Abstract
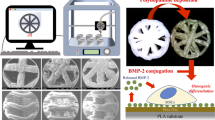
Growth factors such as bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) are potent tools for tissue engineering. Three-dimensional (3D) printing offers a potential strategy for delivery of BMP-2 from polymeric constructs; however, these biomolecules are sensitive to inactivation by the elevated temperatures commonly employed during extrusion-based 3D printing. Therefore, we aimed to correlate printing temperature to the bioactivity of BMP-2 released from 3D printed constructs composed of a model polymer, poly(propylene fumarate). Following encapsulation of BMP-2 in poly(dl-lactic-co-glycolic acid) particles, growth factor-loaded fibers were fabricated at three different printing temperatures. Resulting constructs underwent 28 days of aqueous degradation for collection of released BMP-2. Supernatants were then assayed for the presence of bioactive BMP-2 using a cellular assay for alkaline phosphatase activity. Cumulative release profiles indicated that BMP-2 released from constructs that were 3D printed at physiologic and intermediate temperatures exhibited comparable total amounts of bioactive BMP-2 release as those encapsulated in non-printed particulate delivery vehicles. Meanwhile, the elevated printing temperature of 90 °C resulted in a decreased amount of total bioactive BMP-2 release from the fibers. These findings elucidate the effects of elevated printing temperatures on BMP-2 bioactivity during extrusion-based 3D printing, and enlighten polymeric material selection for 3D printing with growth factors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM F2131: Standard test method for in vitro biological activity of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rh-BMP-2) using the W-20 mouse stromal cell line. 2012.
Bittner, S. M., J. L. Guo, and A. G. Mikos. Spatiotemporal control of growth factors in three-dimensional printed scaffolds. Bioprinting 12:2018, 2018.
Bracaglia, L. G., M. Messina, C. Vantucci, H. B. Baker, A. Pandit, and J. P. Fisher. Controlled delivery of tissue inductive factors in a cardiovascular hybrid biomaterial scaffold. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 3:1350–1358, 2016.
Busatto, C., J. Pesoa, I. Helbling, J. Luna, and D. Estenoz. Heterogeneous hydrolytic degradation of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres: mathematical modeling. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 134:45464, 2017.
Caballero Aguilar, L. M., S. M. Silva, and S. E. Moulton. Growth factor delivery: defining the next generation platforms for tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 306:40–58, 2019.
Cai, Z., Y. Wan, M. L. Becker, Y. Z. Long, and D. Dean. Poly(propylene fumarate)-based materials: synthesis, functionalization, properties, device fabrication and biomedical applications. Biomaterials 208:45–71, 2019.
Clark, A., T. A. Milbrandt, J. Z. Hilt, and D. A. Puleo. Retention of insulin-like growth factor I bioactivity during the fabrication of sintered polymeric scaffolds. Biomed. Mater. 9:025015, 2014.
Coleman, J., and A. Lowman. Biodegradable nanoparticles for protein delivery: analysis of preparation conditions on particle morphology and protein loading, activity and sustained release properties. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 23:1129–1151, 2012.
Comminal, R., M. P. Serdeczny, D. B. Pedersen, and J. Spangenberg. Numerical modeling of the strand deposition flow in extrusion-based additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 20:68–76, 2018.
Emmermacher, J., D. Spura, J. Cziommer, D. Kilian, T. Wollborn, U. Fritsching, J. Steingroewer, T. Walther, M. Gelinsky, and A. Lode. Engineering considerations on extrusion-based bioprinting: interactions of material behavior, mechanical forces and cells in the printing needle. Biofabrication 12:025022, 2020.
England, J. L., and G. Haran. Role of solvation effects in protein denaturation: from thermodynamics to single molecules and back. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 62:257–277, 2011.
Farshid, B., G. Lalwani, M. ShirMohammadi, J. Simonsen, and B. Sitharaman. Boron nitride nanotubes and nanoplatelets as reinforcing agents of polymeric matrices for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 105:406–419, 2017.
Fox, N., and I. Streinu. Redundant and critical noncovalent interactions in protein rigid cluster analysis. In: Discrete and Topological Models in Molecular Biology, edited by N. Jonoska, and M. Saito. Berlin: Springer, 2014, pp. 167–196.
Freeman, F. E., P. Pitacco, L. H. A. van Dommelen, J. Nulty, D. C. Browe, J.-Y. Shin, E. Alsberg, and D. J. Kelly. 3D bioprinting spatiotemporally defined patterns of growth factors to tightly control tissue regeneration. Sci. Adv. 6:5093, 2020.
Galarraga, J. H., M. Y. Kwon, and J. A. Burdick. 3D bioprinting via an in situ crosslinking technique towards engineering cartilage tissue. Sci. Rep. 9:19987, 2019.
Holland, T. A., Y. Tabata, and A. G. Mikos. In vitro release of transforming growth factor-β1 from gelatin microparticles encapsulated in biodegradable, injectable oligo(poly(ethylene glycol) fumarate) hydrogels. J. Control. Release 91:299–313, 2003.
Jain, S., T. Fuoco, M. A. Yassin, K. Mustafa, and A. Finne-Wistrand. Printability and critical insight into polymer properties during direct-extrusion based 3D printing of medical grade polylactide and copolyesters. Biomacromolecules 21:388–396, 2020.
Ji, S., K. Dube, J. P. Chesterman, S. L. Fung, C. Y. Liaw, J. Kohn, and M. Guvendiren. Polyester-based ink platform with tunable bioactivity for 3D printing of tissue engineering scaffolds. Biomater. Sci. 7:560–570, 2019.
Kasper, F. K., K. Tanahashi, J. P. Fisher, and A. G. Mikos. Synthesis of poly(propylene fumarate). Nat. Protoc. 4:518–525, 2009.
Kempen, D. H., L. Lu, T. E. Hefferan, L. B. Creemers, A. Maran, K. L. Classic, W. J. Dhert, and M. J. Yaszemski. Retention of in vitro and in vivo BMP-2 bioactivities in sustained delivery vehicles for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 29:3245–3252, 2008.
Kempen, D. H., L. Lu, C. Kim, X. Zhu, W. J. Dhert, B. L. Currier, and M. J. Yaszemski. Controlled drug release from a novel injectable biodegradable microsphere/scaffold composite based on poly(propylene fumarate). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 77:103–111, 2006.
Kim, K., D. Dean, J. Wallace, R. Breithaupt, A. G. Mikos, and J. P. Fisher. The influence of stereolithographic scaffold architecture and composition on osteogenic signal expression with rat bone marrow stromal cells. Biomaterials 32:3750–3763, 2011.
Kim, S., Y. Kang, C. A. Krueger, M. Sen, J. B. Holcomb, D. Chen, J. C. Wenke, and Y. Yang. Sequential delivery of BMP-2 and IGF-1 using a chitosan gel with gelatin microspheres enhances early osteoblastic differentiation. Acta Biomater. 8:1768–1777, 2012.
Kim, K., J. Lam, S. Lu, P. P. Spicer, A. Lueckgen, Y. Tabata, M. E. Wong, J. A. Jansen, A. G. Mikos, and F. K. Kasper. Osteochondral tissue regeneration using a bilayered composite hydrogel with modulating dual growth factor release kinetics in a rabbit model. J. Control. Release 168:166–178, 2013.
Koons, G. L., M. Diba, and A. G. Mikos. Materials design for bone-tissue engineering. Nat. Rev. Mater. 5:584–603, 2020.
Koons, G. L., and A. G. Mikos. Progress in three-dimensional printing with growth factors. J. Control. Release 295:50–59, 2019.
Kyle, S., Z. M. Jessop, A. Al-Sabah, and I. S. Whitaker. ‘Printability’ of candidate biomaterials for extrusion based 3D printing: state-of-the-art. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 6:1700264, 2017.
Lakshmanan, R., P. Kumaraswamy, U. M. Krishnan, and S. Sethuraman. Engineering a growth factor embedded nanofiber matrix niche to promote vascularization for functional cardiac regeneration. Biomaterials 97:176–195, 2016.
Lee, C.-U., J. Vandenbrande, A. E. Goetz, M. A. Ganter, D. W. Storti, and A. J. Boydston. Room temperature extrusion 3D printing of polyether ether ketone using a stimuli-responsive binder. Addit. Manuf. 28:430–438, 2019.
Lee, J., J. Walker, K. S. Kang, S. H. Lee, J. Y. Kim, B. K. Lee, and D. W. Cho. Bone regeneration using a microstereolithography-produced customized poly(propylene fumarate)/diethyl fumarate photopolymer 3D scaffold incorporating BMP-2 loaded PLGA microspheres. Biomaterials 32:744–752, 2011.
Lee, J., J. Walker, S. Natarajan, and S. Yi. Prediction of geometric characteristics in polycaprolactone (PCL) scaffolds produced by extrusion-based additive manufacturing technique for tissue engineering. Rapid Prototyp. J. 26:238–248, 2020.
Luca, L., A.-L. Rougemont, B. H. Waploth, R. Gurny, and O. Jordan. The effects of carrier nature and pH on rhBMP-2-induced ectopic bone formation. J. Control. Release 147:38–44, 2010.
Luo, Y., G. Le Fer, D. Dean, and M. L. Becker. 3D printing of poly(propylene fumarate) oligomers: evaluation of resin viscosity, printing characteristics and mechanical properties. Biomacromolecules 20:1699–1708, 2019.
Mistry, A. S., A. G. Mikos, and J. A. Jansen. Degradation and biocompatibility of a poly(propylene fumarate)-based/alumoxane nanocomposite for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 83:940–953, 2007.
Nyberg, E., C. Holmes, T. Witham, and W. L. Grayson. Growth factor-eluting technologies for bone tissue engineering. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 6:184–194, 2016.
Ohta, H., S. Wakitani, K. Tensho, H. Horiuchi, S. Wakabayashi, N. Saito, Y. Nakamura, K. Nozaki, Y. Imai, and K. Takaoka. The effects of heat on the biological activity of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 23:420–425, 2005.
Olthof, M. G. L., D. H. R. Kempen, J. L. Herrick, M. J. Yaszemski, W. J. A. Dhert, and L. Lu. Effect of different sustained bone morphogenetic protein-2 release kinetics on bone formation in poly(propylene fumarate) scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 106:477–487, 2018.
Placone, J. K., and A. J. Engler. Recent advances in extrusion-based 3D printing for biomedical applications. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 7:e1701161, 2018.
Ramburrun, P., P. Kumar, Y. E. Choonara, D. Bijukumar, L. C. du Toit, and V. Pillay. A review of bioactive release from nerve conduits as a neurotherapeutic strategy for neuronal growth in peripheral nerve injury. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014:132350, 2014.
Roberts, J. J., P. Naudiyal, L. Jugé, L. E. Bilston, A. M. Granville, and P. J. Martens. Tailoring stimuli responsiveness using dynamic covalent cross-linking of poly(vinyl alcohol)-heparin hydrogels for controlled cell and growth factor delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 1:1267–1277, 2015.
Seto, S. P., T. Miller, and J. S. Temenoff. Effect of selective heparin desulfation on preservation of bone morphogenetic protein-2 bioactivity after thermal stress. Bioconjug. Chem. 26:286–293, 2015.
Sevim, K., and J. Pan. A mechanistic model for acidic drug release using microspheres made of PLGA 50:50. Mol. Pharm. 13:2729–2735, 2016.
Shah, S. R., A. M. Henslee, P. P. Spicer, S. Yokota, S. Petrichenko, S. Allahabadi, G. N. Bennett, M. E. Wong, F. K. Kasper, and A. G. Mikos. Effects of antibiotic physicochemical properties on their release kinetics from biodegradable polymer microparticles. Pharm. Res. 31:3379–3389, 2014.
Smith, B. T., S. M. Bittner, E. Watson, M. M. Smoak, L. Diaz-Gomez, E. R. Molina, Y. S. Kim, C. D. Hudgins, A. J. Melchiorri, D. W. Scott, K. J. Grande-Allen, J. J. Yoo, A. Atala, J. P. Fisher, and A. G. Mikos. Multi-material dual gradient 3D printing for osteogenic differentiation and spatial segregation. Tissue Eng. Part A 26:239–252, 2020.
Suntornnond, R., E. Y. S. Tan, J. An, and C. K. Chua. A highly printable and biocompatible hydrogel composite for direct printing of soft and perfusable vasculature-like structures. Sci. Rep. 7:16902, 2017.
Tarafder, S., A. Koch, Y. Jun, C. Chou, M. R. Awadallah, and C. H. Lee. Micro-precise spatiotemporal delivery system embedded in 3D printing for complex tissue regeneration. Biofabrication 8:025003, 2016.
Thibault, R. A., L. S. Baggett, A. G. Mikos, and F. K. Kasper. Osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on pregenerated extracellular matrix scaffolds in the absence of osteogenic cell culture supplements. Tissue. Eng. Part A 16:431–440, 2010.
Timmer, M. D., H. Shin, R. A. Horch, C. G. Ambrose, and A. G. Mikos. In vitro cytotoxicity of injectable and biodegradable poly(propylene fumarate)-based networks: unreacted macromers, cross-linked networks, and degradation products. Biomacromolecules 4:1026–1033, 2003.
Tousif Ayyub, K., K. Moravkar, M. Maniruzzaman, and P. Amin. Effect of melt extrudability and melt binding efficiency of polyvinyl caprolactam polyvinyl acetate polyethylene glycol graft copolymer (Soluplus®) on release pattern of hydrophilic and high dose drugs. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 99:563–574, 2019.
Trachtenberg, J. E., J. K. Placone, B. T. Smith, C. M. Piard, M. Santoro, D. W. Scott, J. P. Fisher, and A. G. Mikos. Extrusion-based 3D printing of poly(propylene fumarate) in a full-factorial design. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2:1771–1780, 2016.
Turner, B. N., R. Strong, and S. A. Gold. A review of melt extrusion additive manufacturing processes: I. Process design and modeling. Rapid Prototyping J. 20:192–204, 2014.
Wang, M. O., J. M. Etheridge, J. A. Thompson, C. E. Vorwald, D. Dean, and J. P. Fisher. Evaluation of the in vitro cytotoxicity of cross-linked biomaterials. Biomacromolecules 14:1321–1329, 2013.
Wang, M. O., C. M. Piard, A. Melchiorri, M. L. Dreher, and J. P. Fisher. Evaluating changes in structure and cytotoxicity during in vitro degradation of three-dimensional printed scaffolds. Tissue Eng. Part A 21:1642–1653, 2015.
Wei, C., N. G. Solanki, J. M. Vasoya, A. V. Shah, and A. T. M. Serajuddin. Development of 3D printed tablets by fused deposition modeling using polyvinyl alcohol as polymeric matrix for rapid drug release. J. Pharm. Sci. 109:1558–1572, 2020.
Xiao, J., Y. Wang, S. Bellusci, and X. Li. Pharmacological application of growth factors: basic and clinical. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015:141794, 2015.
Xu, Y., C.-S. Kim, D. M. Saylor and D. Koo. Polymer degradation and drug delivery in PLGA-based drug–polymer applications: a review of experiments and theories. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 105:1692–1716, 2017.
Yamakawa, S. and K. Hayashida. Advances in surgical applications of growth factors for wound healing. Burns Trauma 7:10, 2019.
Yao, B., R. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Zhang, T. Hu, W. Song, Z. Li, S. Huang and X. Fu. Biochemical and structural cues of 3D-printed matrix synergistically direct MSC differentiation for functional sweat gland regeneration. Sci. Adv. 6:eaaz1094, 2020.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (Grant P41 EB023833). G.L.K. is supported by the Robert and Janice McNair Foundation MD/PhD Student Scholar Program. M.D. is supported by a Rubicon postdoctoral fellowship from the Dutch Research Council (NWO; Project No. 019.182EN.004). The authors gratefully acknowledge Anthony J. Melchiorri and Yu Seon Kim for their guidance on polymer synthesis, and Luis Diaz-Gomez for his input on 3D printing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Stefan M Duma oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the Supplementary Information.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koons, G.L., Kontoyiannis, P.D., Diba, M. et al. Effect of 3D Printing Temperature on Bioactivity of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Released from Polymeric Constructs. Ann Biomed Eng 49, 2114–2125 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-021-02736-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-021-02736-9