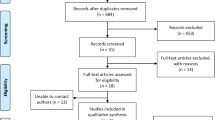
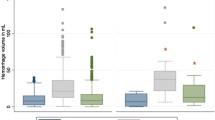
Abstract
Primary intraventricular hemorrhage (PIVH) is a special subtype of intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) without a hemorrhagic parenchymal component. Different conditions may cause this uncommon hemorrhage including trauma, vascular anomalies, coagulation disorders, and others. Frequently, PIVH is associated with structural vascular anomalies such as aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, and dural fistulas. Traditionally, hypertension has been considered a predisposing factor for PIVH. A wide variety of studies have been published describing patients with PIVH; however, studies describing exclusively patients with hypertensive PIVH are lacking in the literature. For this reason, the features of PIVH secondary to hypertension are not well described. The purpose of this study is to analyze and describe the characteristics of hypertensive PIVH. A PubMed and Scopus search adhering to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines was performed to include studies reporting patients with hypertensive PIVH. The search yielded 19 articles reporting retrospective case series. The diagnosis of hypertensive PIVH should be established in patients meeting the following criteria: (a) elevation of blood pressure is observed at admission, (b) a cerebral angiography is negative for vascular anomalies, and (c) other causes of intracranial hemorrhage are ruled out. The prognosis is poorer in patients who present with low Glasgow Coma Score (GCS), old age, hydrocephalus, or more extensive intraventricular bleeding. The results of this study show that hypertension is the most common cause of PIVH, followed by hemorrhage caused by vascular anomalies. Hypertension may be a direct cause of PIVH, but also it may be a predisposing factor for bleeding in cases of an associated vascular anomaly.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Angelopoulos M, Gupta SR, Azat Kia B (1995) Primary intraventricular hemorrhage in adults: clinical features, risk factors, and outcome. Surg Neurol 44(5):433–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/0090-3019(95)00261-8 (discussion 437)
Arboix A, García-Eroles L, Vicens A et al (2012) Spontaneous primary intraventricular hemorrhage: clinical features and early outcome. ISRN Neurol 2012(Aug):498303
Chen HC, Chuang CC, Tzaan WC et al (2011) Application of neuroendoscopy in the treatment of obstructive hydrocephalus secondary to hypertensive intraventricular hemorrhage. Neurol India 59:861–866
El-Saadany WF, Hassan T (2012) Adult intraventricular hemorrhage: presentations, management, and analysis of outcome. Neurosurg Q 2:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNQ.0b013e318227967b
Findlay M (2016) Stroke: pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. 6th edn, p 1148–1157
Flint AC, Roebken A, Singh V (2008) Primary intraventricular hemorrhage: yield of diagnostic angiography and clinical outcome. Neurocrit Care 8(3):330–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-008-9070-2
Fu C, Liu L, Chen B et al (2017) Risk factors for poor outcome in hypertensive intraventricular hemorrhage treated by external ventricular drainage with intraventricular fibrinolysis. World Neurosurg 102:240–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.03.029
Gaberel T, Magheru C, Emery E (2012) Management of non-traumatic intraventricular hemorrhage. Neurosurg Rev 35:485–495
Gates PC, Barnett HJ, Vinters HV et al (1986) Primary intraventricular hemorrhage in adults. Stroke 17(5):872–877. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.17.5.872
Giray S, Sen O, Sarica FB et al (2009) Spontaneous primary intraventricular hemorrhage in adults: clinical data, etiology and outcome. Turk Neurosurg 19(4):338–344
Graeb DA, Robertson WD, Lapointe JS et al (1982) Computed tomographic diagnosis of intraventricular hemorrhage. Etiology and prognosis. Radiology 143(1):91–96. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.143.1.6977795
Guo R, Ma L, Shrestha BK et al (2016) A retrospective clinical study of 98 adult idiopathic primary intraventricular hemorrhage cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 95(42):e5089
Hallevi H, Dar NS, Barreto AD et al (2009) The IVH score: a novel tool for estimating intraventricular hemorrhage volume: clinical and research implications. Crit Care Med 37:969–974, e1
Hameed B, Khealani BA, Mozzafar T et al (2005) Prognostic indicators in patients with primary intraventricular haemorrhage. J Pak Med Assoc 55(8):315–317
Hilkens NA, van Asch CJ, Rinkel GJ et al (2016) Yield of angiographic examinations in isolated intraventricular hemorrhage: a case series and systematic review of the literature. Eur Stroke J 1(4):288–293. https://doi.org/10.1177/2396987316666589
Hwang BY, Bruce SS, Appelboom G et al (2012) Evaluation of intraventricular hemorrhage assessment methods for predicting outcome following intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 116(1):185–192. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.9.JNS10850
Idris Z, Raj J, Abdullah JM (2014) Early experience in endoscopic management of massive intraventricular hemorrhage with literature review. Asian J Neurosurg 9(3):124–129. https://doi.org/10.4103/1793-5482.142731
Jayakumar PN, Taly AB, Bhavani UR et al (1989) Prognosis in solitary intraventricular haemorrhage. Clinical and computed tomographic observations. Acta Neurol Scand 80(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0404.1989.tb03833.x
Jiang Z, Peng Y, Zhang M et al (2020) Etiological factors of spontaneous primary intraventricular hemorrhage. Br J Neurosurg 34(4):423–426. https://doi.org/10.1080/02688697.2020.1751067
Kiymaz N, Demir O, Cirak B (2005) Is external ventricular drainage useful in primary intraventricular hemorrhages? Adv Therapy 22:447–452
Lee SH, Park KJ, Park DH et al (2017) Factors associated with clinical outcomes in patients with primary intraventricular hemorrhage. Med Sci Monit 22(23):1401–1412. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.899309
LeRoux PD, Haglund MM, Newell DW et al (1992) Intraventricular hemorrhage in blunt head trauma: an analysis of 43 cases. Neurosurgery 31:678–685
Longatti PL, Martinuzzi A, Fiorindi A et al (2004) Neuroendoscopic management of intraventricular hemorrhage. Stroke 35(2):e35–e38. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000113736.73632.F6
Martí-Fàbregas J, Piles S, Guardia E et al (1999) Spontaneous primary intraventricular hemorrhage: clinical data, etiology and outcome. J Neurol 246(4):287–291
Nelson SE, Mould WA, Gandhi D et al (2020) Primary intraventricular hemorrhage outcomes in the CLEAR III trial. Int J Stroke 15(8):872–880. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747493020908146
Pai A, Hegde A, Nair R et al (2020) Adult primary intraventricular hemorrhage: clinical characteristics and outcomes. J Neurosci Rural Pract 11(4):623–628. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0040-1716770
Pan K, Pandit A, Bhattacharyya B et al (2018) Primary intraventricular haemorrhage: clinical and aetiological profile with predictors of outcome-a hospital based study. J Clin Diagn Re 12(6):OCO1–OCO4. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2018/32328/11593
Park KJ, Kim JH, Park YK et al (2004) Prognostic factors of primary intraventricular hemorrhage. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 35(3):278–283
Passero S, Ulivelli M, Reale F (2002) Primary intraventricular haemorrhage in adults. Acta Neurol Scand 105(2):115–119. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0404.2002.1o118.x
Sanders E (1881) A study of primary, immediate or direct haemorrhage into the ventricles of brain. Am J Med Sci 82:85–128
Srivastava T, Sannegowda RB, Satija V et al (2014) Primary intraventricular hemorrhage: clinical features, risk factors, etiology, and yield of diagnostic cerebral angiography. Neurol India 62(2):144–148. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.132333
Verma A, Maheshwari MC, Bhargava S (1987) Spontaneous intraventricular haemorrhage. J Neurol 234(4):233–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00618255
Weinstein R, Ess K, Sirdar B et al (2017) Primary intraventricular hemorrhage: clinical characteristics and outcomes. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 26(5):995–999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2016.11.114
Young WB, Lee KP, Pessin MS (1990) Prognostic significance of ventricular blood in supratentorial hemorrhage: a volumetric study. Neurology 40:616–619
Zhang S, Jia B, Li H et al (2017) Primary intraventricular hemorrhage in adults: etiological causes and prognostic factors in Chinese population. J Neurol 264(2):382–390
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.A.R designed the study. L.A.R. and V.V. collected and analyzed the data and drafted and revised the manuscript. V.V analyzed the data, interpreted the results, and performed the statistical analysis. L.A.R. and V.V. revised the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable as it is a systematic review.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robles, L.A., Volovici, V. Hypertensive primary intraventricular hemorrhage: a systematic review. Neurosurg Rev 45, 2013–2026 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-022-01758-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-022-01758-8