Abstract
Purpose
The essential action of B7 homolog 3 (B7-H3) in different diseases and cancers has been documented. We here focused on its role in breast cancer through the Raf/MEK/ERK axis regarding lung metastasis.
Methods
Expression pattern of B7-H3 was determined in breast cancer tissues and cells with its correlation with prognosis analyzed. Then, through transfection of lentivirus vector expressing B7-H3-shRNA, overexpression vector of B7-H3 (B7-H3-LV), U0126 (small molecule inhibitor of MEK), or PD98059 (small molecule inhibitor of ERK), the in vitro and in vivo effects of B7-H3 in breast cancer cell biological processes, and lung metastasis were analyzed in relation to the Raf/MEK/ERK axis.
Results
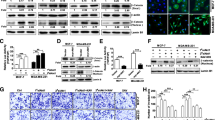
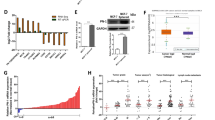
We discovered elevated B7-H3 in breast cancer and its elevation associated with poor prognosis. B7-H3 promoted the malignant properties of breast cancer cells, accompanied with increased N-cadherin and vimentin and reduced E-cadherin. Additionally, overexpression of B7-H3 accelerated the lung metastasis in breast cancer in vivo. All the above promoting action of B7-H3 was achieved through activation of the Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway.
Conclusion
Taken together, B7-H3 can promote lung metastasis in breast cancer through activation of the Raf/MEK/ERK axis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material and further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
References
Latha NR, Rajan A, Nadhan R, Achyutuni S, Sengodan SK, Hemalatha SK, Varghese GR, Thankappan R, Krishnan N, Patra D, Warrier A, Srinivas P (2020) Gene expression signatures: a tool for analysis of breast cancer prognosis and therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 151:102964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2020.102964
Mavaddat N, Antoniou AC, Easton DF, Garcia-Closas M (2010) Genetic susceptibility to breast cancer. Mol Oncol 4(3):174–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molonc.2010.04.011
Neal CH, Helvie MA (2021) Overdiagnosis and risks of breast cancer screening. Radiol Clin North Am 59(1):19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcl.2020.09.005
Yang C, Cheng X, Shen P (2021) Silencing of BCSG1 with specific siRNA via nanocarriers for breast cancer treatment. Bull Cancer 108(3):323–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bulcan.2020.10.022
Zhang X, Huang Y, Song H, Canup BSB, Gou S, She Z, Dai F, Ke B, Xiao B (2020) Inhibition of growth and lung metastasis of breast cancer by tumor-homing triple-bioresponsive nanotherapeutics. J Control Release 328:454–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.08.066
Scribner JA, Brown JG, Son T, Chiechi M, Li P, Sharma S, Li H, De Costa A, Li Y, Chen Y, Easton A, Yee-Toy NC, Chen FZ, Gorlatov S, Barat B, Huang L, Wolff CR, Hooley J, Hotaling TE, Gaynutdinov T, Ciccarone V, Tamura J, Koenig S, Moore PA, Bonvini E, Loo D (2020) Preclinical development of MGC018, a duocarmycin-based antibody-drug conjugate targeting B7–H3 for solid cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-20-0116
Bachawal SV, Jensen KC, Wilson KE, Tian L, Lutz AM, Willmann JK (2015) Breast cancer detection by B7–H3-targeted ultrasound molecular imaging. Cancer Res 75(12):2501–2509. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3361
Dastmalchi N, Safaralizadeh R, Baghbanzadeh A, Hajiasgharzadeh K, Roshani Asl E, Amini M, Baradaran B (2020) Molecular mechanisms of breast cancer chemoresistance by immune checkpoints. Life Sci 263:118604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118604
Ding M, Liao H, Zhou N, Yang Y, Guan S, Chen L (2020) B7–H3-induced signaling in lung adenocarcinoma cell lines with divergent epidermal growth factor receptor mutation patterns. Biomed Res Int 2020:8824805. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8824805
Liu Z, Zhang W, Phillips JB, Arora R, McClellan S, Li J, Kim JH, Sobol RW, Tan M (2019) Immunoregulatory protein B7–H3 regulates cancer stem cell enrichment and drug resistance through MVP-mediated MEK activation. Oncogene 38(1):88–102. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0407-9
Montagut C, Settleman J (2009) Targeting the RAF-MEK-ERK pathway in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett 283(2):125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2009.01.022
Bianchi-Smiraglia A, Paesante S, Bakin AV (2013) Integrin beta5 contributes to the tumorigenic potential of breast cancer cells through the Src-FAK and MEK-ERK signaling pathways. Oncogene 32(25):3049–3058. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.320
Hussain J, Chhabria D, Kirubakaran S (2020) Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of new Myo-inositol derivatives as potential RAS inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 30(16):127290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2020.127290
Giuliano AE, Connolly JL, Edge SB, Mittendorf EA, Rugo HS, Solin LJ, Weaver DL, Winchester DJ, Hortobagyi GN (2017) Breast cancer-major changes in the American Joint Committee on Cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. Cancer J Clin 67(4):290–303. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21393
Cheng R, Chen Y, Zhou H, Wang B, Du Q, Chen Y (2018) B7–H3 expression and its correlation with clinicopathologic features, angiogenesis, and prognosis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. APMIS 126(5):396–402. https://doi.org/10.1111/apm.12837
Saadatmand S, de Kruijf EM, Sajet A, Dekker-Ensink NG, van Nes JG, Putter H, Smit VT, van de Velde CJ, Liefers GJ, Kuppen PJ (2013) Expression of cell adhesion molecules and prognosis in breast cancer. Br J Surg 100(2):252–260. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.8980
Picarda E, Ohaegbulam KC, Zang X (2016) Molecular pathways: targeting B7–H3 (CD276) for human cancer immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 22(14):3425–3431. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2428
Cooke VG, LeBleu VS, Keskin D, Khan Z, O’Connell JT, Teng Y, Duncan MB, Xie L, Maeda G, Vong S, Sugimoto H, Rocha RM, Damascena A, Brentani RR, Kalluri R (2012) Pericyte depletion results in hypoxia-associated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis mediated by met signaling pathway. Cancer Cell 21(1):66–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2011.11.024
Tiwari N, Tiwari VK, Waldmeier L, Balwierz PJ, Arnold P, Pachkov M, Meyer-Schaller N, Schubeler D, van Nimwegen E, Christofori G (2013) Sox4 is a master regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition by controlling Ezh2 expression and epigenetic reprogramming. Cancer Cell 23(6):768–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2013.04.020
Zheng H, Shen M, Zha YL, Li W, Wei Y, Blanco MA, Ren G, Zhou T, Storz P, Wang HY, Kang Y (2014) PKD1 phosphorylation-dependent degradation of SNAIL by SCF-FBXO11 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cancer Cell 26(3):358–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2014.07.022
Tiwari N, Gheldof A, Tatari M, Christofori G (2012) EMT as the ultimate survival mechanism of cancer cells. Semin Cancer Biol 22(3):194–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2012.02.013
Lee J, Lim B, Pearson T, Choi K, Fuson JA, Bartholomeusz C, Paradiso LJ, Myers T, Tripathy D, Ueno NT (2019) Anti-tumor and anti-metastasis efficacy of E6201, a MEK1 inhibitor, in preclinical models of triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 175(2):339–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-019-05166-3
Huth HW, Albarnaz JD, Torres AA, Bonjardim CA, Ropert C (2016) MEK2 controls the activation of MKK3/MKK6-p38 axis involved in the MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell survival: correlation with cyclin D1 expression. Cell Signal 28(9):1283–1291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.05.009
Yu F, Quan F, Xu J, Zhang Y, Xie Y, Zhang J, Lan Y, Yuan H, Zhang H, Cheng S, Xiao Y, Li X (2019) Breast cancer prognosis signature: linking risk stratification to disease subtypes. Brief Bioinform 20(6):2130–2140. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bby073
Yang M, Tang X, Zhang Z, Gu L, Wei H, Zhao S, Zhong K, Mu M, Huang C, Jiang C, Xu J, Guo G, Zhou L, Tong A (2020) Tandem CAR-T cells targeting CD70 and B7–H3 exhibit potent preclinical activity against multiple solid tumors. Theranostics 10(17):7622–7634. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.43991
Kim NI, Park MH, Kweon SS, Lee JS (2020) B7–H3 and B7–H4 expression in breast cancer and their association with clinicopathological variables and T cell infiltration. Pathobiology 87(3):179–192. https://doi.org/10.1159/000505756
Fang J, Chen F, Liu D, Gu F, Chen Z, Wang Y (2020) Prognostic value of immune checkpoint molecules in breast cancer. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20201054
Maeda N, Yoshimura K, Yamamoto S, Kuramasu A, Inoue M, Suzuki N, Watanabe Y, Maeda Y, Kamei R, Tsunedomi R, Shindo Y, Inui M, Tamada K, Yoshino S, Hazama S, Oka M (2014) Expression of B7–H3, a potential factor of tumor immune evasion in combination with the number of regulatory T cells, affects against recurrence-free survival in breast cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol 21(Suppl 4):S546-554. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-3564-2
Cheng N, Bei Y, Song Y, Zhang W, Xu L, Zhang W, Yang N, Bai X, Shu Y, Shen P (2021) B7–H3 augments the pro-angiogenic function of tumor-associated macrophages and acts as a novel adjuvant target for triple-negative breast cancer therapy. Biochem Pharmacol 183:114298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114298
Pizon M, Schott DS, Pachmann U, Pachmann K (2018) B7–H3 on circulating epithelial tumor cells correlates with the proliferation marker, Ki-67, and may be associated with the aggressiveness of tumors in breast cancer patients. Int J Oncol 53(5):2289–2299. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2018.4551
Arigami T, Narita N, Mizuno R, Nguyen L, Ye X, Chung A, Giuliano AE, Hoon DS (2010) B7–h3 ligand expression by primary breast cancer and associated with regional nodal metastasis. Ann Surg 252(6):1044–1051. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181f1939d
Ma Y, Zhan S, Lu H, Wang R, Xu Y, Zhang G, Cao L, Shi T, Zhang X, Chen W (2020) B7–H3 regulates KIF15-activated ERK1/2 pathway and contributes to radioresistance in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis 11(10):824. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03041-4
Nagaria TS, Williams JL, Leduc C, Squire JA, Greer PA, Sangrar W (2013) Flavopiridol synergizes with sorafenib to induce cytotoxicity and potentiate antitumorigenic activity in EGFR/HER-2 and mutant RAS/RAF breast cancer model systems. Neoplasia 15(8):939–951. https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.13804
Sahu R, Pattanayak SP (2020) Strategic developments & future perspective on gene therapy for breast cancer: role of mTOR and Brk/ PTK6 as molecular targets. Curr Gene Ther 20(4):237–258. https://doi.org/10.2174/1566523220999200731002408
Li Y, Zhang Z, Zhou X, Li L, Liu Q, Wang Z, Bai X, Zhao Y, Shi H, Zhang X, Ye L (2014) The oncoprotein HBXIP enhances migration of breast cancer cells through increasing filopodia formation involving MEKK2/ERK1/2/Capn4 signaling. Cancer Lett 355(2):288–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2014.09.047
Fujii S, Tokita K, Wada N, Ito K, Yamauchi C, Ito Y, Ochiai A (2011) MEK-ERK pathway regulates EZH2 overexpression in association with aggressive breast cancer subtypes. Oncogene 30(39):4118–4128. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.118
Yu Y, Luk F, Yang JL, Walsh WR (2011) Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway is associated with lung metastasis of osteosarcoma in an orthotopic mouse model. Anticancer Res 31(4):1147–1152
Dushyanthen S, Teo ZL, Caramia F, Savas P, Mintoff CP, Virassamy B, Henderson MA, Luen SJ, Mansour M, Kershaw MH, Trapani JA, Neeson PJ, Salgado R, McArthur GA, Balko JM, Beavis PA, Darcy PK, Loi S (2017) Agonist immunotherapy restores T cell function following MEK inhibition improving efficacy in breast cancer. Nat Commun 8(1):606. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00728-9
Zhao Y, Ge CC, Wang J, Wu XX, Li XM, Li W, Wang SS, Liu T, Hou JZ, Sun H, Fang D, Xie SQ (2017) MEK inhibitor, PD98059, promotes breast cancer cell migration by inducing beta-catenin nuclear accumulation. Oncol Rep 38(5):3055–3063. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.5955
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by General Project of Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2020MH242; ZR2020MH293); Department of Health of Shandong Province (2018WS068).
Funding
This study was supported by General Project of Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2020MH242; ZR2020MH293); Department of Health of Shandong Province (2018WS068).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors designed the study. SD, GW, and RS collated the data, designed and developed the database, carried out data analyses, and produced the initial draft of the manuscript. SW, XZ, and HN contributed to drafting the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final submitted manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The present study was performed with the approval of the ethics committee of Affiliated Hospital of Weifang Medical University, with signed informed consent obtained from all participating individuals. The animal experiment was conducted following the guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals issued by the National Institutes of Health.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Zhang, X., Ning, H. et al. B7 homolog 3 induces lung metastasis of breast cancer through Raf/MEK/ERK axis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 193, 405–416 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-022-06520-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-022-06520-8