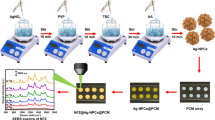
Abstract
Cellulose-based surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) platforms have attracted extensive attention as a flexible, sustainable, eco-friendly and ultrasensitive sensor for trace detection of chemical and biological molecules. However, preparation of cellulose-based SERS substrates usually suffers from high cost, complicated fabrication step, time-consuming process and poor signal reproducibility. In this research, the flexible Ag nanoparticle-coated bacterial nanocellulose (AgNP@BNC) SERS substrates are successfully developed by a facile, low-cost, efficient and scalable magnetron sputtering technology. Taking advantage of the characteristics of magnetron sputtering technology, silver nanoparticles are rapidly and uniformly deposited onto the surface of BNC membrane. In addition, due to the large specific surface area, excellent permeability and adsorption properties of hydrophilic nanocellulose, the target molecules are also uniformly distributed on the surface of nanocellulose membrane. As a result, the optimal AgNP-120@BNC SERS substrate exhibits high sensitivity of 10–9 M for crystal violet, remarkable signal homogeneity and excellent storage stability. The flexible AgNP-120@BNC SERS substrate also exhibits ultra-sensitive pesticide detection with a detection limit of 7.8 × 10–8 M for lambda-cyhalothrin on irregular fruit surfaces by a feasible paste-and-read way. This research demonstrates promising application of magnetron sputtering technology in the development of flexible, low-cost and large-scale nanocellulose-based SERS sensors for trace detection of toxic materials.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data and materials are available from authors by reasonable request.
References
Abolfotouh D, Hassan MA, Shokry H, Roig A, Azab MS, Kashyout AE (2020) Bacterial nanocellulose from agro-industrial wastes: low-cost and enhanced production by Komagataeibacter saccharivorans MD1. Sci Rep 10:1–14
Agarwal UP, Ralph SA, Baez C, Reiner RS (2021) Contributions of crystalline and noncrystalline cellulose can occur in the same spectral regions: evidence based on Raman and IR and its implication for crystallinity measurements. Biomacromol 22:1357–1373
Atanasov PA, Nedyalkov NN, Fukata N, Jevasuwan W (2021) Advanced silver and gold substrates for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of pesticides. Spectrosc Lett 54:528–538
Basir A, Khan A, Mustafa R, Zargham KM, Rizvi F, Mahmood F, Yousaf A (2011) Toxicopathological effects of lambda-cyhalothrin in female rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Hum Exp Toxicol 30:591–602
Bian X, Xu J, Yang J, Kl C, Jiang S (2021) Flexible Ag SERS substrate for non-destructive and rapid detection of toxic materials on irregular surface. Surf Interfaces 23:100995
Botta R, Eiamchai P, Horprathum M, Limwichean S, Chananonnawathorn C, Patthanasettakul V, Nuntawong N (2018) Investigation of silver nanorods as reusable SERS-active substrates for trace level detection of 2-MIB volatile organic compound. Sensor Actuat B Chem 271:122–127
Botta R, Eiamchai P, Horprathum M, Limwichean S, Chananonnawathorn C, Patthanasettakul V, Maezono R, Jomphoak A, Nuntawong N (2020) 3D structured laser engraves decorated with gold nanoparticle SERS chips for paraquat herbicide detection in environments. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 304:127327
Botta R, Limwichean S, Limsuwan N, Moonlek C, Horprathum M, Eiamchai P, Chananonnawathorn C, Patthanasettakul V, Chindaudom P, Nuntawong N, Ngernsutivorakul T (2022) An efficient and simple SERS approach for trace analysis of tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabinol and multi-cannabinoid detection. Spectrochim Acta A 281:121598
Çelik A, Mazmanci B, Çamlica Y, Çömelekoğlu Ü, Aşkin A (2005) Evaluation of cytogenetic effects of lambda-cyhalothrin on Wistar rat bone marrow by gavage administration. Ecotox Environ Safe 61:128–133
Chen J, Huang M, Kong L, Lin M (2019) Jellylike flexible nanocellulose SERS substrate for rapid in-situ non-invasive pesticide detection in fruits/vegetables. Carbohyd Polymers 205:596–600
Chen J, Huang M, Kong L (2020) Flexible Ag/nanocellulose fibers SERS substrate and its applications for in-situ hazardous residues detection on food. Appl Surf Sci 533:147454
Deshmukh AR, Dikshit PK, Kim BS (2022) Green in situ immobilization of gold and silver nanoparticles on bacterial nanocellulose film using Punica granatum peels extract and their application as reusable catalysts. Int J Biol Macromol 205:169–177
Du J, Jing C (2011) Preparation of Fe3O4@Ag SERS substrate and its application in environmental Cr (VI) analysis. J Colloid Interf Sci 358:54–61
Dufresne A (2013) Nanocellulose: a new ageless bionanomaterial. Mater Today 16:220–227
Fan X, Zhao S, Hu J (2019) Dissipation behavior and dietary risk assessment of lambda-cyhalothrin, thiamethoxam and its metabolite clothianidin in apple after open field application. Regul Toxicol Pharm 101:135–141
Gomez M, Lazzari M (2014) Reliable and cheap SERS active substrates. Mater Today 7:358–359
Gu J, Dichiara A (2020) Hybridization between cellulose nanofibrils and faceted silver nanoparticles used with surface enhanced Raman scattering for trace dye detection. Int J Biol Macromol 143:85–92
Gullace S, Montes-García V, Martín V, Larios D, Girelli Consolaro V, Obelleiro F, Calogero G, Casalini S, Samorì P (2021) Universal fabrication of highly efficient plasmonic thin-films for label-free SERS detection. Small 17:2100755
Hu H, Gao W, Zang R, Gao J, Tang S, Li X, Liang L, Zhang H, Cao H (2020) Direct growth of vertically orientated nanocavity arrays for plasmonic color generation. Adv Funct Mater 30:2002287
Huang F, Ma G, Liu J, Lin J, Wang X, Guo L (2016) High-yield synthesis of hollow octahedral silver nanocages with controllable pack density and their high-performance sers application. Small 12:5442–5448
Huang X, Wang A, Luo J, Gao Y, Guan L, Zhang P, Liu F, Mu W, Li B (2022) Lambda-cyhalothrin-loaded nanocapsules pose an unacceptable acute toxicological risk to zebrafish (Danio rerio) at the adult and larval stages but present an acceptable risk to embryos. J Hazard Mater 422:126853
Huo D, Chen B, Meng G, Huang Z, Li M, Lei Y (2020) Ag-nanoparticles@ bacterial nanocellulose as a 3D flexible and robust surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:50713–50720
Kavkler K, Demšar A (2011) Examination of cellulose textile fibres in historical objects by micro-Raman spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta A 78:740–746
Kelly PJ, Arnell RD (2000) Magnetron sputtering: a review of recent developments and applications. Vacuum 56:159–172
Kim D, Kim J, Henzie J, Ko Y, Lim H, Kwon G, Na J, Kim HJ, Yamauchi Y, You J (2021) Mesoporous Au films assembled on flexible cellulose nanopaper as high-performance SERS substrates. Chem Eng J 419:129445
Klemm D, Cranston ED, Fischer D, Gama M, Kedzior SA, Kralisch D, Kramer F, Kondo T, Lindström T, Nietzsche S (2018) Nanocellulose as a natural source for groundbreaking applications in materials science: today’s state. Mater Today 21:720–748
Li L, Chin WS (2020) Rapid fabrication of a flexible and transparent Ag nanocubes@PDMS film as a SERS substrate with high performance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:37538–37548
Li C, Huang Y, Li X, Zhang Y, Chen Q, Ye Z, Alqarni Z, Bell S, Xu Y (2021) Towards practical and sustainable SERS: a review of recent developments in the construction of multifunctional enhancing substrates. J Mater Chem C 9:11517–11552
Li X, Zhang T, Chen Z, Yu J, Cao A, Liu D, Cai W, Li Y (2022) Au polyhedron array with tunable crystal facets by PVP-assisted thermodynamic control and its sharp shape as well as high-energy exposed planes co-boosted SERS activity. Small 18:2105045
Liang J, Liu Q, Li T, Luo Y, Lu S, Shi X, Zhang F, Asiri AM, Sun X (2021) Magnetron sputtering enabled sustainable synthesis of nanomaterials for energy electrocatalysis. Green Chem 23:2834–2867
Liu DY, Sui G, Bhattacharyya D (2014) Synthesis and characterisation of nanocellulose-based polyaniline conducting films. Compos Sci Technol 99:31–36
Luo Y, Xing L, Hu C, Zhang W, Lin X, Gu J (2022) Facile synthesis of nanocellulose-based Cu2O/Ag heterostructure as a surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate for trace dye detection. Int J Biol Macromol 205:366–375
Mohammadkazemi F, Faria M, Cordeiro N (2016) In situ biosynthesis of bacterial nanocellulose-CaCO3 hybrid bionanocomposite: one-step process. Mater Sci Eng C 65:393–399
Peng Y, Lin C, Long L, Masaki T, Tang M, Yang L, Liu J, Huang Z, Li Z, Luo X, Lombardi JR, Yang Y (2021) Charge-transfer resonance and electromagnetic enhancement synergistically enabling mxenes with excellent SERS sensitivity for SARS-CoV-2 S protein detection. Nano-Micro Lett 13:52
Sharma KK, Tripathy V, Mohapatra S, Matadha NY, Pathan ARK, Sharma BN, Dubey JK, Katna S, George T, Tayade A (2021) Dissipation kinetics and consumer risk assessment of novaluron+ lambda-cyhalothrin co-formulation in cabbage. Ecotox Environ Safe 208:111494
Shen Y, Wu X, Wu B, Tan Y, Liu J (2021) Qualitative analysis of lambda-cyhalothrin on chinese cabbage using mid-infrared spectroscopy combined with fuzzy feature extraction algorithms. Agriculture 11:275
Shi Y, Li Y, Zhang J, Yu Z, Yang D (2015) Electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers loaded with silver nanoparticles by silver mirror reaction. Mater Sci Eng C 51:346–355
Sivashanmugan K, Liao JD, You JW, Wu CL (2013) Focused-ion-beam-fabricated Au/Ag multilayered nanorod array as SERS-active substrate for virus strain detection. Sensor Actuat B Chem 181:361–367
Song Y, Huang HC, Lu W, Li N, Su J, Cheng SB, Lai Y, Chen J, Zhan J (2021) Ag@WS2 quantum dots for Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: enhanced charge transfer induced highly sensitive detection of thiram from honey and beverages. Food Chem 344:128570
Sutter P, Lahiri J, Zahl P, Wang B, Sutter E (2013) Scalable synthesis of uniform few-layer hexagonal boron nitride dielectric films. Nano Lett 13:276–281
Thomas B, Raj MC, Joy J, Moores A, Drisko GL, Sanchez C (2018) Nanocellulose, a versatile green platform: from biosources to materials and their applications. Chem Rev 118:11575–11625
Tian Y, Liu H, Chen Y, Zhou C, Jiang Y, Gu C, Jiang T, Zhou J (2019) Seedless one-spot synthesis of 3D and 2D Ag nanoflowers for multiple phase SERS-based molecule detection. Sensor Actuat B- Chem 301:127142
Trache D, Tarchoun AF, Derradji M, Hamidon TS, Masruchin N, Brosse N, Hussin MH (2020) Nanocellulose: from fundamentals to advanced applications. Front Chem 8:392
Wang Y, Wang M, Sun X, Shi G, Zhang J, Ma W, Ren L (2018) Grating-like SERS substrate with tunable gaps based on nanorough Ag nanoislands/moth wing scale arrays for quantitative detection of cypermethrin. Opt Exp 26:22168–22181
Wang K, Sun DW, Pu H, Wei Q (2019) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering of core-shell Au@Ag nanoparticles aggregates for rapid detection of difenoconazole in grapes. Talanta 191:449–456
Wen P, Yang F, Ge C, Li S, Xu Y, Chen L (2021) Self-assembled nano-Ag/Au@ Au film composite SERS substrates show high uniformity and high enhancement factor for creatinine detection. Nanotechnology 32:395502
Wu J, Du Y, Wang C, Bai S, Zhang T, Chen T, Hu A (2019) Reusable and long-life 3D Ag nanoparticles coated Si nanowire array as sensitive SERS substrate. Appl Surf Sci 494:583–590
Wu D, Hu M, Zhang Y, Zhou J, Wang Z (2020a) Long-range ordered silver nanoflower array structure for surface enhanced Raman scattering detecting. Appl Surf Sci 505:144520
Wu L, Zhang W, Liu C, Foda MF, Zhu Y (2020b) Strawberry-like SiO2/Ag nanocomposites immersed filter paper as SERS substrate for acrylamide detection. Food Chem 328:127106
Wu J, Xi J, Chen H, Li S, Zhang L, Li P, Wu W (2022) Flexible 2D nanocellulose-based SERS substrate for pesticide residue detection. Carbohyd Polym 277:118890
Xing C, Liu D, Chen J, Fan Y, Zhou F, Kaur K, Cai W, Li Y (2021a) Convective self-assembly of 2D nonclose-packed binary Au nanoparticle arrays with tunable optical properties. Chem Mater 33:310–319
Xing C, Zhong S, Liu D, Zhang T, Cao A, Zeng P, Men D, Li C, Cai W, Li Y (2021b) Hydrogel film@Au nanoparticle arrays based on self-assembly co-assisted by electrostatic attraction and hydrogel-shrinkage for SERS detection with active gaps. Adv Mater Interfaces 8:2101055
Xu J, Li X, Wang Y, Guo R, Shang S, Jiang S (2019) Flexible and reusable cap-like thin Fe2O3 film for SERS applications. Nano Res 12:381–388
Xu Y, Kutsanedzie FYH, Hassan M, Zhu J, Ahmad W, Li H, Chen Q (2020) Mesoporous silica supported orderly-spaced gold nanoparticles SERS-based sensor for pesticides detection in food. Food Chem 315:126300
Xu D, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Yang W, Chen J (2021) Ultrasensitive SERS detection of crystal violet and malachite green based on high surface roughness copper nanocorns prepared via solid-state ionics method. Sensor Actuat A-Physl 331:113042
Xu D, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Yang W, Wang Z, Li J (2022) Copper nanoleaves SERS substrates with high surface roughness for sensitive detection crystal violet and rhodamine 6G. Opt Laser Technol 145:107502
Yan X, Wang M, Sun X, Wang Y, Shi G, Ma W, Hou P (2019) Sandwich-like Ag@Cu@CW SERS substrate with tunable nanogaps and component based on the plasmonic nanonodule structures for sensitive detection crystal violet and 4-aminothiophenol. Appl Surf Sci 479:879–886
Yang L, Peng Y, Yang Y, Liu J, Huang H, Yu B, Zhao J, Lu Y, Huang Z, Li Z (2019) A novel ultra-sensitive semiconductor SERS substrate boosted by the coupled resonance effect. Adv Sci 6:1900310
Zeng M, Laromaine A, Roig A (2014) Bacterial cellulose films: influence of bacterial strain and drying route on film properties. Cellulose 21:4455–4469
Zhai J, Zhang Y, Cui C, Li A, Wang W, Guo R, Qin W, Ren E, Xiao H, Zhou M (2021) Flexible waterborne polyurethane/cellulose nanocrystal composite aerogels by integrating graphene and carbon nanotubes for a highly sensitive pressure sensor. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 9:14029–14039
Zhang S, Sun G, He Y, Fu R, Gu Y, Chen S (2017) Preparation, characterization, and electrochromic properties of nanocellulose-based polyaniline nanocomposite films. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:16426–16434
Zhang T, Li X, Li C, Cai W, Li Y (2021) One-pot synthesis of ultrasmooth, precisely shaped gold nanospheres via surface self-polishing etching and regrowth. Chem Mater 33:2593–2603
Zheng J, Huang Z, Zeng Y, Liu W, Wei B, Qi Z, Wang Z, Xia C, Liang H (2022) Electrostatic shielding regulation of magnetron sputtered Al-based alloy protective coatings enables highly reversible zinc anodes. Nano Lett 22:1017–1023
Zhong F, Wu Z, Guo J, Jia D (2018) Porous silicon photonic crystals coated with Ag nanoparticles as efficient substrates for detecting trace explosives using SERS. Nanomaterials 8:872
Zhou X, Hu Z, Yang D, Xie S, Jiang Z, Niessner R, Haisch C, Zhou H, Sun P (2020) Bacteria detection: from powerful SERS to its advanced compatible techniques. Adv Sci 7:2001739
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Hong Kong Innovation & Technology Commission and China Resources Co., Ltd. for financial support.
Funding
This work is financially supported by the Hong Kong Innovation and Technology Funding (No. PRP/104/20TI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.J. supervised this study. S.Z. and S.J. conceived this idea and designed the experiment. S.Z. wrote the main original manuscript and carried out the main experiment. S.Z. and J.X. performed the FDTD simulations. S.Z., J.X., Z.L. and Y.H. analyzed the experimental data. All the authors reviewed and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This research does not involve any human participants and/or animals for studies by any of the authors.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to submit and publish this manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Xu, J., Liu, Z. et al. Rapid and scalable preparation of flexible Ag nanoparticle-decorated nanocellulose SERS sensors by magnetron sputtering for trace detection of toxic materials. Cellulose 29, 9865–9879 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04871-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04871-5