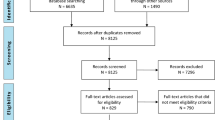
Abstract
Biomarkers such as calcium channel binding protein S100 subunit beta (S100B), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), ubiquitin c-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1) and neuron-specific enolase (NSE) have been proposed to aid in screening patients presenting with mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI). As such, we aimed to characterise their accuracy at various thresholds. MEDLINE, SCOPUS and EMBASE were searched, and articles reporting the diagnostic performance of included biomarkers were eligible for inclusion. Risk of bias was assessed using the QUADAS-II criteria. A meta-analysis was performed to assess the predictive value of biomarkers for imaging abnormalities on CT. A total of 2939 citations were identified, and 38 studies were included. Thirty-two studies reported data for S100B. At its conventional threshold of 0.1 μg/L, S100B had a pooled sensitivity of 91% (95%CI 87–94) and a specificity of 30% (95%CI 26–34). The optimal threshold for S100B was 0.72 μg/L, with a sensitivity of 61% (95% CI 50–72) and a specificity of 69% (95% CI 64–74). Nine studies reported data for GFAP. The optimal threshold for GFAP was 626 pg/mL, at which the sensitivity was 71% (95%CI 41–91) and specificity was 71% (95%CI 43–90). Sensitivity of GFAP was maximised at a threshold of 22 pg/mL, which had a sensitivity of 93% (95%CI 73–99) and a specificity of 36% (95%CI 12–68%). Three studies reported data for NSE and two studies for UCH-L1, which precluded meta-analysis. There is evidence to support the use of S100B as a screening tool in mild TBI, and potential advantages to the use of GFAP, which requires further investigation.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The dataset used to generate the results is available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Code availability
The statistical code used to generate the results is available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
References
Allouchery G, Moustafa F, Roubin J, Pereira B, Schmidt J, Raconnat J, Pic D, Sapin V, Bouvier D (2018) Clinical validation of S100B in the management of a mild traumatic brain injury: issues from an interventional cohort of 1449 adult patients. Clin Chem Lab Med 56:1897–1904. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2018-0471, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=14374331&id=doi:10.1515%2Fcclm-2018-0471&atitle=Clinical+validation+of+S100B+in+the+management+of+a+mild+traumatic+brain+injury%3A+Issues+from+an+interventional+cohort+of+1449+adult+patients&stitle=Clin.+Chem.+Lab.+Med.&title=Clinical+Chemistry+and+Laboratory+Medicine&volume=56&issue=11&spage=1897&epage=1904&aulast=Allouchery&aufirst=Gautier&auinit=G.&aufull=Allouchery+G.&coden=CCLMF&isbn=&pages=1897-1904
Amoo M, O’Halloran PJ, Henry J, Ben HM, Brennan P, Campbell M, Caird J, Curley GF (2021) Permeability of the blood–brain barrier after traumatic brain injury; radiological considerations. J Neurotrauma. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2020.7545
Asadollahi S, Heidari K, Taghizadeh M, Seidabadi AM, Jamshidian M, Vafaee A, Manoochehri M, Shojaee AH, Hatamabadi HR (2016) Reducing head computed tomography after mild traumatic brain injury: screening value of clinical findings and S100B protein levels. Brain Inj 30:172–178. https://doi.org/10.3109/02699052.2015.1091504, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=1362301X&id=doi:10.3109%2F02699052.2015.1091504&atitle=Reducing+head+computed+tomography+after+mild+traumatic+brain+injury%3A+Screening+value+of+clinical+findings+and+S100B+protein+levels&stitle=Brain+Inj.&title=Brain+Injury&volume=30&issue=2&spage=172&epage=178&aulast=Asadollahi&aufirst=Shadi&auinit=S.&aufull=Asadollahi+S.&coden=BRAIE&isbn=&pages=172-178&date=2016&auinit1=S&auinitm=
Babl FE, Borland ML, Phillips N, Kochar A, Dalton S, McCaskill M, Cheek JA, Gilhotra Y, Furyk J, Neutze J, Lyttle MD, Bressan S, Donath S, Molesworth C, Jachno K, Ward B, Williams A, Baylis A, Crowe L, Oakley E, Dalziel SR (2017) Accuracy of PECARN, CATCH, and CHALICE head injury decision rules in children: a prospective cohort study. Lancet 389:2393–2402. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30555-X
Barry TWL, Lopez KG, Thambiah J, Kumar N, Jeanette TSLJ, Ashokka B (2020) In the extraordinary times of coronavirus disease2019: clinical strategies for performing spinal. Asian Spine J 14:721–729. https://doi.org/10.31616/asj.2020.0306
Bazarian JJ, Biberthaler P, Welch RD, Lewis LM, Barzo P, Bogner-Flatz V, Gunnar Brolinson P, Büki A, Chen JY, Christenson RH, Hack D, Huff JS, Johar S, Jordan JD, Leidel BA, Lindner T, Ludington E, Okonkwo DO, Ornato J, Peacock WF, Schmidt K, Tyndall JA, Vossough A, Jagoda AS (2018) Serum GFAP and UCH-L1 for prediction of absence of intracranial injuries on head CT (ALERT-TBI): a multicentre observational study. Lancet Neurol 17:782–789. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30231-X, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=14744465&id=doi:10.1016%2FS1474-4422%2818%2930231-X&atitle=Serum+GFAP+and+UCH-L1+for+prediction+of+absence+of+intracranial+injuries+on+head+CT+%28ALERT-TBI%29%3A+a+multicentre+observational+study&stitle=Lancet+Neurol.&title=The+Lancet+Neurology&volume=17&issue=9&spage=782&epage=789&aulast=Bazarian&aufirst=Jeffrey+J&auinit=J.J.&aufull=Bazarian+J.J.&coden=LNAEA&isbn=&pages=782-789&date=2018&auinit1=J
Bazarian JJ, Blyth BJ, He H, Mookerjee S, Jones C, Kiechle K, Moynihan R, Wojcik SM, Grant WD, Secreti LM, Triner W, Moscati R, Leinhart A, Ellis GL, Khan J (2013) Classification accuracy of serum Apo A-I and S100B for the diagnosis of mild traumatic brain injury and prediction of abnormal initial head computed tomography scan. J Neurotrauma 30:1747–1754. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2013.2853
Biberthaler P, Linsenmeier U, Pfeifer K-J, Kroetz M, Mussack T, Kanz K-G, Hoecherl EFJ, Jonas F, Marzi I, Leucht P, Jochum M, Mutschler W (2006) Serum S-100B concentration provides additional information fot the indication of computed tomography in patients after minor head injury: a prospective multicenter study. Shock 25:446–453
Biberthaler P, Mussack T, Wiedemann E, Gilg T, Soyka M, Koller G, Pfeifer KJ, Linsenmaier U, Mutschler W, Gippner-Steppert C, Jochum M (2001) Elevated serum levels of S-100B reflect the extent of brain injury in alcohol intoxicated patients after mild head trauma. Shock 16:97–101
Biberthaler P, Mussack T, Wiedemann E, Kanz KG, Koelsch M, Gippner-Steppert C, Jochum M (2001) Evaluation of S-100b as a specific marker for neuronal damage due to minor head trauma. World J Surg 25:93–97
Blais Lécuyer J, Mercier É, Tardif P-A, Archambault PM, Chauny J-M, Berthelot S, Frenette J, Perry J, Stiell I, Émond M, Lee J, Lang E, McRae A, Boucher V, Le Sage N (2020) S100B protein level for the detection of clinically significant intracranial haemorrhage in patients with mild traumatic brain injury: a subanalysis of a prospective cohort study. Emerg Med J. https://doi.org/10.1136/emermed-2020-209583, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=14720213&id=doi:10.1136%2Femermed-2020-209583&atitle=S100B+protein+level+for+the+detection+of+clinically+significant+intracranial+haemorrhage+in+patients+with+mild+traumatic+brain+injury%3A+A+subanalysis+of+a+prospective+cohort+study&stitle=Emerg.+Med.+J.&title=Emergency+Medicine+Journal&volume=&issue=&spage=&epage=&aulast=Blais+L%C3%A9cuyer&aufirst=Julien&auinit=J.&aufull=Blais+L%C3%A9cuyer+J.&coden
Bramlett HM, Dietrich WD (2015) Long-term consequences of traumatic brain injury: current status of potential mechanisms of injury and neurological outcomes. J Neurotrauma 32:1834–1848. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2014.3352
Calcagnile O, Unden L, Unden J (2012) Clinical validation of S100B use in management of mild head injury. BMC Emerg Med 12:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-227X-12-13
Cervellin G, Benatti M, Carbucicchio A, Mattei L, Cerasti D, Aloe R, Lippi G (2012) Serum levels of protein S100B predict intracranial lesions in mild head injury. Clin Biochem 45:408–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2012.01.006
Cevik S, Ozgenc MM, Guneyk A, Evran S, Akkaya E, Calis F, Katar S, Soyalp C, Hanimoglu H, Kaynar MY (2019) NRGN, S100B and GFAP levels are significantly increased in patients with structural lesions resulting from mild traumatic brain injuries. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 183:105380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2019.105380
Cevik S, Ozgenc MM, Guneyk A, Evran S, Akkaya E, Calis F, Katar S, Soyalp C, Hanimoglu H, Kaynar MY, Çevik S, Özgenç MM, Güneyk A, Evran Ş, Akkaya E, Çalış F, Katar S, Soyalp C, Hanımoğlu H, Kaynar MY (2019) NRGN, S100B and GFAP levels are significantly increased in patients with structural lesions resulting from mild traumatic brain injuries. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 183:105380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2019.105380
Czeiter E, Amrein K, Gravesteijn BY, Lecky F, Menon DK, Mondello S, Newcombe VFJ, Richter S, Steyerberg EW, Vyvere T V, Verheyden J, Xu H, Yang Z, Maas AIR, Wang KKW, Büki A (2020) Blood biomarkers on admission in acute traumatic brain injury: relations to severity, CT findings and care path in the CENTER-TBI study. EBioMedicine 56. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102785, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=23523964&id=doi:10.1016%2Fj.ebiom.2020.102785&atitle=Blood+biomarkers+on+admission+in+acute+traumatic+brain+injury%3A+Relations+to+severity%2C+CT+findings+and+care+path+in+the+CENTER-TBI+study&stitle=EBioMedicine&title=EBioMedicine&volume=56&issue=&spage=&epage=&aulast=Czeiter&aufirst=Endre&auinit=E.&aufull=Czeiter+E.&coden=&isbn=&pages=-&date=2020&auinit1=E&auinitm=
Czeiter E, Amrein K, Gravesteijn BY, Lecky F, Menon DK, Mondello S, Newcombe VFJ, Richter S, Steyerberg EW, Vande VT, Verheyden J, Xu H, Yang Z, Maas AIR, Wang KKW, Büki A (2020) Blood biomarkers on admission in acute traumatic brain injury: relations to severity, CT findings and care path in the CENTER-TBI study. EBioMedicine 56:102785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102785
David A, Mari C, Vignaud F, Masson D, Planche L, Bord E, Bourcier R, Frampas E, Batard E, Desal H (2017) Evaluation of S100B blood level as a biomarker to avoid computed tomography in patients with mild head trauma under antithrombotic medication. Diagn Interv Imaging 98:551–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diii.2017.03.010, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=22115684&id=doi:10.1016%2Fj.diii.2017.03.010&atitle=Evaluation+of+S100B+blood+level+as+a+biomarker+to+avoid+computed+tomography+in+patients+with+mild+head+trauma+under+antithrombotic+medication&stitle=Daign.+Intervent.+Imaging&title=Diagnostic+and+Interventional+Imaging&volume=98&issue=7-8&spage=551&epage=556&aulast=David&aufirst=A.&auinit=A.&aufull=David+A.&coden=&isbn=&pages=551-556&date=2017&auinit
Edalatfar M, Piri SM, Mehrabinejad MM, Mousavi MS, Meknatkhah S, Fattahi MR, Kavyani Z, Hajighadery A, Kaveh M, Aryannejad A, Ghafouri M, Jamshidi E, Rezwanifar MM, Sadeghi-Naini M, Bari A, Sharif-Alhoseini M (2021) Biofluid biomarkers in traumatic brain injury: a systematic scoping review. Neurocrit Care. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12028-020-01173-1
Egea-Guerrero JJ, Revuelto-Rey J, Murillo-Cabezas F, Munoz-Sanchez MA, Vilches-Arenas A, Sanchez-Linares P, Dominguez-Roldan JM, Leon-Carrion J (2012) Accuracy of the S100beta protein as a marker of brain damage in traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj 26:76–82. https://doi.org/10.3109/02699052.2011.635360
Egea-Guerrero JJ, Rodríguez-Rodríguez A, Quintana-Díaz M, Freire-Aragón MD, Raya-Collados D, Hernández-García C, Ortiz-Manzano Á, Vilches-Arenas Á, Díez-Naz A, Guerrero JM, Murillo-Cabezas F (2018) Validation of S100B use in a cohort of Spanish patients with mild traumatic brain injury: a multicentre study. Brain Inj 32:459–463. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699052.2018.1429019, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=1362301X&id=doi:10.1080%2F02699052.2018.1429019&atitle=Validation+of+S100B+use+in+a+cohort+of+Spanish+patients+with+mild+traumatic+brain+injury%3A+a+multicentre+study&stitle=Brain+Inj.&title=Brain+Injury&volume=32&issue=4&spage=459&epage=463&aulast=Egea-Guerrero&aufirst=Juan+Jos%C3%A9&auinit=J.J.&aufull=Egea-Guerrero+J.J.&coden=BRAIE&isbn=&pages=459-463&date=2018&auinit1=J&auinitm=J
Filippidis AS, Papadopoulos DC, Kapsalaki EZ, Fountas KN (2010) Role of the S100B serum biomarker in the treatment of children suffering from mild traumatic brain injury. Neurosurg Focus 29:1–5. https://doi.org/10.3171/2010.8.FOCUS10185
Foks KA, Van Den Brand CL, Lingsma HF, Van Der Naalt J, Jacobs B, De Jong E, Den Boogert HF, Sir Ö, Patka P, Polinder S, Gaakeer MI, Schutte CE, Jie KE, Visee HF, Hunink MGM, Reijners E, Braaksma M, Schoonman GG, Steyerberg EW, Jellema K, Dippel DWJ (2018) External validation of computed tomography decision rules for minor head injury: prospective, multicentre cohort study in the Netherlands. BMJ 362. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k3527
Gardner RC, Rubenstein R, Wang KKW, Korley FK, Yue JK, Yuh EL, Mukherje P, Valadka AB, Okonkwo DO, Diaz-Arrastia R, Manley GT (2018) Age-related differences in diagnostic accuracy of plasma glial fibrillary acidic protein and tau for identifying acute intracranial trauma on computed tomography: a TRACK-TBI study. J Neurotrauma 35:2341–2350. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2018.5694
Goyal A, Failla MD, Niyonkuru C, Amin K, Fabio A, Berger RP, Wagner AK (2013) S100b as a prognostic biomarker in outcome prediction for patients with severe traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 30:946. https://doi.org/10.1089/NEU.2012.2579
Harty E, Bellis F (2010) CHALICE head injury rule: an implementation study. Emerg Med J 27:750–752. https://doi.org/10.1136/emj.2009.077644
Haydel MJ, Preston CA, Mills TJ, Luber S, Blaudeau E, DeBlieux PMC (2000) Indications for computed tomography in patients with minor head injury. N Engl J Med 343:100–105. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm200007133430204
Ingebrigtsen T, Romner B, Marup-Jensen S, Dons M, Lundqvist C, Bellner J, Alling C, Borgesen SE (2000) The clinical value of serum S-100 protein measurements in minor head injury: a Scandinavian multicentre study. Brain Inj 14:1047–1055
Isokuortti H, Iverson GL, Silverberg ND, Kataja A, Brander A, Öhman J, Luoto TM (2018) Characterizing the type and location of intracranial abnormalities in mild traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg 129:1588–1597. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.7.JNS17615
Iverson GL, Lovell MR, Smith S, Franzen MD (2000) Prevalence of abnormal CT-scans following mild head injury. Brain Inj 14:1057–1061. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699050050203559
Janigro D, Kawata K, Silverman E, Marchi N, Diaz-Arrastia R (2020) Is salivary S100B a biomarker of traumatic brain injury? A pilot study. Front Neurol 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/FNEUR.2020.00528
Jones CMC, Harmon C, McCann M, Gunyan H, Bazarian JJ (2020) S100B outperforms clinical decision rules for the identification of intracranial injury on head CT scan after mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj 34:407–414. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699052.2020.1725123
Kahouadji S, Salamin P, Praz L, Coiffier J, Frochaux V, Durif J, Pereira B, Arlettaz L, Oris C, Sapin V, Bouvier D (2020) S100B blood level determination for early management of ski-related mild traumatic brain injury: a pilot study. Front Neurol 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.00856, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=16642295&id=doi:10.3389%2Ffneur.2020.00856&atitle=S100B+Blood+Level+Determination+for+Early+Management+of+Ski-Related+Mild+Traumatic+Brain+Injury%3A+A+Pilot+Study&stitle=Front.+Neurol.&title=Frontiers+in+Neurology&volume=11&issue=&spage=&epage=&aulast=Kahouadji&aufirst=Samy&auinit=S.&aufull=Kahouadji+S.&coden=&isbn=&pages=-&date=2020&auinit1=S&auinitm=
Kuppermann N, Holmes JF, Dayan PS, Hoyle JD, Atabaki SM, Holubkov R, Nadel FM, Monroe D, Stanley RM, Borgialli DA, Badawy MK, Schunk JE, Quayle KS, Mahajan P, Lichenstein R, Lillis KA, Tunik MG, Jacobs ES, Callahan JM, Gorelick MH, Glass TF, Lee LK, Bachman MC, Cooper A, Powell EC, Gerardi MJ, Melville KA, Muizelaar JP, Wisner DH, Zuspan SJ, Dean JM, Wootton-Gorges SL (2009) Identification of children at very low risk of clinically-important brain injuries after head trauma: a prospective cohort study. Lancet 374:1160–1170. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61558-0
Lagerstedt L, Egea-Guerrero JJ, Bustamante A, Montaner J, Rodriguez-Rodriguez A, El Rahal A, Turck N, Quintana M, Garcia-Armengol R, Prica CM, Andereggen E, Rinaldi L, Sarrafzadeh A, Schaller K, Sanchez J-C (2017) H-FABP: a new biomarker to differentiate between CT-positive and CT-negative patients with mild traumatic brain injury. PLoS ONE 12:e0175572. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0175572
Lagerstedt L, Egea-Guerrero JJ, Bustamante A, Rodríguez-Rodríguez A, Rahal AE, Quintana-Diaz M, García-Armengol R, Prica CM, Andereggen E, Rinaldi L, Sarrafzadeh A, Schaller K, Montaner J, Sanchez J-C (2018) Combining H-FABP and GFAP increases the capacity to differentiate between CT-positive and CT-negative patients with mild traumatic brain injury. PLoS One 13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0200394
Lagerstedt L, Egea-Guerrero JJ, Montaner J, Busmante A, El Rahal A, Andereggen E, Bulla A, Rinaldi L, Schaller K, Sarrafzadeh A, Sanchez J-C (2016) A S100B/H-FABP panel to rule-out CT-scan lesions in mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj 30:648. https://doi.org/10.3109/02699052.2016.1162060, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=1362301X&id=doi:10.3109%2F02699052.2016.1162060&atitle=A+S100B%2FH-FABP+panel+to+rule-out+CT-scan+lesions+in+mild+traumatic+brain+injury&stitle=Brain+Inj.&title=Brain+Injury&volume=30&issue=5-6&spage=648&epage=&aulast=Lagerstedt&aufirst=Linnea&auinit=L.&aufull=Lagerstedt+L.&coden=&isbn=&pages=648-&date=2016&auinit1=L&auinitm=
Lagerstedt L, Tiberti N, Turck N, Andereggen E, Bulla A, Rinaldi L, Sarrafzadeh-Khorassani A, Schaller K, Sanchez JC (2016) A biomarker panel to rule-out unnecessary CT-scans in mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI). J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36:782–783. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X16645239, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=15597016&id=doi:10.1177%2F0271678X16645239&atitle=A+biomarker+panel+to+rule-out+unnecessary+CT-scans+in+mild+traumatic+brain+injury+%28mTBI%29&stitle=J.+Cereb.+Blood+Flow+Metab.&title=Journal+of+Cerebral+Blood+Flow+and+Metabolism&volume=36&issue=&spage=782&epage=783&aulast=Lagerstedt&aufirst=L.&auinit=L.&aufull=Lagerstedt+L.&coden=&isbn=&pages=782-783&date=2016&auinit1=L&auinitm=
Laribi S, Kansao J, Borderie D, Collet C, Deschamps P, Ababsa R, Mouniam L, Got L, Leon A, Thoannes H, Santin A, Kouyoumdjian J-C, Dahyot-Fizelier C, Millet C, Golmard J-L, Beaudeux J-L, Groupa S-SS (2014) S100B blood level measurement to exclude cerebral lesions after minor head injury: the multicenter STIC-S100 French study. Clin Chem Lab Med 52:527–536. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2013-0621
Maas AIR, Menon DK, Adelson PD, Andelic N, Bell MJ, Belli A, Bragge P, Brazinova A, Büki A, Chesnut RM, Citerio G, Coburn M, Cooper DJ, Crowder AT, Czeiter E, Czosnyka M, Diaz-Arrastia R, Dreier JP, Duhaime AC, Ercole A, van Essen TA, Feigin VL, Gao G, Giacino J, Gonzalez-Lara LE, Gruen RL, Gupta D, Hartings JA, Hill S, Jiang J-Y, Ketharanathan N, Kompanje EJO, Lanyon L, Laureys S, Lecky F, Levin H, Lingsma HF, Maegele M, Majdan M, Manley G, Marsteller J, Mascia L, McFadyen C, Mondello S, Newcombe V, Palotie A, Parizel PM, Peul W, Piercy J, Polinder S, Puybasset L, Rasmussen TE, Rossaint R, Smielewski P, Söderberg J, Stanworth SJ, Stein MB, von Steinbüchel N, Stewart W, Steyerberg EW, Stocchetti N, Synnot A, Te Ao B, Tenovuo O, Theadom A, Tibboel D, Videtta W, Wang KKW, Williams WH, Wilson L, Yaffe K, Adams H, Agnoletti V, Allanson J, Amrein K, Andaluz N, Anke A, Antoni A, van As AB, Audibert G, Azaševac A, Azouvi P, Azzolini ML, Baciu C, Badenes R, Barlow KM, Bartels R, Bauerfeind U, Beauchamp M, Beer D, Beer R, Belda FJ, Bellander BM, Bellier R, Benali H, Benard T, Beqiri V, Beretta L, Bernard F, Bertolini G, Bilotta F, Blaabjerg M, den Boogert H, Boutis K, Bouzat P, Brooks B, Brorsson C, Bullinger M, Burns E, Calappi E, Cameron P, Carise E, Castaño-León AM, Causin F, Chevallard G, Chieregato A, Christie B, Cnossen M, Coles J, Collett J, Della Corte F, Craig W, Csato G, Csomos A, Curry N, Dahyot-Fizelier C, Dawes H, DeMatteo C, Depreitere B, Dewey D, van Dijck J, Đilvesi Đ, Dippel D, Dizdarevic K, Donoghue E, Duek O, Dulière GL, Dzeko A, Eapen G, Emery CA, English S, Esser P, Ezer E, Fabricius M, Feng J, Fergusson D, Figaji A, Fleming J, Foks K, Francony G, Freedman S, Freo U, Frisvold SK, Gagnon I, Galanaud D, Gantner D, Giraud B, Glocker B, Golubovic J, Gómez López PA, Gordon WA, Gradisek P, Gravel J, Griesdale D, Grossi F, Haagsma JA, Håberg AK, Haitsma I, Van Hecke W, Helbok R, Helseth E, van Heugten C, Hoedemaekers C, Höfer S, Horton L, Hui J, Huijben JA, Hutchinson PJ, Jacobs B, van der Jagt M, Jankowski S, Janssens K, Jelaca B, Jones KM, Kamnitsas K, Kaps R, Karan M, Katila A, Kaukonen KM, De Keyser V, Kivisaari R, Kolias AG, Kolumbán B, Kolundžija K, Kondziella D, Koskinen LO, Kovács N, Kramer A, Kutsogiannis D, Kyprianou T, Lagares A, Lamontagne F, Latini R, Lauzier F, Lazar I, Ledig C, Lefering R, Legrand V, Levi L, Lightfoot R, Lozano A, MacDonald S, Major S, Manara A, Manhes P, Maréchal H, Martino C, Masala A, Masson S, Mattern J, McFadyen B, McMahon C, Meade M, Melegh B, Menovsky T, Moore L, Morgado Correia M, Morganti-Kossmann MC, Muehlan H, Mukherjee P, Murray L, van der Naalt J, Negru A, Nelson D, Nieboer D, Noirhomme Q, Nyirádi J, Oddo M, Okonkwo DO, Oldenbeuving AW, Ortolano F, Osmond M, Payen JF, Perlbarg V, Persona P, Pichon N, Piippo-Karjalainen A, Pili-Floury S, Pirinen M, Ple H, Poca MA, Posti J, Van Praag D, Ptito A, Radoi A, Ragauskas A, Raj R, Real RGL, Reed N, Rhodes J, Robertson C, Rocka S, Røe C, Røise O, Roks G, Rosand J, Rosenfeld JV, Rosenlund C, Rosenthal G, Rossi S, Rueckert D, de Ruiter GCW, Sacchi M, Sahakian BJ, Sahuquillo J, Sakowitz O, Salvato G, Sánchez-Porras R, Sándor J, Sangha G, Schäfer N, Schmidt S, Schneider KJ, Schnyer D, Schöhl H, Schoonman GG, Schou RF, Sir Ö, Skandsen T, Smeets D, Sorinola A, Stamatakis E, Stevanovic A, Stevens RD, Sundström N, Taccone FS, Takala R, Tanskanen P, Taylor MS, Telgmann R, Temkin N, Teodorani G, Thomas M, Tolias CM, Trapani T, Turgeon A, Vajkoczy P, Valadka AB, Valeinis E, Vallance S, Vámos Z, Vargiolu A, Vega E, Verheyden J, Vik A, Vilcinis R, Vleggeert-Lankamp C, Vogt L, Volovici V, Voormolen DC, Vulekovic P, Vande Vyvere T, Van Waesberghe J, Wessels L, Wildschut E, Williams G, Winkler MKL, Wolf S, Wood G, Xirouchaki N, Younsi A, Zaaroor M, Zelinkova V, Zemek R, Zumbo F (2017) Traumatic brain injury: integrated approaches to improve prevention, clinical care, and research. Lancet Neurol 16:987–1048
Mahan MY, Thorpe M, Ahmadi A, Abdallah T, Casey H, Sturtevant D, Judge-Yoakam S, Hoover C, Rafter D, Miner J, Richardson C, Samadani U (2019) Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) outperforms S100 calcium-binding protein B (S100B) and ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1) as predictor for positive computed tomography of the head in trauma subjects. World Neurosurg 128:e434–e444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.04.170
McGuinness LA, Higgins JPT (2020) Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): an R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Res Synth Methods 12:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1411
McMahon PJ, Panczykowski DM, Yue JK, Puccio AM, Inoue T, Sorani MD, Lingsma HF, Maas AIR, Valadka AB, Yuh EL, Mukherjee P, Manley GT, Okonkwo DO, Casey SS, Cheong M, Cooper SR, Dams-O’Connor K, Gordon WA, Hricik AJ, Lawless K, Menon D, Schnyer DM, Vassar MJ (2015) Measurement of the glial fibrillary acidic protein and its breakdown products GFAP-BDP biomarker for the detection of traumatic brain injury compared to computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurotrauma 32:527–533. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2014.3635
Menon DK, Schwab K, Wright DW, Maas AI (2010) Position statement: definition of traumatic brain injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 91:1637–1640
Minkkinen M, Iverson GL, Kotilainen AK, Pauniaho SL, Mattila VM, Lehtimäki T, Berghem K, Posti JP, Luoto TM (2019) Prospective validation of the Scandinavian guidelines for initial management of minimal, mild, and moderate head injuries in adults. J Neurotrauma 36:2904–2912. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2018.6351
Mondello S, Papa L, Buki A, Bullock MR, Czeiter E, Tortella FC, Wang KK, Hayes RL (2011) Neuronal and glial markers are differently associated with computed tomography findings and outcome in patients with severe traumatic brain injury: a case control study. Crit Care 15:R156. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc10286
Morochovič R, Rácz O, Kitka M, Pingorová S, Cibur P, Tomková D, Lenártová R, Morochovic R, Racz O, Kitka M, Pingorova S, Cibur P, Tomkova D, Lenartova R (2009) Serum S100B protein in early management of patients after mild traumatic brain injury. Eur J Neurol 16:1112–1117. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2009.02653.x
Muller B, Evangelopoulos DS, Bias K, Wildisen A, Zimmermann H, Exadaktylos AK, Müller B, Evangelopoulos DS, Bias K, Wildisen A, Zimmermann H, Exadaktylos AK (2011) Can S-100B serum protein help to save cranial CT resources in a peripheral trauma centre? A study and consensus paper. Emerg Med J 28:938–940. https://doi.org/10.1136/emj.2010.095372
Muller K, Townend W, Biasca N, Unden J, Waterloo K, Romner B, Ingebrigtsen T, Müller K, Townend W, Biasca N, Undén J, Waterloo K, Romner B, Ingebrigtsen T (2007) S100B serum level predicts computed tomography findings after minor head injury. J Trauma 62:1452–1456. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e318047bfaa
Mussack T, Biberthaler P, Kanz KG, Heckl U, Gruber R, Linsenmaier U, Mutschler W, Jochum M (2002) Immediate S-100B and neuron-specific enolase plasma measurements for rapid evaluation of primary brain damage in alcohol-intoxicated, minor head-injured patients. Shock 18:395–400
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (2019) Head injury: assessment and early management [CG176]
Okonkwo DO, Puffer RC, Jain S, Puccio AM, Yue JK, Sun X, Diaz-Arrastia R, Korley FK, Wang KKW, Mukherjee P, Yuh EL, Temkin NR, Robertson C, Manley GT (2018) Point-of-care GFAP vs core lab s100b biomarker testing for CT abnormalities in TBI: a prospective track-tbi study. J Neurotrauma 35:A222. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2018.29013.abstracts, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=15579042&id=doi:10.1089%2Fneu.2018.29013.abstracts&atitle=Point-of-care+GFAP+vs+core+lab+s100b+biomarker+testing+for+CT+abnormalities+in+TBI%3A+A+prospective+track-tbi+study&stitle=J.+Neurotrauma&title=Journal+of+Neurotrauma&volume=35&issue=16&spage=A222&epage=&aulast=Okonkwo&aufirst=David+O.&auinit=D.O.&aufull=Okonkwo+D.O.&coden=&isbn=&pages=A222-&date=2018&auinit1=D&auinitm=O
Okonkwo DO, Puffer RC, Puccio AM, Yuh EL, Yue JK, Diaz-Arrastia R, Korley FK, Wang KKW, Sun X, Taylor SR, Mukherjee P, Markowitz AJ, Jain S, Manley GT, Manley GT (2020) Point-of-care platform blood biomarker testing of glial fibrillary acidic protein versus S100 calcium-binding protein B for prediction of traumatic brain injuries: a transforming research and clinical knowledge in traumatic brain injury study. J Neurotrauma 37:2460–2467. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2020.7140
Oris C, Bouillon-Minois J-B, Pinguet J, Kahouadji S, Durif J, Meslé V, Pereira B, Schmidt J, Sapin V, Bouvier D (2021) Predictive performance of blood S100B in the management of patients over 65 years old with mild traumatic brain injury. Journals Gerontol Ser A. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glab055
Osmond MH, Klassen TP, Wells GA, Correll R, Jarvis A, Joubert G, Bailey B, Chauvin-Kimoff L, Pusic M, McConnell D, Nijssen-Jordan C, Silver N, Taylor B, Stiell IG (2010) CATCH: a clinical decision rule for the use of computed tomography in children with minor head injury. CMAJ 182:341–348. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.091421
Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, Elmagarmid A (2016) Rayyan—a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev 5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0384-4
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan SE, Chou R, Glanville J, Grimshaw JM, Hróbjartsson A, Lalu MM, Li T, Loder EW, Mayo-Wilson E, McDonald S, McGuinness LA, Stewart LA, Thomas J, Tricco AC, Welch VA, Whiting P, Moher D (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
Papa L, Braga C, Demery J, Dixit N, Brophy G, Hayes R, Wang KKW (2012) Early serum levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) are associated with global outcome at 1 month postinjury in mild and moderate traumatic brain injury. Can J Emerg Med 14:S16
Papa L, Braga C, Tan C, Ameli N, Demery J, Dixit N, Burks S, Hayes RL, Wang KKW, Brophy GM (2013) Serum glial fibrillary acidic protein outperforms s100b in detecting traumatic intracranial lesions on CT in a general trauma population with mild traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 30:A69. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2013.9938, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=08977151&id=doi:10.1089%2Fneu.2013.9938&atitle=Serum+glial+fibrillary+acidic+protein+outperforms+s100b+in+detecting+traumatic+intracranial+lesions+on+CT+in+a+general+trauma+population+with+mild+traumatic+brain+injury&stitle=J.+Neurotrauma&title=Journal+of+Neurotrauma&volume=30&issue=15&spage=A69&epage=&aulast=Papa&aufirst=Linda&auinit=L.&aufull=Papa+L.&coden=&isbn=&pages=A69-&date=2013&auinit1=L&auinitm=
Papa L, Brophy GM, Welch RD, Lewis LM, Braga CF, Tan CN, Ameli NJ, Lopez MA, Haeussler CA, Mendez Giordano DI, Silvestri S, Giordano P, Weber KD, Hill-Pryor C, Hack DC (2016) Time course and diagnostic accuracy of glial and neuronal blood biomarkers GFAP and UCH-L1 in a large cohort of trauma patients with and without mild traumatic brain injury. JAMA Neurol 73:551–560. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.0039
Papa L, Demery J, Dixit N, Braga C, Zhang Z, Brophy G, Burks S, Ilic S, Streeter J, Tortella F, Hayes R, Wang KKW (2011) Early serum levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein breakdown product (GFAP-BDP) are associted with global outcome at one month post injury in mild and moderate traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 28:A63–A64. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2011.9945, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=08977151&id=doi:10.1089%2Fneu.2011.9945&atitle=Early+serum+levels+of+glial+fibrillary+acidic+protein+breakdown+product+%28GFAP-BDP%29+are+associted+with+global+outcome+at+one+month+post+injury+in+mild+and+moderate+traumatic+brain+injury&stitle=J.+Neurotrauma&title=Journal+of+Neurotrauma&volume=28&issue=6&spage=A63&epage=A64&aulast=Papa&aufirst=Linda&auinit=L.&aufull=Papa+L.&coden=&isbn=&pages=A63-A64&date=
Papa L, Lewis L, Falk J, Demery J, Brophy G, Liu M-C, Mo J, Mondello S, Schmid K, Robertson C, Tortella F, Hayes R, Wang KKW (2011) Serum levels of UCH-L1 distinguishes mild and moderate traumatic brain injury from trauma controls and is associated with lesions on computed tomography. J Neurotrauma 28:A5. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2011.9945, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=08977151&id=doi:10.1089%2Fneu.2011.9945&atitle=Serum+levels+of+UCH-L1+distinguishes+mild+and+moderate+traumatic+brain+injury+from+trauma+controls+and+is+associated+with+lesions+on+computed+tomography&stitle=J.+Neurotrauma&title=Journal+of+Neurotrauma&volume=28&issue=6&spage=A5&epage=&aulast=Papa&aufirst=Linda&auinit=L.&aufull=Papa+L.&coden=&isbn=&pages=A5-&date=2011&auinit1=L&auinitm=
Papa L, Lewis LM, Silvestri S, Falk JL, Giordano P, Brophy GM, Demery JA, Liu MC, Mo J, Akinyi L, Mondello S, Schmid K, Robertson CS, Tortella FC, Hayes RL, Wang KKW (2012) Serum levels of ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase distinguish mild traumatic brain injury from trauma controls and are elevated in mild and moderate traumatic brain injury patients with intracranial lesions and neurosurgical intervention. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 72:1335–1344. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e3182491e3d
Papa L, Ramia M, Kirby S, Ramirez J, Carr B, Florez C, Cramm-Morgan K, Chaar-Alvarez F, Braga C, Tan CN, Ameli NJ, Lopez M, Mittal M, Zonfrillo M (2014) Serum GFAP out-performs S100B in detecting traumatic intracranial lesions on CT in children with suspected mild traumatic brain injury. Acad Emerg Med 21:S315. https://doi.org/10.1111/acem.12365, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=10696563&id=doi:10.1111%2Facem.12365&atitle=Serum+GFAP+out-performs+S100B+in+detecting+traumatic+intracranial+lesions+on+CT+in+children+with+suspected+mild+traumatic+brain+injury&stitle=Acad.+Emerg.+Med.&title=Academic+Emergency+Medicine&volume=21&issue=5&spage=S315&epage=&aulast=Papa&aufirst=Linda&auinit=L.&aufull=Papa+L.&coden=&isbn=&pages=S315-&date=2014&auinit1=L&auinitm=
Papa L, Ramia MM, Edwards D, Johnson BD, Slobounov SM (2015) Systematic review of clinical studies examining biomarkers of brain injury in athletes after sports-related concussion. J Neurotrauma 32:661–673. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2014.3655
Pelinka LE, Hertz H, Mauritz W, Harada N, Jafarmadar M, Albrecht M, Redl H, Bahrami S (2005) Nonspecific increase of systemic neuron-specific enolase after trauma: clinical and experimental findings. Shock 24:119–123. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.shk.0000168876.68154.43
Pelinka LE, Kroepfl A, Schmidhammer R, Krenn M, Buchinger W, Redl H, Raabe A (2004) Glial fibrillary acidic protein in serum after traumatic brain injury and multiple trauma. J Trauma - Inj Infect Crit Care 57:1006–1012. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.TA.0000108998.48026.C3
Poli-de-Figueiredo LF, Biberthaler P, Simao Filho C, Hauser C, Mutschler W, Jochum M (2006) Measurement of S-100B for risk classification of victims sustaining minor head injury—first pilot study in Brazil. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 61:41–46
Posti JP, Takala RSK, Lagerstedt L, Dickens AM, Hossain I, Mohammadian M, Ala-Seppälä H, Frantzén J, Van Gils M, Hutchinson PJ, Katila AJ, Maanpaä HR, Menon DK, Newcombe VF, Tallus J, Hrusovsky K, Wilson DH, Gill J, Sanchez JC, Tenovuo O, Zetterberg H, Blennow K (2019) Correlation of blood biomarkers and biomarker panels with traumatic findings on computed tomography after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 36:2178–2189. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2018.6254
Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AWS, Scholten RJPM, Bossuyt PM, Zwinderman AH (2005) Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol 58:982–990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.02.022
Romner B, Ingebrigtsen T, Kongstad P, Borgesen SE (2000) Traumatic brain damage: serum S-100 protein measurements related to neuroradiological findings. J Neurotrauma 17:641–647
Salameh JP, Bossuyt PM, McGrath TA, Thombs BD, Hyde CJ, MacAskill P, Deeks JJ, Leeflang M, Korevaar DA, Whiting P, Takwoingi Y, Reitsma JB, Cohen JF, Frank RA, Hunt HA, Hooft L, Rutjes AWS, Willis BH, Gatsonis C, Levis B, Moher D, McInnes MDF (2020) Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy studies (PRISMA-DTA): explanation, elaboration, and checklist. BMJ 370:2632
Schachar JL, Zampolin RL, Miller TS, Farinhas JM, Freeman K, Taragin BH (2011) External validation of the New Orleans Criteria (NOC), the Canadian CT Head Rule (CCHR) and the National Emergency X-Radiography Utilization Study II (NEXUS II) for CT scanning in pediatric patients with minor head injury in a non-trauma center. Pediatr Radiol 41:971–979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-011-2032-4
Schulte S, Podlog LW, Hamson-Utley JJ, Strathmann FG, Strüder HK (2014) A systematic review of the biomarker S100B: implications for sport-related concussion management. J Athl Train 49:830–850. https://doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-49.3.33
Seidenfaden S-C, Kjerulff JL, Juul N, Kirkegaard H, Møller MF, Münster AB, Bøtker MT (2021) Diagnostic accuracy of prehospital serum S100B and GFAP in patients with mild traumatic brain injury: a prospective observational multicenter cohort study—“the PreTBI I study.” Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med 29. https://doi.org/10.1186/S13049-021-00891-5
Shakeri M, Dokht YGM, Panahi F, Mahdkhah A, Foladi P (2014) S100B protein value in predicting brain death after head trauma. Neurosurg Q 24:291–296. https://doi.org/10.1097/wnq.0b013e3182a2fc6e
Shenton ME, Hamoda HM, Schneiderman JS, Bouix S, Pasternak O, Rathi Y, Vu M-A, Purohit MP, Helmer K, Koerte I, Lin AP, Westin C-F, Kikinis R, Kubicki M, Stern RA, Zafonte R (2012) A review of magnetic resonance imaging and diffusion tensor imaging findings in mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Imaging Behav 6:137–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11682-012-9156-5
Stein S, Ross S (1992) Mild head injury: a plea for routine early CT scanning. J Trauma 33:11–13
Stein SC, Ross SE (1990) The value of computed tomographic scans in patients with low-risk head injuries. Neurosurgery 26:638. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-199004000-00012
Steinhauser S, Schumacher M, Rücker G (2016) Modelling multiple thresholds in meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy studies. BMC Med Res Methodol 16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-016-0196-1
Stiell IG, Wells GA, Vandemheen K, Clement C, Lesiuk H, Laupacis A, Douglas McKnight R, Verbeek R, Brison R, Cass D, Eisenhauer A, M, Greenberg G, Worthington J, (2001) The Canadian CT Head Rule for patients with minor head injury. Lancet 357:1391–1396. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04561-X
Stranjalis G, Korfias S, Papapetrou C, Kouyialis A, Boviatsis E, Psachoulia C, Sakas DE (2004) Elevated serum S-100B protein as a predictor of failure to short-term return to work or activities after mild head injury. J Neurotrauma 21:1070–1075. https://doi.org/10.1089/0897715041651088
Susie Zoltewicz J, Scharf D, Yang B, Chawla A, Newsom KJ, Fang L (2012) Characterization of antibodies that detect human GFAP after traumatic brain injury. Biomark Insights 7:71–79. https://doi.org/10.4137/BMI.S9873
Tagliaferri F, Compagnone C, Korsic M, Servadei F, Kraus J (2006) A systematic review of brain injury epidemiology in Europe. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148:255–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00701-005-0651-Y
Thaler HW, Schmidsfeld J, Pusch M, Pienaar S, Wunderer J, Pittermann P, Valenta R, Gleiss A, Fialka C, Mousavi M (2015) Evaluation of S100B in the diagnosis of suspected intracranial hemorrhage after minor head injury in patients who are receiving platelet aggregation inhibitors and in patients 65 years of age and older. J Neurosurg 123:1202–1208. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.12.JNS142276
Thelin E, Al Nimer F, Frostell A, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Nyström H, Svensson M, Bellander B-M, Piehl F, Nelson DW (2019) A serum protein biomarker panel improves outcome prediction in human traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 36:2850–2862. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2019.6375, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=15579042&id=doi:10.1089%2Fneu.2019.6375&atitle=A+Serum+protein+biomarker+panel+improves+outcome+prediction+in+human+traumatic+brain+injury&stitle=J.+Neurotrauma&title=Journal+of+Neurotrauma&volume=36&issue=20&spage=2850&epage=2862&aulast=Thelin&aufirst=Eric&auinit=E.&aufull=Thelin+E.&coden=JNEUE&isbn=&pages=2850-2862&date=2019&auinit1=E&auinitm=
Thelin EP, Jeppsson E, Frostell A, Svensson M, Mondello S, Bellander BM, Nelson DW (2016) Utility of neuron-specific enolase in traumatic brain injury; relations to S100B levels, outcome, and extracranial injury severity. Crit Care 20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-016-1450-y
Thelin EP, Nelson DW, Bellander B-MM (2017) A review of the clinical utility of serum S100B protein levels in the assessment of traumatic brain injury. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 159:209–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-016-3046-3
Turtzo LC, Jikaria N, Cota MR, Williford JP, Uche V, Davis T, MacLaren J, Moses AD, Parikh G, Castro MA, Pham DL, Butman JA, Latour LL (2020) Meningeal blood–brain barrier disruption in acute traumatic brain injury. Brain Commun 2. https://doi.org/10.1093/braincomms/fcaa143
Undén J, Ingebrigtsen T, Romner B (2013) Scandinavian guidelines for initial management of minimal, mild and moderate head injuries in adults: an evidence and consensus-based update. BMC Med 11:50. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-11-50
Undén L, Calcagnile O, Undén J, Reinstrup P, Bazarian J (2015) Validation of the Scandinavian guidelines for initial management of minimal, mild and moderate traumatic brain injury in adults. BMC Med 13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-015-0533-y
Unden L, Calcagnile O, Unden J, Reinstrup P, Bazarian J, Undén L, Calcagnile O, Undén J, Reinstrup P, Bazarian J (2015) Validation of the Scandinavian guidelines for initial management of minimal, mild and moderate traumatic brain injury in adults. BMC Med 13:292. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-015-0533-y
Wang M, Li W (2016) Cognitive impairment after traumatic brain injury: the role of MRI and possible pathological basis. J Neurol Sci 370:244–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JNS.2016.09.049
Weissberg I, Veksler R, Kamintsky L, Saar-Ashkenazy R, Milikovsky DZ, Shelef I, Friedman A (2014) Imaging blood-brain barrier dysfunction in football players. JAMA Neurol 71:1453–1455. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.2682
Welch RD, Ayaz SI, Lewis LM, Unden J, Chen JY, Mika VH, Saville B, Tyndall JA, Nash M, Buki A, Barzo P, Hack D, Tortella FC, Schmid K, Hayes RL, Vossough A, Sweriduk ST, Bazarian JJ (2016) Ability of serum glial fibrillary acidic protein, ubiquitin C-Terminal Hydrolase-L1, and S100B to differentiate normal and abnormal head computed tomography findings in patients with suspected mild or moderate traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 33:203–214. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2015.4149
Welch RD, Ellis M, Lewis LM, Ayaz SI, Mika VH, Millis S, Papa L (2017) Modeling the kinetics of serum glial fibrillary acidic protein, ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase-L1, and S100B concentrations in patients with traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 34:1957–1971. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2016.4772, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=15579042&id=doi:10.1089%2Fneu.2016.4772&atitle=Modeling+the+Kinetics+of+Serum+Glial+Fibrillary+Acidic+Protein%2C+Ubiquitin+Carboxyl-Terminal+Hydrolase-L1%2C+and+S100B+Concentrations+in+Patients+with+Traumatic+Brain+Injury&stitle=J.+Neurotrauma&title=Journal+of+Neurotrauma&volume=34&issue=11&spage=1957&epage=1971&aulast=Welch&aufirst=Robert+D.&auinit=R.D.&aufull=Welch+R.D.&coden=JNEUE&isbn=&pages=1957-1971&
Welch RD, Ellis MM, Lewis LM, Ayaz SI, Mika VH, Chawla A, Catania M, Millis SR, Hayes R, Papa L (2016) The association of CT findings with repeated measurements of serum biomarker levels in patients with acute mild to moderate traumatic brain injury. Acad Emerg Med 23:S20. https://doi.org/10.1111/acem.12974, http://jq6am9xs3s.search.serialssolutions.com/?sid=EMBASE&issn=15532712&id=doi:10.1111%2Facem.12974&atitle=The+association+of+CT+findings+with+repeated+measurements+of+serum+biomarker+levels+in+patients+with+acute+mild+to+moderate+traumatic+brain+injury&stitle=Acad.+Emerg.+Med.&title=Academic+Emergency+Medicine&volume=23&issue=&spage=S20&epage=&aulast=Welch&aufirst=Robert+D.&auinit=R.D.&aufull=Welch+R.D.&coden=&isbn=&pages=S20-&date=2016&auinit1=R&auinitm=D
Whiting PF, Rutjes AWS, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, Leeflang MMG, Sterne JAC, Bossuyt PMM (2011) Quadas-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med 155:529–536
Willoughby KA, Kleindienst A, Müller C, Chen T, Muir JK, Ellis EF (2004) S100B protein is released by in vitro trauma and reduces delayed neuronal injury. J Neurochem 91:1284–1291. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02812.x
Wolf H, Frantal S, Pajenda GS, Salameh O, Widhalm H, Hajdu S, Sarahrudi K (2013) Predictive value of neuromarkers supported by a set of clinical criteria in patients with mild traumatic brain injury: S100B protein and neuron-specific enolase on trial. J Neurosurg 118:1298–1303. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.1.JNS121181
Yeung C, Bhatia R, Bhattarai B, Sinha M (2020) Role of Salivary biomarkers in predicting significant traumatic brain injury: an exploratory study. Pediatr Emerg Care. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0000000000002050
Zongo D, Ribereau-Gayon R, Masson F, Laborey M, Contrand B, Salmi LR, Montaudon D, Beaudeux JL, Meurin A, Dousset V, Loiseau H, Lagarde E (2012) S100-B protein as a screening tool for the early assessment of minor head injury. Ann Emerg Med 59:209–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2011.07.027
Funding
Michael Amoo received funding through the Royal College of Surgeons/Beacon Hospital StAR MD scholarship programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Concept and design: MA, JH, PB, MBH, MC, JC, MJ, GFC.
Data acquisition: MA, JH.
Statistical analysis: MA, JH.
Interpretation of data: MA, JH, PJOH, PB, MBH, MC, JC, MJ, GFC.
Writing: MA, JH.
Review and revision of manuscript: MA, JH, PJOH, PB, MBH, MC, JC, MJ, GFC.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amoo, M., Henry, J., O’Halloran, P.J. et al. S100B, GFAP, UCH-L1 and NSE as predictors of abnormalities on CT imaging following mild traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy. Neurosurg Rev 45, 1171–1193 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01678-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01678-z