Abstract
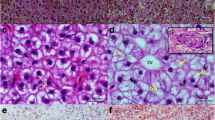
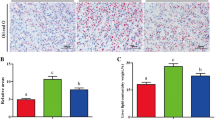
Clostridium butyricum (CB) has received much attention as a probiotic; however, few studies have focused on its effects on liver health. Here, we studied the influence of CB on the liver health of spotted sea bass through transcriptomics and metabolomics studies and preliminarily explored its molecular mechanisms. This study showed that CB significantly reduced hepatic aspartate aminotransferase (AST) activity and increased alkaline phosphatase (AKP) and acid phosphatase (ACP) activity (P < 0.05). CB has demonstrated significant effects in strengthening liver immunity and can increase hepatic amylase and trypsin activities and promote hepatic catabolism of carbohydrates and amino acids. Integration of the liver transcriptomics and metabolomics showed altered transcript levels of mainly gluconeogenic, lipogenic, and amino acid metabolic pathways. It regulated the abundance of metabolic biomarkers such as arachidonate, crotonyl-CoA, and D-glucose 1-phosphate. Our findings support that CB can reduce liver damage in spotted sea bass, enhance liver immunity, and improve liver metabolism.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, and further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
References
Abasubong KP, Liu WB, Zhang DD, Yuan XY, Xia SL, Xu C, Li XF (2018) Fishmeal replacement by rice protein concentrate with xylooligosaccharides supplement benefits the growth performance, antioxidant capability and immune responses against Aeromonas hydrophila in blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Fish Shellfish Immunol 78:177–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.04.044
Anderson LC, Lewis AJ, Peo ER, Crenshaw JD (1984) Effects of excess arginine with and without supplemental lysine on performance, plasma amino - acid - concentrations and nitrogen - balance of young swine. J Anim Sci 58(2):369–377. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas1984.582369x
Bi XJ, Lv CJ, Wang MM, Chen YY, Lv XJ, Hua SM, Mu CK (2023) Effects of dietary supplementation of Clostridium butyricum H129 on growth performance and intestinal health of turbot, Scophthalmus maximus. Aquac Rep 30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2023.101544
Chan A, Kow A, Hibi T, Di Benedetto F, Serrablo A (2020) Liver resection in Cirrhotic liver: are there any limits? Int J Surg 82S:109–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.06.050
Desale SE, Dubey T, Chinnathambi S (2021) Alpha-Linolenic acid inhibits Tau aggregation and modulates Tau conformation. Int J Biol Macromol 166:687–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.226
Douglas SE, Mandla S, Gallant JW (2000) Molecular analysis of the amylase gene and its expression during development in the winter flounder, Pleuronectes americanus. Aquaculture 190(3-4):247–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(00)00398-7
Gan C, Cai Q, Tang C, Gao J (2022) Inflammasomes and pyroptosis of liver cells in liver fibrosis. Front Immunol 13:896473. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.896473
Girija A, Vijayanathan M, Sreekumar S, Basheer J, Menon TG, Krishnankutty RE et al (2022) Harnessing the natural pool of polyketide and non-ribosomal peptide family: a route map towards novel drug development. Curr Mol Pharmacol 15(2):265–291. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874467214666210319145816
Holloway AC, Keene JL, Noakes DG, Moccia RD (2004) Effects of clove oil and MS-222 on blood hormone profiles in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum. Aquac Res 35:1025–1030. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2004.01108.x
Kong LM, Ma JR, Zhou SS, Lin H, Long ZY, Qin HH, Liu LH, Lin Y, Huang ZF, Li ZB (2023) Effects of dietary Clostridium butyricum on the growth performance, digestion, and intestinal health of spotted sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus). Front Immunol 14:1181471. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1181471
Li HD, Tian XL, Dong SL (2019) Growth performance, non-specific immunity, intestinal histology and disease resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei fed on a diet supplemented with live cells of Clostridium butyricum. Aquaculture 498:470–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.09.003
Liu Y, Li X, Zhang X, Chen Y, Liu Y, Zhang H et al (2023) Uncovering the key pharmacodynamic material basis and possible molecular mechanism of extract of Epimedium against liver cancer through a comprehensive investigation. J Ethnopharmacol 317:116765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2023.116765]
Liu Y, Miao Y, Xu N, Ding T, Cui K, Chen QC et al (2020) Effects of dietary astragalus aolysaccharides (APS) on survival, growth performance, activities of digestive enzyme, antioxidant responses and intestinal development of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae. Aquaculture 520:734997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734997
Louis P, Flint HJ (2009) Diversity, metabolism and microbial ecology of butyrate-producing bacteria from the human large intestine. FEMS Microbiol Lett 294(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01514.x
Lu H, Zhu X, Wu L, Lou X, Pan X, Liu B et al (2023) Alterations in the intestinal microbiome and metabolic profile of patients with cirrhosis supplemented with lactulose, Clostridium butyricum, and Bifidobacterium longum infantis: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Front Microbiol 14:1169811. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1169811
Manco R, Itzkovitz S (2021) Liver zonation. J Hepatol 74(2):466–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2020.09.003
Mencarelli A, Renga B, D'Amore C, Santorelli C, Graziosi L, Bruno A et al (2013) Dissociation of intestinal and hepatic activities of FXR and LXRalpha supports metabolic effects of terminal ileum interposition in rodents. Diabetes 62(10):3384–3393. https://doi.org/10.2337/db13-0299
Mun C, Cai J, Hu X, Zhang W, Zhang N, Cao Y (2022) Clostridium butyricum and its culture supernatant alleviate the Escherichia coli-Induced endometritis in mice. Animals (Basel) 12(19):2719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192719
Oku H, Koizumi N, Okumura T, Kobayashi T, Umino T (2006) Molecular characterization of lipoprotein lipase, hepatic lipase and pancreatic lipase genes: effects of fasting and refeeding on their gene expression in red sea bream Pagrus major. Comp Biochem Physiol B 145(2):168–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2006.06.008
Popovic PJ, Zeh HJ, Ochoa JB (2007) Arginine and immunity. J Nutr 137(6):1681S–1686S. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/137.6.1681S
Ruan Y (2014) Sucrose metabolism: gateway to diverse carbon use and sugar signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 65:33–67. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050213-040251
Sae-Leaw T, Benjakul S (2018) Lipase from liver of seabass (Lates calcarifer): characteristics and the use for defatting of fish skin. Food Chem 240:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.07.089
Seedorf H, Fricke WF, Veith B, Bruggemann H, Liesegang H, Strittimatter A et al (2008) The genome of Clostridium kluyveri, a strict anaerobe with unique metabolic features. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(6):2128–2133. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0711093105
Shahkar E, Yun H, Lee S, Kim DJ, Kim SK, Lee BI et al (2016) Evaluation of the optimum dietary arachidonic acid level and its essentiality based on growth and non-specific immune responses in Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica. Aquaculture 452:209–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.10.034
Slaninova A, Smutna M, Modra H, Svobodova Z (2009) A review: oxidative stress in fish induced by pesticides. Neuroendocrinol Lett 30:2–12. https://doi.org/10.1159/000197899
Song ZF, Wu TX, Cai LS, Zhang LJ, Zheng XD (2006) Effects of dietary supplementation with Clostridium butyricum on the growth performance and humoral immune response in Miichthys miiuy. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 7(7):596–602. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2006.B0596
Sparks MA, Crowley SD, Gurley SB, Mirotsou M, Coffman TM (2014) Classical renin-angiotensin system in kidney physiology. Compr Physiol 4(3):1201–1228. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c130040
Sun J, Xu J, Yang B, Chen K, Kong Y, Fang N et al (2020) Effect of Clostridium butyricum against microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease via regulating gut microbiota and metabolites butyrate. Mol Nutr Food Res 64(2):e1900636. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201900636
Tang J, Lin G, Langdon WY, Tao L, Zhang J (2018) Regulation of C-Type lectin receptor-mediated antifungal immunity. Front Immunol 9:123. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00123
Wang RM, Yao LL, Lin X, Hu XP, Wang L (2022a) Exploring the potential mechanism of Rhodomyrtus tomentosa (Ait.) Hassk fruit phenolic rich extract on ameliorating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by integration of transcriptomics and metabolomics profiling. Food Res Int 151:110824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110824
Wang S, Lin Y, Gao L, Yang Z, Lin J, Ren S et al (2022b) PPAR-gamma integrates obesity and adipocyte clock through epigenetic regulation of Bmal1. Theranostics 12(4):1589–1606. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.69054
Whitcomb DC, Lowe ME (2007) Human pancreatic digestive enzymes. Dig Dis Sci 52(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9589-z
Wu JP, Yang DQ, Du H, Yu T, Luo J, Xu QQ et al (2021) The influence of dietary arachidonic acid on growth, fatty acid profile and sex steroid hormones of F-2 generation Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis). Aquac Rep 21:100818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2021.100818
Xu HG, Wang CQ, Zhang YQ, Wei YL, Liang MQ (2018) Moderate levels of dietary arachidonic acid reduced lipid accumulation and tended to inhibit cell cycle progression in the liver of Japanese seabass lateolabrax japonicus. Sci Rep 8(1):10682. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-28867-z
Yalcin SS, Gucer S, Yalcin S, Onbasilar I, Kale G, Coskun T (2011) Effects of probiotic (Primalac 454) on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in broilers. Rev Med Vet 162(7):371–376
Yamamoto M, Ohmori H, Takei D, Matsumoto T, Takemoto M, Ikeda M et al (2022) Clostridium butyricum affects nutrition and immunology by modulating gut microbiota. Biosci Microbiota Food Health 41(2):30–36. https://doi.org/10.12938/bmfh.2021-046
Yang K, Xun PW, Huang JB, Jiang K, Huang XL, Yu W, Lin HZ (2023) Effects of dietary Clostridium butyricum on the growth performance and intestinal health of hybrid groupers (Epinephelus lanceolatus♂ x E. fuscoguttatus♀). Aquac Rep 30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2023.101588
Yang X, Gao M, Liu Y, Jiang WH, Wang ZR, Zhou QB (2019) Comparison of nutrient composition of common Monopterus albus feed in the market. Feed Rev 08:19–22. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-0084.2019.08.005 (in Chinese)
Ye YT, Xue M, Lin SM, Wang YH, Luo L, Tian JS (2003) Enzymolysis kinetics of digestive enzyme from intestine and hepatopancreas in grass carp to four kinds of raw feed materials. J Fish Sci China 02:173–176. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2003.02.018
Zhang MQ, Dong B, Lai XX, Chen Z, Hou LP, Shu R et al (2021) Effects of Clostridium butyricum on growth, digestive enzyme activity, antioxidant capacity and gut microbiota in farmed tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac Res 52(4):1573–1584. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.15009
Funding
This experiment was funded by the Science and Technology Planning Project in Fujian, China (Grant No. 2015N0010) and Science and Technology Planning Project in Xiamen, China (Grant No. 3502Z20143017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lumin Kong and Zhongbao Li conceived and designed the experiments.Lumin Kong, Sishun Zhou, Hao Lin, Jianrong Ma, Zhongying Long, Huihui Qin, Zhangfan Huang, Longhui Liu and Yi Lin performed the experiments.Lumin Kong performed the analyses.Lumin Kong analyzed the data, wrote the paper, and prepared figures and tables.Lumin Kong and Zhongbao Li discussed the result together.Zhongbao Li reviewed drafts of the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Brian Austin
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 512 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, L., Ma, J., Lin, H. et al. Analyzing the influence of Clostridium butyricum on liver health in spotted sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus) via transcriptomics and metabolomics. Aquacult Int (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-024-01398-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-024-01398-3