Abstract
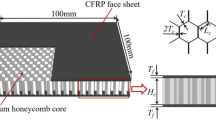
The experimental and numerical investigations on the dynamic responses and failure mechanisms of honeycomb panels under low-velocity impact were carried out in the present work. The carbon fiber composite hexagonal honeycomb panels were fabricated using the hot press molding method. Then, low-velocity drop-weight impact tests on the composite honeycomb panels were conducted under impact energy levels of 5J, 10J, 30J, 50J, 60J, 70J, and 100J to study the deformation mechanisms and damage modes. The VUMAT was developed to model the behavior of sandwich panels, in which a progressive damage model based on the strain-based failure criterion of composite fabric and Yeh delamination failure criteria was implemented in ABAQUS/Explicit. Two-dimensional topological honeycomb configurations with the same relative density were established. The energy absorption and load-bearing capacity of hexagonal, square, triangular, Kagome, and two kinds of circular (CS and CH types) honeycombs under 100J impact energy were discussed. The results showed that the circular honeycomb (CH type) had the largest first peak force of 6.714 kN, while the hexagonal honeycomb had the smallest first peak force of 3.715 kN. Compared with hexagonal honeycomb, the energy absorption of the triangle, Kagome, and circular honeycombs (CH type) were increased by 37.15%, 38.18%, and 47.06%, respectively. This study provided a series of experimental and numerical results, which could provide a reference for selecting suitable honeycomb configurations in the protection field.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Zhang, J.J., Lu, G.X., You, Z.: Large deformation and energy absorption of additively manufactured auxetic materials and structures: a review. Compos. B Eng. 201, 108340 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108340
de Souza, E.F., Gomes, G.F., Ancelotti, A.C., Jr., et al.: A numerical-experimental dynamic analysis of composite sandwich beam with magnetorheological elastomer honeycomb core. Compos. Struct. 209, 242–257 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.10.041
Kösedağ, E., Ekici, R.: Free vibration analysis of foam-core sandwich structures Politeknik Dergisi. J. Polytech. 24(1), 69–74 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2339/politeknik.571396
Rosmmi, N.H.M., Khan, Z.I., Mohamad, Z., et al.: Impact strength and morphology of sustainably sourced recycling polyethylene terephthalate blends. Chem. Eng. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3303/CET2183045
Wei, X.Y., Xiong, J., Wang, J., et al.: New advances in fiber-reinforced composite honeycomb materials. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 63(8), 1348–1370 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-020-1650-9
Muhammed Raji, A., Hambali, H.U., Khan, Z.I., et al.: Emerging trends in flame retardancy of rigid polyurethane foam and its composites: a review. J. Cell. Plast. 59(1), 65–122 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1177/0021955x221144564
Khosravani, M.R., Weinberg, K.: Experimental investigations of the environmental effects on stability and integrity of composite sandwich T-joints: experimentelle Untersuchung des Umwelteinflusses auf die Belastbarkeit von T-Stößen in Sandwich-Platten. Materialwiss. Werkstofftech. 48(8), 753–759 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/mawe.201600747
Mohamad, Z., Raji, A.M., Hassan, A., et al.: Novel intumescent flame retardant of ammonium polyphosphate/sepiolite/melamine on rigid polyurethane foam: morphologies, and flammability properties. Chem. Eng. Trans. 89, 619–624 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3303/CET2189104
Khan, Z.I., Habib, U., Mohamad, Z.B., et al.: Enhanced mechanical properties of a novel compatibilized recycled polyethylene terephthalate/polyamide 11 (rPET/PA11) blends. eXPRESS Polym. Lett. 15(12), 1206–1215 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3144/EXPRESSPOLYMLETT.2021.96
Wang, H.X., Ramakrishnan, K.R., Shankar, K.: Experimental study of the medium velocity impact response of sandwich panels with different cores. Mater. Des. 99, 68–82 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.03.048
Meo, M., Vignjevic, R., Marengo, G.: The response of honeycomb sandwich panels under low-velocity impact loading. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 47(9), 1301–1325 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2005.05.006
Kosedag, E., Ekici, R.: Low-velocity and ballistic impact resistances of particle reinforced metal–matrix composites: an experimental study. J. Compos. Mater. 56(7), 991–1002 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1177/00219983211068101
Khan, Z.I., Mohamad, Z.B., Rahmat, A.R.B., et al.: A novel recycled polyethylene terephthalate/polyamide 11 (rPET/PA11) thermoplastic blend. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 37(3), 233–244 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/14777606211001074
Wei, X., Li, D., Xiong, J.: Fabrication and mechanical behaviors of an all-composite sandwich structure with a hexagon honeycomb core based on the tailor-folding approach. Compos. Sci. Technol. 184, 107878 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.107878
Wei, X., Wu, Q., Gao, Y., et al.: Bending characteristics of all-composite hexagon honeycomb sandwich beams: experimental tests and a three-dimensional failure mechanism map. Mech. Mater. 148, 103401 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmat.2020.103401
Li, J., Zhang, W., Wang, Z., et al.: Dynamic response and failure of CFRP Kagome lattice core sandwich panels subjected to low-velocity impact. Int. J. Impact Eng. 181, 104737 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104737
Zeng, W., Jiang, W., Liu, J., et al.: Fabrication method and dynamic responses of composite sandwich structure with reentrant honeycomb cores. Compos. Struct. 299, 116084 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.116084
Yu, S., Yu, X., Ao, Y., et al.: The impact resistance of composite Y-shaped cores sandwich structure. Thin-Walled Struct. 169, 108389 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2021.108389
Khaliulin, V.I., Sh, G.R., Markovtsev, V.A., et al.: Process of forming mirror-shaped relief plates of folded structure. Vestnik of Samara University. Aerosp. Mech. Eng. 18(4), 180 (2019). https://doi.org/10.18287/2541-7533-2019-18-4-169-182
Sun, G., Huo, X., Chen, D., et al.: Experimental and numerical study on honeycomb sandwich panels under bending and in-panel compression. Mater. Des. 133, 154–168 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.07.057
Sun, G., Chen, D., Huo, X., et al.: Experimental and numerical studies on indentation and perforation characteristics of honeycomb sandwich panels. Compos. Struct. 184, 110–124 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.09.025
Sun, G., Huo, X., Wang, H., et al.: On the structural parameters of honeycomb-core sandwich panels against low-velocity impact. Compos. B Eng. 216, 108881 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.108881
Sun, G., Chen, D., Wang, H., et al.: High-velocity impact behaviour of aluminium honeycomb sandwich panels with different structural configurations. Int. J. Impact Eng. 122, 119–136 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.08.007
Yang, K., Li, Z., Ge, D.: Quasi-static and dynamic out-of-plane crashworthiness of 3D curved-walled mixed-phase honeycombs. Thin-Walled Struct. 182, 110305 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2022.110305
Qi, J.Q., Li, C., Tie, Y., et al.: Energy absorption characteristics of origami-inspired honeycomb sandwich structures under low-velocity impact loading. Mater. Des. 207, 109837 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2021.109837
Pehlivan, L., Baykasoğlu, C.: An experimental study on the compressive response of CFRP honeycombs with various cell configurations. Compos. B Eng. 162, 653–661 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.01.044
Qiu, X.M., Zhang, J., Yu, T.X.: Collapse of periodic planar lattices under uniaxial compression, part II: dynamic crushing based on finite element simulation. Int. J. Impact Eng. 36(10–11), 1231–1241 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2009.05.010
Ruan, D., Lu, G., Wang, B., et al.: In-plane dynamic crushing of honeycombs—a finite element study. Int. J. Impact Eng. 28(2), 161–182 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0734-743x(02)00056-8
Wang, Y., Yu, Y., Wang, C., et al.: On the out-of-plane ballistic performances of hexagonal, reentrant, square, triangular and circular honeycomb panels. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 173, 105402 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.105402
Ul Haq, A., Gunashekar, G., Narala, S.K.R.: The dynamic response of AuxHex and Star-Reentrant honeycomb cored sandwich panels subject to blast loading. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07564-0
Deng, Y., Zhou, N., Li, X., et al.: Dynamic response and failure mechanism of S-shaped CFRP foldcore sandwich structure under low-velocity impact. Thin-Walled Struct. 173, 109007 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2022.109007
Deng, Y., Li, X., Hu, X., et al.: Low-velocity impact behavior of interlayer hybrid foldcore sandwich structures with carbon/glass fibers. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2023.2172236
Deng, Y.F., Hu, X.Y., Yang, X.Y., et al.: Dynamic response of Nomex honeycomb sandwich panels subjected to aluminum foam projectile impact–an experimental study. Polym. Compos. 44(2), 1017–1037 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.27151
ASTM, D7316-05. Standard test method for measuring the damage resistance of a fiber-reinforced polymer matrix composite to a drop-weight impact event. (2014)
He, W., Yao, L., Meng, X., et al.: Effect of structural parameters on low-velocity impact behavior of aluminum honeycomb sandwich structures with CFRP face sheets. Thin-Walled Struct. 137, 411–432 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2019.01.022
Zhao, Y., Yang, Z., Yu, T., et al.: Mechanical properties and energy absorption capabilities of aluminium foam sandwich structure subjected to low-velocity impact. Constr. Build. Mater. 273, 121996 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121996
Tian, J., Xu, T., An, L., et al.: Study on behavior and mechanism of low-velocity impact and post-impact flexural properties of carbon-aramid/epoxy resin laminated composites. Compos. Struct. 300, 116166 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.116166
Zhang, X., Xu, F., Zang, Y., et al.: Experimental and numerical investigation on damage behavior of honeycomb sandwich panel subjected to low-velocity impact. Compos. Struct. 236, 111882 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.111882
Khosravani, M.R., Rezaei, S., Ruan, H., et al.: Fracture behavior of anisotropic 3D-printed parts: experiments and numerical simulations. J. Market. Res. 19, 1260–1270 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.05.068
Chen, Y., Hou, S., Fu, K., et al.: Low-velocity impact response of composite sandwich structures: modelling and experiment. Compos. Struct. 168, 322–334 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.02.064
Labeas, G., Johnson, A., Mines, R., et al.: The impact performance of sandwich structures with innovative cellular metal and folded composite cores[C]//SAMPE Europe Int. Conf.DLR, 2009.DOI:Labeas, George und Johnson, Alastair und Mines, Robert und Klaus
Xue, X., Zhang, C., Chen, W., et al.: Study on the impact resistance of honeycomb sandwich structures under low-velocity/heavy mass. Compos. Struct. 226, 111223 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111223
He, W., Liu, J., Tao, B., et al.: Experimental and numerical research on the low velocity impact behavior of hybrid corrugated core sandwich structures. Compos. Struct. 158, 30–43 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.09.009
Liu, L., Meng, P., Wang, H., et al.: The flatwise compressive properties of Nomex honeycomb core with debonding imperfections in the double cell wall. Compos. B Eng. 76, 122–132 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.02.017
Hu, L.L., He, X.L., Wu, G.P., et al.: Dynamic crushing of the circular-celled honeycombs under out-of-plane impact. Int. J. Impact Eng. 75, 150–161 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.08.008
Zhu, G., Sun, G., Li, G., et al.: Modeling for CFRP structures subjected to quasi-static crushing. Compos. Struct. 184, 41–55 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.09.001
Patel, S., Patel, M.: The efficient design of hybrid and metallic sandwich structures under air blast loading. J. Sandwich Struct. Mater. 24(3), 1706–1725 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1177/10996362211065748
Nia, A.A., Hamedani, J.H.: Comparative analysis of energy absorption and deformations of thin walled tubes with various section geometries. Thin-Walled Struct. 48(12), 946–954 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2010.07.003
Gao, W., Yu, Z., Ma, A., et al.: Numerical simulation of composite grid sandwich structure under low-velocity impact. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 29(1), 516–528 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1515/secm-2022-0176
Acknowledgements
Thanks to the Graduate Research Innovation Project of Civil Aviation University of China (2022YJS038) for supporting the present work. The present work was financially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No.: 3122019076).
Funding
Civil Aviation University of China, 2022YJS038, Xiaoyu Hu. Civil Aviation University of China, 3122019076, Yimei Zheng.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yunfei Deng: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Resources. Xiaoyu Hu: Investigation, Conceptualization, Mechanical tests, Data analysis, Writing-original draft, Writing-review & editing. Yijie Niu: Mechanical tests, Data analysis. Yimei Zheng: Project funding, Supervision. Gang Wei: Experimental guidance, resources.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
The manuscript is original and has not been submitted for publication elsewhere (partially or in full). Also, the manuscript has not been submitted to more than one publication for simultaneous consideration.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable (this research did not involve human subjects).
Consent to Publish
The authors consent to the manuscript's publication in the ACMA should the article be accepted by the editor-in-chief upon completion of the refereeing process.
Competing Interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Y., Hu, X., Niu, Y. et al. Experimental and Numerical Study of Composite Honeycomb Sandwich Structures Under Low-Velocity Impact. Appl Compos Mater 31, 535–559 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-023-10190-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-023-10190-0