Abstract
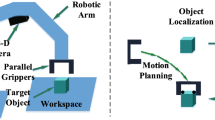
Acupoint stimulation has proven to be of significant importance for rehabilitation and preventive therapy. Moxibustion, a kind of acupoint therapy, has mainly been performed by practitioners relying on manual localization and positioning of acupoints, leading to variance in the accuracy owing to human error. Developments in the automatic detection of acupoints using deep learning techniques have proven to somewhat tackle the problem. But the current methods lack depth-based localization and are thus confined to two-dimensional (2D) localization. In this research, a new approach towards 3D acupoint localization is introduced, based on a fusion of RGB and depth convolutional neural networks (CNN) to guide the manipulator. This research aims to tackle the challenge of real-time 3D acupoint localization in order to provide guidance for robot-controlled moxibustion. In the first step, the 3D sensor (Kinect v1) is calibrated and transformation matrix is computed to project the depth data into the RGB domain. Secondly, a fusion of RGB-CNN and depth-CNN is employed, in order to obtain 3D localization. Lastly, 3D coordinates are fed to the manipulator to perform artificially controlled moxibustion therapy. Furthermore, a 3D acupoint dataset consisting of RGB and depth images of hands, is constructed to train, validate and test the network. The network was able to localize 5 sets of acupoints with an average localization error of less than 0.09. Further experiments prove the efficacy of the approach and lay grounds for development of automatic moxibustion robots.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Aziz, Y. I., and H. M. Karara. Direct linear transformation from comparator coordinates into object space coordinates in close-range photogrammetry. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 81(2):103–107, 2015. https://doi.org/10.14358/PERS.81.2.103.
Bohr, A., and K. Memarzadeh. The rise of artificial intelligence in healthcare applications. INC, 2020.
Bulatov, Y., S. Jambawalikar, P. Kumar, and S. Sethia. Hand recognition using geometric classifiers. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), vol. 3072, pp. 753–760, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-25948-0_102.
Chan, T. W., C. Zhang, W. H. Ip, and A. W. Choy. A combined deep learning and anatomical inch measurement approach to robotic acupuncture points positioning. In: Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, vol. 2021, pp. 2597–2600, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC46164.2021.9629761.
Chang, M., and Q. Zhu. Automatic location of facial acupuncture-point based on facial feature points positioning, vol. 130, no. Fmsmt, pp. 545–549, 2017. https://doi.org/10.2991/fmsmt-17.2017.111.
Córdova-Esparza, D.-M., J. R. Terven, H. Jiménez-Hernández, A. Vázquez-Cervantes, A.-M. Herrera-Navarro, and A. Ramírez-Pedraza. Multiple kinect V2 calibration. Automatika. 57(3):810–821, 2016. https://doi.org/10.7305/automatika.2017.02.1758.
Dornaika, F., and R. Horaud. Simultaneous robot-world and hand-eye calibration. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 14(4):617–622, 1998. https://doi.org/10.1109/70.704233.
Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, vol. 2015 Inter, pp. 1440–1448, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.169.
Grzejszczak, T., M. Kawulok, and A. Galuszka. Hand landmarks detection and localization in color images. Multimed. Tools Appl. 75(23):16363–16387, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2934-5.
Hashemi, J., and E. Fatemizadeh. Biometric identification through hand geometry. EUROCON 2005 Int. Conf. Comput. Tool. II(10):1011–1014, 2005. https://doi.org/10.1109/eurcon.2005.1630119.
Herrera, D. C., J. Kannala, and J. Heikkilä. Accurate and practical calibration of a depth and color camera pair. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), vol. 6855 LNCS, no. PART 2, pp. 437–445, 2011. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-23678-5_52.
Hinman, R. S., et al. Acupuncture for chronic knee pain a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 312(13):1313–1322, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.12660.
Hosbach, I. Atlas of Acupuncture. Atlas Acupunct., pp. 697–722, 2008, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780443100284500126.
Hyvarinen, J., and M. Karlsson. Low resistance skin points that may coincide with acupuncture loci. Med. Biol. 55(2):88–94, 1977.
Jain, A. K., A. Ross, and S. Pankanti. A prototype hand geometry-based verification system. In: 2nd International Conference Audio-Video-Based Biometric Person Authentication, pp. 166–171, 1999, [Online]. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.70.1051&rep=rep1&type=pdf.
Jiang, H., J. Starkman, C. H. Kuo, and M. C. Huang. Acu glass: quantifying acupuncture therapy using google glass. In: BodyNets International Conference on Body Area Networks, pp. 7–10, 2015. https://doi.org/10.4108/eai.28-9-2015.2261520.
Kalauokalani, D., K. J. Sherman, and D. C. Cherkin. Acupuncture for chronic low back pain. South. Med. J. 94(5):486–492, 2001. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007611-200194050-00008.
Lan, K.-C., and G. Litscher. Robot-controlled acupuncture—an innovative step towards modernization of the ancient traditional medical treatment method. Medicines. 6(3):87, 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines6030087.
Laut, J., M. Porfiri, and P. Raghavan. The present and future of robotic technology in rehabilitation. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 4(4):312–319, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40141-016-0139-0.
Le, A. V., S. W. Jung, and C. S. Won. Directional joint bilateral filter for depth images. Sensors. 14(7):11362–11378, 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/s140711362.
Lee, M. S., T. Y. Choi, J. W. Kang, B. J. Lee, and E. Ernst. Moxibustion for treating pain: a systematic review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 38(5):829–838, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X10008275.
Lim, S. WHO standard acupuncture point locations. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 7(2):167–168, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecam/nep006.
Lin, L. M., S. F. Wang, R. P. Lee, B. G. Hsu, N. M. Tsai, and T. C. Peng. Changes in skin surface temperature at an acupuncture point with moxibustion. Acupunct. Med. 31(2):195–201, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1136/acupmed-2012-010268.
Lin, J. Atlas of Acupuncturology Atlas of Acupuncturology, p. 466, 2020.
Linde, K., G. Allais, B. Brinkhaus, E. Manheimer, A. Vickers, and W. Ar. Acupuncture for tension-type headache (Review ), no. 1, 2009.
Lu, J., et al. Moxibustion exerts a neuroprotective effect through antiferroptosis in Parkinson’s disease. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2735492.
Pang, Z., B. Zhang, J. Yu, Z. Sun, and L. Gong. Design and analysis of a Chinese medicine based humanoid robotic arm massage system. Appl. Sci. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204294.
Park, H. J., S. Y. Kim, Y. Chae, S. M. Lee, and H. Lee. The effectiveness of moxibustion: an overview during 10 years. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011(July):2011, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecam/nep163.
Raposo, C., J. P. Barreto, and U. Nunes. Fast and accurate calibration of a kinect sensor. In: Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on 3D Vision, 3DV 2013, pp. 342–349, 2013, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/3DV.2013.52.
Simonyan, K., and A. Zisserman. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition Karen. Am. J. Heal. Pharm. 75(6):398–406, 2018.
Su, J., Y. Zhu, and M. Zhu. Hand-eye-force coordination of acupuncture robot. IEEE Access. 7:82154–82161, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2923632.
Sun, L., S. Sun, Y. Fu, and X. Zhao. Acupoint detection based on deep convolutional neural network, In: Chinese Control Conference, CCC, 2020, vol. 2020-July, pp. 7418–7422. https://doi.org/10.23919/CCC50068.2020.9188367.
Vickers, A. J., et al. Acupuncture for chronic pain: individual patient data meta-analysis. Arch. Intern. Med. 172(19):1444–1453, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinternmed.2012.3654.
Wong, J., M. Reformat, E. Parent, and E. Lou. Convolutional neural network to segment laminae on 3D ultrasound spinal images to assist cobb angle measurement. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-022-02925-0.
Wren, C. R., A. Azarbayejani, T. Darrell, and A. P. Pentland. Pfinder: Real-time tracking of the human body. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 19(7):780–785, 1997.
Wu, Z., G. Allibert, C. Stolz, and C. Demonceaux. Depth-adapted CNN for RGB-D cameras. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), vol. 12625 LNCS, pp. 388–404, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-69538-5_24.
Yau, W. Y., and H. Wang. Robust hand-eye coordination. Adv. Robot. 11(1):57–73, 1996. https://doi.org/10.1163/156855397X00047.
Zhang, F. et al. MediaPipe Hands: On-device Real-time Hand Tracking. https://mediapipe.dev.
Zhou, Y., and O. Tuzel. VoxelNet: end-to-end learning for point cloud based 3D object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4490–4499, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00472.
Zhu, Y., B. Li, M. Cui, Y. Fu, and L. Zhu. Acu3D: a cross-platform three-dimensional visualization system for the meridians and acupoints of human body. In: Proceedings of the 2015 7th International Conference Information Technologies and Educational ITME 2015, pp. 27–31, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/ITME.2015.102.
Zhu, H., J. B. Weibel, and S. Lu. Discriminative multi-modal feature fusion for RGBD indoor scene recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016, vol. 2016-December. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.324.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61973194, and in part by Shenzhen Fundamental Research and Discipline Layout Project under Grant JCYJ20190806155616366.
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interests in this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Ka-Wai Kwok oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masood, D., Qi, J. 3D Localization of Hand Acupoints Using Hand Geometry and Landmark Points Based on RGB-D CNN Fusion. Ann Biomed Eng 50, 1103–1115 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-022-02986-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-022-02986-1