation, properties, and applications of cellulose-based functional materials. Int J Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8973643
Li M, Pu Y, Thomas VM, Yoo CG, Ozcan S, Deng Y, Nelson K, Ragauskas AJ (2020) Recent advancements of plant-based natural fiber-reinforced composites and their applications. Compos Part B Eng 200:108254
Li T, Chen C, Brozena AH, Zhu J, Xu L, Driemeier C, Dai J, Rojas OJ, Isogai A, Wågberg L et al (2021) Developing fibrillated cellulose as a sustainable technological material. Nature 590(7844):47–56
Mader A, Volkmann E, Einsiedel R, Müssig J (2012) Impact and flexural properties of unidirectional man-made cellulose reinforced thermoset composites. J Biobased Mater Bioenergy 6(4):481–492
Mader A, Kondor A, Schmid T, Einsiedel R, Müssig J (2016) Surface properties and fibre-matrix adhesion of man-made cellulose epoxy composites-Influence on impact properties. Compos Sci Technol 123:163–170
Mahfoudhi N, Boufi S (2017) Nanocellulose as a novel nanostructured adsorbent for environmental remediation: a review. Cellulose 24(3):1171–1197
Mahmud S, Hasan K, Jahid M, Mohiuddin K, Zhang R, Zhu J et al (2021) Comprehensive review on plant fiber-reinforced polymeric biocomposites. J Mater Sci 56(12):7231–7264
Mohammadi-Jam S, Waters K (2014) Inverse gas chromatography applications: a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 212:21–44
Nie S, Hao N, Zhang K, Xing C, Wang S (2020) Cellulose nanofibrils-based thermally conductive composites for flexible electronics: a mini review. Cellulose 27(8):4173–4187
Omran AAB, Mohammed AA, Sapuan S, Ilyas R, Asyraf M, Rahimian Koloor SS, PetrM̆, (2021) Micro-and nanocellulose in polymer composite materials: a review. Polymers 13(2):231
Onwukamike KN, Grelier S, Grau E, Cramail H, Meier MA (2018) Critical review on sustainable homogeneous cellulose modification: why renewability is not enough. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7(2):1826–1840
Pal A, Kondor A, Mitra S, Thu K, Harish S, Saha BB (2019) On surface energy and acid-base properties of highly porous parent and surface treated activated carbons using inverse gas chromatography. J Ind Eng Chem 69:432–443
Papirer E, Brendle E, Balard H, Vergelati C (2000) Inverse gas chromatography investigation of the surface properties of cellulose. J Adhes Sci Technol 14(3):321–337
Pefferkorn E (1999) Interfacial Phenomena in Chromatography. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203909867
Peng Y, Gardner DJ, Han Y, Cai Z, Tshabalala MA (2013) Influence of drying method on the surface energy of cellulose nanofibrils determined by inverse gas chromatography. J Colloid Interface Sci 405:85–95
Praveen Kumar B, Ramanaiah S, Madhusudana Reddy T, Reddy K (2014) Surface characterization of cellulose acetate propionate by inverse gas chromatography. Polym Bull 71(1):125–132
Ramanaiah S, Rani PR, Sreekanth T, Reddy K (2011) Determination of Hansen solubility parameters for the solid surface of cellulose acetate butyrate by inverse gas chromatography. J Macromol Sci Phys B 50(3):551–562
Ramanaiah S, Rani PR, Reddy K (2012) Hansen solubility parameters for the solid surface of cellulose acetate propionate by inverse gas chromatography. J Macromol Sci Phys B 51(11):2191–2200
Rani PR, Ramanaiah S, Reddy K (2011) Lewis acid-base properties of cellulose acetate butyrate by inverse gas chromatography. Surf Interface Anal 43(3):683–688
Reddy AS, Ramanaiah S, Reddy K (2013) Hansen solubility parameters of a cellulose acetate propionate-poly (caprolactone) diol blend by inverse gas chromatography. Int J Polym Anal 18(3):172–180
Reddy AS, Rani PR, Reddy KS (2014) Hansen solubility parameters of cellulose acetate phthalate-polycaprolactonediol blend by inverse gas chromatography. J Macromol Sci Phys B 53(8):1335–1347
Sacui IA, Nieuwendaal RC, Burnett DJ, Stranick SJ, Jorfi M, Weder C, Foster EJ, Olsson RT, Gilman JW (2014) Comparison of the properties of cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofibrils isolated from bacteria, tunicate, and wood processed using acid, enzymatic, mechanical, and oxidative methods. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(9):6127–6138
Saint Flour C, Papirer E (1982) Gas-solid chromatography: method of measuring surface free energy characteristics of short fibers. 2. Through retention volumes measured near zero surface coverage. Ind Eng Chem Prod Res Dev 21(4):666–669
Schultz J, Lavielle L, Martin C (1987) The role of the interface in carbon fibre-epoxy composites. J Adhes 23(1):45–60
Shaghaleh H, Xu X, Wang S (2018) Current progress in production of biopolymeric materials based on cellulose, cellulose nanofibers, and cellulose derivatives. RSC Adv 8(2):825–842
Sharma A, Thakur M, Bhattacharya M, Mandal T, Goswami S (2019) Commercial application of cellulose nano-composites—a review. Biotechnol Rep 21:e00316
Shi B, Wang Y, Jia L (2011) Comparison of Dorris-gray and Schultz methods for the calculation of surface dispersive free energy by inverse gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1218(6):860–862
Sood M, Dharmpal D, Gupta V (2015) Effect of fiber chemical treatment on mechanical properties of sisal fiber/recycled HDPE composite. Mater Today Proc 2(4–5):3149–3155
Voelkel A (1991) Inverse gas chromatography: characterization of polymers, fibers, modified silicas, and surfactants. Crit Rev Anal Chem 22(5):411–439
Voelkel A (2004) Inverse gas chromatography in characterization of surface. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 72(2):205–207
Voelkel A, Adamska K, Strzemiecka B, Batko K (2008) Determination of Hansen solubility parameters of solid materials by inverse gas-solid chromatography. Acta Chromatogr 20(1):1–14
Voelkel A, Strzemiecka B, Adamska K, Milczewska K (2009) Inverse gas chromatography as a source of physiochemical data. J Chromatogr A 1216(10):1551–1566
Wang B, Sain M (2007) The effect of chemically coated nanofiber reinforcement on biopolymer based nanocomposites. BioResources 2(3):371–388
Wang H, Zhu E, Yang J, Zhou P, Sun D, Tang W (2012) Bacterial cellulose nanofiber-supported polyaniline nanocomposites with flake-shaped morphology as supercapacitor electrodes. J Phys Chem C 116(24):13013–13019
Wang L, Sanders JE, Gardner DG, Han Y (2016) In-situ modification of cellulose nanofibrils by organosilanes during spray drying. Ind Crops Prod 93:129–135
Acknowledgments
We wish to acknowledge support from Deakin University for the PhD scholarship awarded to the first author. Xungai Wang acknowledges support from the Hong Kong Jockey Club Charities Trust and the JC STEM Lab of Sustainable Fibers and Textiles.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (52203124).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wenli Bai wrote the first draft of the manuscript and prepared Figures. All authors read and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, W., Pakdel, E., Li, Q. et al. Inverse gas chromatography (IGC) for studying the cellulosic materials surface characteristics: a mini review. Cellulose 30, 3379–3396 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05116-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05116-9