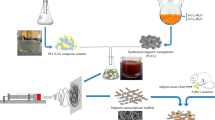
Abstract
This study fabricated a nano-biomaterial of supermagnetized α-cellulose (αCS@Fe3O4) for enhanced osteoconduction of hADSCs (human adipose-derived stem cells). First, the reduction precipitation method was successfully employed to synthesize αCS@Fe3O4. The synthesized material αCS@Fe3O4 was structurally and morphologically characterized by SEM, TEM, XRD, TGA, and XPS analyses. The characterizations confirmed a nanostructural modification of αCS using Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Next, the fabricated material αCS@Fe3O4 was assessed for biocompatibility. The obtained data confirmed the biocompatible nature of the αCS@Fe3O4. Then, the αCS@Fe3O4 was applied for the osteoconductive differentiation of the hADSCs. The hADSCs osteoconduction was enhanced significantly (11.325 fold increase) in the presence of the αCS@Fe3O4 compared to the control hADSCs. The Alizarin Red S (ARS) staining microscopic images corroborated the osteoconduction enhancement. Furthermore, the relative gene expression of the important osteogenic markers ALP, OCN, and RUNX2 was analyzed. The expression levels were significantly enhanced in the presence of the target material αCS@Fe3O4. Finally, the immunofluorescent staining of ALP, OCN, and RUNX2 corroborated the enhanced osteoconduction. Thus, in conclusion, αCS@Fe3O4 is a low-cost, economical, biocompatible nano-biomaterial with significant osteoconduction enhancement potential that can be applied in bone defect treatments in the future.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this submitted article.
References
Adams GA, Bishop CT (1953) Pollysachharide associated with Ailha-Cellulose. Nature 172:28–29
Amarasekara DS, Kim S, Rho J (2021) Regulation of osteoblast differentiation by cytokine networks. Int J Mol Sci 22:1–16. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062851
Azizi A (2020) Green synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and its application in preparation of Fe3O4/Cellulose magnetic nanocomposite: a suitable proposal for drug delivery systems. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 30:3552–3561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01500-1
Byers BA, García AJ (2004) Exogenous Runx2 expression enhances in vitro osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization in primary bone marrow stromal cells. Tissue Eng 10:1623–1632
Debnath T, Chelluri LK (2019) Standardization and quality assessment for clinical grade mesenchymal stem cells from human adipose tissue. Hematol Transfus Cell Ther 41:7–16. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.htct.2018.05.001
Ghodake GS, Yang J, Shinde SS et al (2018) Paper waste extracted Α-cellulose fibers super-magnetized and chitosan-functionalized for covalent laccase immobilization. Bioresour Technol 261:420–427. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.04.051
Ghodake GS, Shinde SK, Saratale GD et al (2021) α-Cellulose fibers of paper-waste origin surface-modified with Fe3O4 and thiolated-chitosan for efficacious immobilization of laccase. Polymers 13:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040581
Gong J, Li J, Xu J et al (2017) Research on cellulose nanocrystals produced from cellulose sources with various polymorphs. RSC Adv 7:33486–33493. doi: https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra06222b
Hembrick-Holloman V, Samuel T, Mohammed Z et al (2020) Ecofriendly production of bioactive tissue engineering scaffolds derived from egg- and sea-shells. J Mater Res Technol 9:13729–13739. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.09.093
Hickey RJ, Pelling AE (2019) Cellulose biomaterials for tissue engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 7:1–15. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00045
Iwayama T, Okada T, Ueda T et al (2019) Osteoblastic lysosome plays a central role in mineralization. Sci Adv 5:1–10. doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aax0672
Kadam AA, Jang J, Lee DS (2017) Supermagnetically tuned halloysite nanotubes functionalized with aminosilane for covalent laccase immobilization. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:15492–15501. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b02531
Kadam A, Saratale RG, Shinde S et al (2019) Adsorptive remediation of cobalt oxide nanoparticles by magnetized a-cellulose fibers from waste paper biomass. Bioresour Technol 273:386–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.11.041
Kadam AA, Lone S, Shinde S et al (2019) Treatment of hazardous engineered nanomaterials by supermagnetized α-cellulose fibers of renewable paper-waste origin. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:5764–5775. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b05268
Kadam AA, Sharma B, Saratale GD et al (2020) Super-magnetization of pectin from orange-peel biomass for sulfamethoxazole adsorption. Cellulose 27:3301–3318. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-02988-z
Kadam AA, Sung JS, Sharma B (2021) Fe3O4-HNTs-APTES-palladium nanocomposites with enhanced high-temperature gas response properties. J Alloys Compd 854:157041. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157041
Karimi Z, Seyedjafari E, Mahdavi FS et al (2019) Baghdadite nanoparticle-coated poly l-lactic acid (PLLA) ceramics scaffold improved osteogenic differentiation of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 107:1284–1293. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.36638
Kim M, Jee SC, Sung JS, Kadam AA (2020) Supermagnetic sugarcane bagasse hydrochar for enhanced osteoconduction in human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Nanomaterials 10:1–17. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091793
Konno M, Hamabe A, Hasegawa S et al (2013) Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and regenerative medicine. Dev Growth Differ 55:309–318. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/dgd.12049
Kunusa WR, Abdullah R, Bilondatu K, Tulie WZ (2020) Analysis of cellulose isolated from sugar bagasse: optimization and treatment process scheme. In: Journal of Physics Conference Series, vol. 1422. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1422/1/012040
Lee BC, Kang KS (2020) Functional enhancement strategies for immunomodulation of mesenchymal stem cells and their therapeutic application. Stem Cell Res Ther 11:1–10. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-01920-3
Lee YJ, Lee SC, Jee SC et al (2019) Surface functionalization of halloysite nanotubes with supermagnetic iron oxide, chitosan and 2-D calcium-phosphate nanoflakes for synergistic osteoconduction enhancement of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 173:18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.09.045
Li Y, Ye D, Li M et al (2018) Adaptive materials based on iron oxide nanoparticles for bone regeneration. ChemPhysChem 19:1965–1979. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201701294
Lu D, Wu X, Wang W et al (2021) Synthesis and application of iron oxide nanoparticles in bone tissue repair. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3762490
Mahendra IP, Wirjosentono B, Tamrin et al (2019) Thermal and morphology properties of cellulose nanofiber from TEMPO-oxidized lower part of empty fruit bunches (LEFB). Open Chem 17:526–536. doi: https://doi.org/10.1515/chem-2019-0063
Moll G, Hoogduijn MJ, Ankrum JA (2020) Editorial: safety, efficacy and mechanisms of action of mesenchymal stem cell therapies. Front Immunol 11:1–4. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.00243
Murshed M (2018) Mechanism of bone mineralization. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 8:1–11. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/CSHPERSPECT.A031229
Porgham Daryasari M, Dusti Telgerd M, Hossein Karami M et al (2019) Poly-l-lactic acid scaffold incorporated chitosan-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as pH-sensitive composite for enhanced osteogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue stem cells by dexamethasone delivery. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:4020–4029. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1658594
Prakash S, Khan A, Paul A (2010) Nanoscaffold based stem cell regeneration therapy: recent advancement and future potential. Expert Opin Biol Ther 10:1649–1661. doi: https://doi.org/10.1517/14712598.2010.528387
Safari B, Aghazadeh M, Roshangar L et al (2022) A bioactive porous scaffold containing collagen/ phosphorous-modified polycaprolactone for osteogenesis of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Eur Polym J 171:111220. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2022.111220
Schneider MGM, Martín MJ, Otarola J et al (2022) Biomedical applications of iron oxide nanoparticles: current insights progress and perspectives. Pharmaceutics. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010204
Shibli JA, Nagay BE, Suárez LJ et al (2022) Bone tissue engineering using osteogenic cells: from the bench to the clinical application. Tissue Eng Part C Methods 28:179–192. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.tec.2022.0021
Tang Z, Li X, Tan Y et al (2018) The material and biological characteristics of osteoinductive calcium phosphate ceramics. Regen Biomater 5:43–59. https://doi.org/10.1093/rb/rbx024
Telgerd MD, Sadeghinia M, Birhanu G et al (2019) Enhanced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on metal–organic framework based on copper, zinc, and imidazole coated poly-l-lactic acid nanofiber scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 107:1841–1848. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.36707
Thulluri C, Balasubramaniam R, Velankar HR (2021) Generation of highly amenable cellulose-Iβ via selective delignification of rice straw using a reusable cyclic ether-assisted deep eutectic solvent system. Sci Rep 11:1–14. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-80719-x
Wu X, Jiang J, Gu Z et al (2020) Mesenchymal stromal cell therapies: immunomodulatory properties and clinical progress. Stem Cell Res Ther 11:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-01855-9
Zhang X, Yang M, Lin L et al (2006) Runx2 overexpression enhances osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization in adipose - derived stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Calcif Tissue Int 79:169–178. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-006-0083-6
Zhao X, Hu DA, Wu D et al (2021) Applications of biocompatible scaffold materials in stem cell-based cartilage tissue engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 9:1–23. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.603444
Zhuang L, Zhang W, Zhao Y et al (2015) Preparation and characterization of Fe3O4 particles with novel nanosheets morphology and magnetochromatic property by a modified solvothermal method. Sci Rep 5:1–6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09320
Zoch ML, Clemens TL, Riddle RC (2016) New insights into the biology of osteocalcin. Bone 82:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2015.05.046
Acknowledgments
The all authors acknowledge Dongguk University for providing all facilities. This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2022R1A6A1A03053343), and the Rural Development Administration (S-2022-A0353-00004).
Funding
This work was carried out with the support by (S-2022-A0353-00004). This research was also supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education (2022R1A6A1A03053343).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Supervision, AAK; Investigation, SCL, SHL, AAK; Methodology, SCL, AAK, DHK, MK, JSS; Writing-Original Draft, SCL, AAK; Writing—Review & Editing, SCL, AAK, JSS. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Human or animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, SC., Lee, SH., Kang, DH. et al. Supermagnetic α-cellulosic nano-scaffolds for human adipose-derived stem cells osteoconduction enhancement. Cellulose 30, 2385–2398 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05045-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05045-7