Abstract
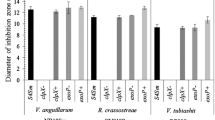
Edwardsiella piscicida (E. piscicida) is a common pathogen in freshwater and marine environments and an important intestinal pathogen of fish. Fucose large presence in the intestines could possibly regulate relevant genes to promote bacterial infectivity. In this study, the wild-type E. piscicida and the fucP gene-deleted strain ΔfucP were used to identify its virulence-regulating pathway and colonization. The results showed that the gene transcription levels of key FusKR and type III secretion system (T3SS) in E. piscicida were upregulated by different concentrations of fucose. Both the wild-type and the ΔfucP strain grew faster with 30 mM fucose added than that without fucose added. In addition, the penetration of the wild-type E. piscicida with fucose added was significantly stronger than that of both ΔfucP with fucose and the wild-type E. piscicida without fucose. Meanwhile, the gene transcription levels of T3SS-related genes eseB, eseC, eseD, eseE, and eseG in E. piscicida were significantly downregulated after the fucP gene mutant. Finally, tilapia infected with the wild-type strain showed a significant increase in the E. piscicida colonization compared to those infected with the mutant strain. All results indicate that FucP of E. piscicida mediated fucose to promote the growth, motility, and intestinal colonization in tilapia.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abayneh T, Duncan JC, Henning S (2013) Edwardsiella piscicida sp nov, a novel species pathogenic to fish. J Appl Microbiol 114:644–654
Becerra JE, Yebra MJ, Monedero V (2015) An L-fucose operon in the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG is involved in adaptation to gastrointestinal conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:3880–3888
Buján N, Toranzo AE, Magariños B (2018) Edwardsiella piscicida: a significant bacterial pathogen of cultured fish. Dis Aquat Org 131:59–71
Cao H, Han F, Tan J (2018) Edwardsiella piscicida type III secretion system effector EseK inhibits mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation and promotes bacterial colonization in zebrafish Larvae. Infect Immun 86(9):e00233–e00218
Chen J, Mu C, Ye T, Sun Y, Luo Q, Wang X (2020) The UhpA mutant of Edwardsiella piscicida enhanced its motility and the colonization in the intestine of tilapia. Fish Shellfish Immun 104:144–154
Chen J, Wang W, Wang X, Zhang Q, Ren Y, Song J, Wang X (2018) First detection of yellow head virus genotype 3 (YHV-3) in cultured Penaeus monodon, mainland China. J Fish Dis 41(9):1449–1451
Dwivedi R, Nothaft H, Garber J (2016) L-fucose influences chemotaxis and biofilm formation in Campylobacter jejuni. Mol Microbiol 101:575–589
Hou M, Chen R, Yang D (2017) Identification and functional characterization of EseH, a new effector of the type III secretion system of Edwardsiella piscicida. Cell Microbiol 19(1):e12638ss
Kaper JB, Nataro JP, Mobley HL (2004) Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat Rev Microbiol 2:123–140
Leung K, Wang Q, Yang Z, Siame B (2019) Edwardsiella piscicida: a versatile emerging pathogen of fish. Virulence 10(1):555–567
Liu J, Sun Y, Huang J, Ding L, Ye T, Wang X (2020) UhpA in Edwardsiella piscicida decreases the pathogenicity and the capability of inducing cytokine response in zebrafish. Aquacult Rep 100293
Liu Y, Zhao L, Yang M, Yin K (2017) Transcriptomic dissection of the horizontally acquired response regulator EsrB reveals its global regulatory roles in the physiological adaptation and activation of T3SS and the cognate effector repertoire in Edwardsiella piscicida during infection toward turbot. Virulence 8:1355–1377
Mou KT, Plummer PJ (2016) The impact of the LuxS mutation on phenotypic expression of factors critical for Campylobacter jejuni colonization. Vet Microbiol 192:43–51
Pacheco AR, Curtis MM, Ritchie JM, Munera D, Waldor MK, Moreira CG, Sperandio V (2012) Fucose sensing regulates bacterial intestinal colonization. Nature 492:113–117
Pan T, Yan M, Chen S, Wang X (2013) Effects of ten traditional Chinese herbs on immune response and disease resistance of Sciaenops ocellatus. Acta Ichthyol Piscat 43:41–49
Ren P, Xu L, Yang Y, He S, Liu W, Einar R, Zhou Z (2013) Lactobacillus planarum subsp. plantarum JCM 1149 vs. Aeromonas hydrophila NJ-1 in the anterior intestine and posterior intestine of hybrid tilapia Oreochromis niloticus × Oreochromis aureus: an ex vivo study. Fish Shellfish Immun 35:146–153
Robbe C, Capon C, Coddeville B, Michalski JC (2004) Structural diversity and specific distribution of Oglycans in normal human mucins along the intestinal tract. Biochem J 384:307–316
Stahl M, Friis LM, Nothaft H, Liu X, Li J, Szymanski CM, Stintzi A (2011) L-Fucose utilization provides Campylobacter jejuni with a competitive advantage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:7194–7199
Sun Y, Chen J, Liu J, Huang J, Ye T, Wang X (2020a) The role of uhpA in Edwardsiella piscicida and the inflammatory cytokine response in tilapia. Fish Shellfish Immunol 101:192–197
Sun Y, Li Y, Luo Q, Huang J, Chen J, Zhang R, Wang X (2020b) LuxS/AI-2 quorum sensing system in Edwardsiella piscicida promotes its biofilm formation and pathogenicity. Infect Immun 9:07–19
Wang Q, Fu T, Li X, Luo Q, Huang J, Sun Y, Wang X (2020a) Cross-immunity in Nile tilapia vaccinated with Streptococcus agalactiae and Streptococcus iniae vaccines. Fish Shellfish Immun 97:382–389
Wang Q, Wang X, Wang X, Feng R, Luo Q, Huang J (2018) Generation of a novel Streptococcus agalactiae ghost vaccine and examination of its immunogenicity against virulent challenge in tilapia. Fish Shellfish Immun 81:49–56
Wang Q, Yang M, Xiao J, Wu H, Wang X, Lv Y, Xu L, Zheng H, Wang S, Zhao G, Liu Q, Zhang Y (2009) Genome sequence of the versatile fish pathogen Edwardsiella tarda provides insights into its adaptation to broad host ranges and intracellular niches. PLoS One 4:e7646
Wang Q, Zhang C, Xu L, Chen J, Wang X (2020b) Characterization of Streptococcus iniae ghost vaccine and its immunization in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac Res 52:1359–1368. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.14990
Wang X, Lu C (2009) Mice orally vaccinated with Edwardsiella tarda ghosts are significantly protected against infection. Vaccine 27:1571–1578
Wang X, Lu R, Ding L, Yan M, Chai X, Chen S, Xie Q (2012a) Polysaccharides, saponins and water decoction of Astragalus membranaceus significantly enhance the non-specific immune response in Spotted maigre (Nibea albiflora). Israeli J Aquacult-Bamidgeh 64:1–6
Wang X, Yan M, Hu W, Chen S, Zhang S, Xie Q (2012b) Visualization of Sparus macrocephalus infection by GFP-labeled Edwardsiella tarda. Israeli J Aquacult-Bamidgeh 64:401–407
Wang Y, Wang X, Zhang B, Li Z, Yang L, Li X, Ma H (2020c) A lysin motif-containing protein (SpLysMD3) functions as a PRR involved in the antibacterial responses of mud crab, Scylla paramamosain. Fish Shellfish Immun 97:257–267
Wei L, Wu Y, Qiao H (2018) YebC controls virulence by activating T3SS gene expression in the pathogen Edwardsiella piscicida. FEMS Microbiol Lett 365:14
Wu J, Liu G, Sun Y, Wang X, Fang H, Jiang H, Guo Z, Dong J (2018) The role of regulator FucP in Edwardsiella tarda pathogenesis and the inflammatory cytokine response in tilapia. Fish Shellfish Immun 80:624–630
Xiao JF, Wang QY, Liu Q, Wang X, Liu H, Zhang YX (2008) Isolation and identification of fish pathogen Edwardsiella tarda from mariculture in China. Aquac Res 40:13–17
Yan MC, Liu JY, Li Y, Wang XP, Jiang H, Fang H, Guo ZM, Sun YC (2018) Different concentrations of Edwardsiella tarda ghost vaccine induces immune responses in vivo and protects Sparus macrocephalus against a homologous challenge. Fish Shellfish Immun 80:467–472
Ye T, Mu C, Chen J, Pan G, Wang X (2020) The role of UhpA in regulating the virulence gene expression in Edwardsiella piscicida. Fish Dis. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.13298
Yu J, Ji X, Wang X, Li T, Wang H, Zeng Q (2019) Identification and characterization of differentially expressed genes in hepatopancreas of oriental river prawn Macrobrachium nipponense under nitrite stress. Fish Shellfish Immun 87:144–154
Zhang X, Yan M, Sun Y, Wu J, Mu C, Chen J, Pan G, Wang X (2020) FucP promotes the pathogenicity of Edwardsiella piscicida to infect zebrafish. Aquaculture reports AQREP-D-20-00076.
Acknowledgements
We thank Shannon Whitehead at the Harding University and Caroline Whitehead at the Auburn University for performing manuscript editing.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China(2019YFD0900101), the earmarked fund for the Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System in Shandong Province (No. SDAIT-14-07), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2019MC031), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31402325), and funds of the Shandong “Double Tops” Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The Animal Ethics Committee of the Shandong Agricultural University has approved this study.
Originality-significance statement
It is the first time to testify that 30-mM L-fucose upregulates the transcription of T3SS genes by activating the FucP and FusKR system, thereby promoting the intestinal colonization of E. piscicida in tilapia.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Gavin Burnell
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Jiayan Wu and Cuimin Mu are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, T., Wu, J., Mu, C. et al. FucP mediates fucose to regulate T3SS in Edwardsiella piscicida and promotes intestinal colonization in Tilapia. Aquacult Int 29, 1233–1243 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-021-00688-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-021-00688-4