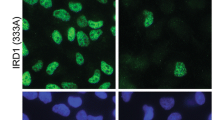
Abstract
Microdeletion of the 15q11.2 BP1-BP2 region, also known as Burnside–Butler susceptibility region, is associated with phenotypes like delayed developmental language abilities along with motor skill disabilities, combined with behavioral and emotional problems. The 15q11.2 microdeletion region harbors four evolutionarily conserved and non-imprinted protein-coding genes: NIPA1, NIPA2, CYFIP1, and TUBGCP5. This microdeletion is a rare copy number variation frequently associated with several pathogenic conditions in humans. The aim of this study is to investigate the RNA-binding proteins binding with the four genes present in 15q11.2 BP1-BP2 microdeletion region. The results of this study will help to better understand the molecular intricacies of the Burnside-Butler Syndrome and also the possible involvement of these interactions in the disease aetiology. Our results of enhanced crosslinking and immunoprecipitation data analysis indicate that most of the RBPs interacting with the 15q11.2 region are involved in the post-transcriptional regulation of the concerned genes. The RBPs binding to this region are found from the in silico analysis, and the interaction of RBPs like FASTKD2 and EFTUD2 with exon-intron junction sequence of CYFIP1 and TUBGCP5 has also been validated by combined EMSA and western blotting experiment. The exon-intron junction binding nature of these proteins suggests their potential involvement in splicing process. This study may help to understand the intricate relationship of RBPs with mRNAs within this region, along with their functional significance in normal development, and lack thereof, in neurodevelopmental disorders. This understanding will help in the formulation of better therapeutic approaches.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that (the/all other) data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Abekhoukh S, Bardoni B (2014) CYFIP family proteins between autism and intellectual disability: links with fragile X syndrome. Front Cell Neurosci 8:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2014.00081
Avdjieva-Tzavella D, Hadjidekova S, Rukova B, Nesheva D, Litvinenko I, Hristova-Naydenova D, Simeonov E, Tincheva R, Toncheva D (2012) Detection of genomic imbalances by array-based comparative genomic hybridization in Bulgarian patients with autism spectrum disorders. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 26(6):3389–3393. https://doi.org/10.5504/bbeq.2012.0097
Beni FA, Kazemi M, Dianat-Moghadam H, Behjati M (2022) MicroRNAs regulating Wnt signaling pathway in colorectal cancer: biological implications and clinical potentials. Funct Integrat Genom. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-022-00908-x
Bird CW, Gardiner AS, Bolognani F, Tanner DC, Chen CY, Lin WJ, Yoo S, Twiss JL, Perrone-Bizzozero N (2013) KSRP modulation of GAP-43 MRNA stability restricts axonal outgrowth in embryonic hippocampal neurons. PLoS ONE 8(11):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0079255
Braeutigam C, Rago L, Rolke A, Waldmeier L, Christofori G, Winter J (2014) The RNA-binding protein Rbfox2: an essential regulator of EMT-driven alternative splicing and a mediator of cellular invasion. Oncogene 33(9):1082–1092. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.50
Burnside RD, Pasion R, Mikhail FM, Carroll AJ, Robin NH, Youngs EL, Gadi IK et al (2011) Microdeletion/microduplication of proximal 15q11.2 between BP1 and BP2: a susceptibility region for neurological dysfunction including developmental and language delay. Hum Genet 130(4):517–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-011-0970-4
Butler MG (2017) Clinical and genetic aspects of the 15q11.2 BP1–BP2 microdeletion disorder. J Intellect Disabil Res 61(6):568–579. https://doi.org/10.1111/jir.12382
Butler MG (2019) Magnesium supplement and the 15q11.2 BP1–BP2 microdeletion (Burnside–Butler) syndrome: a potential treatment? Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122914
Chai JH, Locke DP, Greally JM, Knoll JHM, Ohta T, Dunai J, Yavor A, Eichler EE, Nicholls RD (2003) Identification of four highly conserved genes between breakpoint hotspots BP1 and BP2 of the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndromes deletion region that have undergone evolutionary transposition mediated by flanking duplicons. Am J Hum Genet 73(4):898–925. https://doi.org/10.1086/378816
Chen S, Song C, Guo H, Pingyi X, Huang W, Zhou Y, Sun J et al (2005) Distinct novel mutations affecting the same base in the NIPA1 gene cause autosomal dominant hereditary spastic paraplegia in two Chinese families. Hum Mutat 25(2):135–141. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.20126
Clifton NE, Thomas KL, Wilkinson LS, Hall J, Trent S (2020) FMRP and CYFIP1 at the synapse and their role in psychiatric vulnerability. Complex Psychiatry 6(1–2):5–19. https://doi.org/10.1159/000506858
Curinha A, Braz SO, Pereira-Castro I, Cruz A, Moreira A (2014) Implications of polyadenylation in health and disease. Nucleus 5(6):508–519. https://doi.org/10.4161/nucl.36360
Denli AM, Tops BBJ, Plasterk RHA, Ketting RF, Hannon GJ (2004) Processing of primary MicroRNAs by the microprocessor complex. Nature 432(7014):231–235. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03049
Duan S, Cui C, Chen L, Yang Z, Yin Gang H (2022) Fine mapping and candidate gene analysis of dwarf Gene Rht14 in durum wheat (Triticum Durum). Funct Integrat Genom 22(2):141–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-021-00825-5
van der Feltz C, Hoskins AA (2019) Structural and functional modularity of the U2 SnRNP in Pre-MRNA splicing. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 54(5):443–465. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409238.2019.1691497
Galgano A, Forrer M, Jaskiewicz L, Kanitz A, Zavolan M, Gerber AP (2008) Comparative analysis of MRNA targets for human PUF-family proteins suggests extensive interaction with the MiRNA regulatory system. PLoS ONE 3(9). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0003164
Gallo S, Furler M, Sigel RKO (2005) In vitro transcription and purification of RNAs of different size. Chimia. https://doi.org/10.2533/000942905777675589
Gaudet P, Livstone MS, Lewis SE, Thomas PD (2011) Phylogenetic-based propagation of functional annotations within the Gene Ontology consortium. Brief Bioinform 12(5):449–462. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbr042
Goytain A, Hines RM, El-Husseini A, Quamme GA (2007) NIPA1(SPG6), the basis for autosomal dominant form of hereditary spastic paraplegia, encodes a functional Mg2+ transporter. J Biol Chem 282(11):8060–8068. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M610314200
Goytain A, Hines RM, Quamme GA (2008) Functional characterization of NIPA2, a selective Mg2+ transporter. Am J Phys Cell Physiol 295(4):944–953. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00091.2008
Gregory RI, Yan KP, Amuthan G, Chendrimada T, Doratotaj B, Cooch N, Shiekhattar R (2004) The microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of MicroRNAs. Nature 432(7014):235–240. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03120
Grozdanov PN, Masoumzadeh E, Kalscheuer VM, Bienvenu T, Billuart P, Delrue MA, Latham MP, MacDonald CC (2020) A missense mutation in the CSTF2 gene that impairs the function of the RNA recognition motif and causes defects in 3’ end processing is associated with intellectual disability in humans. Nucleic Acids Res 48(17):9804–9821. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa689
Han J, Lee Y, Yeom KH, Kim YK, Jin H, Narry Kim V (2004) The Drosha-DGCR8 complex in primary MicroRNA processing. Genes Develop 18(24):3016–3027. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1262504
Han Y, Seon Mi Y, Shah FH, Kim SJ (2022) Subversive molecular role of Krüppel-like factor 5 in extracellular matrix degradation and chondrocyte dedifferentiation. Funct Integrat Genom 22(6):1307–1313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-022-00892-2
Havens MA, Reich AA, Hastings ML (2014) Drosha promotes splicing of a pre-MicroRNA-like alternative exon. PLoS Genetics 10(5). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004312
Hirayama-Kurogi M, Takizawa Y, Kunii Y, Matsumoto J, Wada A, Hino M, Akatsu H et al (2017) Downregulation of GNA13-ERK network in prefrontal cortex of schizophrenia brain identified by combined focused and targeted quantitative proteomics. J Proteomics 158:31–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2017.02.009
Huang L, Vanstone MR, Hartley T, Osmond M, Barrowman N, Allanson J, Baker L, Dabir TA, Dipple KM, Dobyns WB, Estrella J, Faghfoury H, Favaro FP, Goel H, Gregersen PA, Gripp KW, Grix A, Guion-Almeida ML, Harr MH, … Lines MA (2016) Mandibulofacial dysostosis with microcephaly: mutation and database update. Hum Mutat 37(2):148–154. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.22924
Jin P, Alisch RS, Warren ST (2004) RNA and MicroRNAs in fragile X mental retardation. Nat Cell Biol 6(11):1048–1053. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1104-1048
Jourdain AA, Popow J, De La Fuente MA, Martinou JC, Anderson P, Simarro M (2017) Survey and summary: the FASTK family of proteins: emerging regulators of mitochondrial RNA biology. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx772
Kawano Y, Yoshimura T, Tsuboi D, Kawabata S, Kaneko-Kawano T, Shirataki H, Takenawa T, Kaibuchi K (2005) CRMP-2 is involved in Kinesin-1-dependent transport of the Sra-1/WAVE1 complex and axon formation. Mol Cell Biol 25(22):9920–9935. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.25.22.9920-9935.2005
Koedoot E, van Steijn E, Vermeer M, González-Prieto R, Vertegaal ACO, Martens JWM, le Dévédec SE, van de Water B (2021) Splicing factors control triple-negative breast cancer cell mitosis through SUN2 interaction and sororin intron retention. J Experiment Clin Cancer Res 40(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-021-01863-4
Kuhn AN, Li Z, Brow DA (1999) Splicing factor Prp8 governs U4/U6 RNA unwinding during activation of the spliceosome. Mol Cell 3(1):65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80175-6
Kumar S, Velasco ADR, Michlewski G (2017) Oleic acid induces MiR-7 processing through remodeling of Pri-MiR-7/protein complex. J Mol Biol 429(11):1638–1649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2017.05.001
Lee Y, Ahn C, Han J, Choi H, Kim J, Yim J, Lee J, Provost P, Kim S, Kim VN (2003) Nature01957.Pdf. p 425
Li J-R, Tang M, Li Y, Amos CI, Cheng C (2022) Genetic variants associated MRNA stability in lung. BMC Genom 23(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-022-08405-y
Liaud N, Horlbeck MA, Gilbert LA, Gjoni K, Weissman JS, Cate JHD (2019) Cellular response to small molecules that selectively stall protein synthesis by the ribosome. PLoS Genet 15(3):1–30. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1008057
Lingeman E, Jeans C, Corn JE (2017) Production of purified CasRNPs for efficacious genome editing. Curr Protoc Mol Biol 2017:31.10.1. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpmb.43
Liu NN, Xie H, Xiang-wei WS, Gao K, Wang TS, Jiang YW (2019) The absence of NIPA2 enhances neural excitability through BK (big potassium) channels. CNS Neurosci Therapeut 25(8):865–875. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.13119
Martello G, Rosato A, Ferrari F, Manfrin A, Cordenonsi M, Dupont S, Enzo E et al (2010) A microrna targeting dicer for metastasis control. Cell 141(7):1195–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.05.017
Martin CA, Ahmad I, Klingseisen A, Hussain MS, Bicknell LS, Leitch A, Nürnberg G et al (2014) Mutations in PLK4, encoding a master regulator of centriole biogenesis, cause microcephaly, growth failure and retinopathy. Nat Genet 46(12):1283–1292. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3122
Maver A, Čuturilo G, Kovanda A, Miletić A, Peterlin B (2019) Rare missense TUBGCP5 gene variant in a patient with primary microcephaly. Eur J Med Genet 62(12):103598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmg.2018.12.003
McKinney BC, Grossman AW, Elisseou NM, Greenough WT (2005) Dendritic spine abnormalities in the occipital cortex of C57BL/6 Fmr1 knockout mice. Am J Med Genet - Neuropsychiat Genet 136B(1):98–102. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.30183
Min H, Turck CW, Nikolic JM, Black DL (1997) A new regulatory protein, KSRP, mediates exon inclusion through an intronic splicing enhancer. Genes Develop 11(8):1023–1036. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.11.8.1023
Mozaffari-Jovin S, Santos KF, Hsiao HH, Will CL, Urlaub H, Wahl MC, Lührmann R (2012) The Prp8 RNase H-like domain inhibits Brr2-mediated U4/U6 SnRNA unwinding by blocking Brr2 loading onto the U4 SnRNA. Genes Develop 26(21):2422–2434. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.200949.112
Mozaffari-Jovin S, Wandersleben T, Santos KF, Will CL, Luḧrmann R, Wahl MC (2013) Inhibition of RNA helicase Brr2 by the C-terminal tail of the spliceosomal protein Prp8. Science 341(6141):80–84. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1237515
Mozaffari-Jovin S, Wandersleben T, Santos KF, Will CL, Luḧrmann R, Wahl MC (2014) Novel regulatory principles of the Spliceosomal Brr2 RNA helicase and links to retinal disease in humans. RNA Biol 11(4):298–312. https://doi.org/10.4161/rna.28353
Murphy SM, Preble AM, Patel UK, O’Connell KL, Prabha Dias D, Moritz M, Agard D, Stults JT, Stearns T (2001) GCP5 and GCP6: two new members of the human γ-tubulin complex. Mol Biol Cell 12(11):3340–3352. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.12.11.3340
Napoli I, Mercaldo V, Boyl PP, Eleuteri B, Zalfa F, de Rubeis S, di Marino D et al (2008) The fragile X syndrome protein represses activity-dependent translation through CYFIP1, a New 4E-BP. Cell 134(6):1042–1054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.031
Nguyen TH, Duong JL, Galej WP, Oshikane H, Newman AJ, Nagai K (2013) Structural basis of Brr2-prp8 interactions and implications for U5 SnRNP biogenesis and the spliceosome active site. Structure 21(6):910–919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2013.04.017
Nostrand EL, Freese P, Pratt GA, Wang X, Wei X, Xiao R, Blue SM et al (2020) A large-scale binding and functional map of human RNA-binding proteins. Nature 583(7818):711–719. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2077-3
Pathania M, Davenport EC, Muir J, Sheehan DF, López-Doménech G, Kittler JT (2014) The autism and schizophrenia associated gene CYFIP1 is critical for the maintenance of dendritic complexity and the stabilization of mature spines. Translat Psychiatry 4. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2014.16
Puffenberger EG, Jinks RN, Sougnez C, Cibulskis K, Willert RA, Achilly NP, Cassidy RP et al (2012) Genetic mapping and exome sequencing identify variants associated with five novel diseases. PLoS One 7(1). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028936
Quinlan AR, Hall IM (2010) BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 26(6):841–842. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq033
Rafi SK, Butler MG (2020) The 15q11.2 Bp1-Bp2 microdeletion (Burnside–Butler) syndrome: in silico analyses of the four coding genes reveal functional associations with neurodevelopmental phenotypes. Int J Mol Sci 21(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093296
Rainier S, Chai JH, Tokarz D, Nicholls RD, Fink JK (2003) NIPA1 gene mutations cause autosomal dominant hereditary spastic paraplegia (SPG6). Am J Hum Genet 73(4):967–971. https://doi.org/10.1086/378817
Silvia de R, Bagni C (2010). Fragile X mental retardation protein control of neuronal MRNA metabolism: insights into MRNA stability. Mol Cell Neurosci. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2009.09.013.
Silvia de R, Bagni C (2011) Regulation of molecular pathways in the fragile X syndrome: insights into autism spectrum disorders. J Neurodevelop Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11689-011-9087-2.
Scheidecker S, Etard C, Haren L, Stoetzel C, Hull S, Arno G, Plagnol V et al (2015) Mutations in TUBGCP4 alter microtubule organization via the γ-tubulin ring complex in autosomal-recessive microcephaly with chorioretinopathy. Am J Hum Genet 96(4):666–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.02.011
Small EC, Leggett SR, Winans AA, Staley JP (2006) The EF-G-like GTPase Snu114p regulates spliceosome dynamics mediated by Brr2p, a DExD/H Box ATPase. Mol Cell 23(3):389–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2006.05.043
Snee M, Kidd GJ, Munro TP, Smith R (2002) RNA trafficking and stabilization elements associate with multiple brain proteins. J Cell Sci 115(23):4661–4669. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.00137
Soong HK, Dong WK, Weiler IJ, Greenough WT (2006) Fragile X mental retardation protein shifts between polyribosomes and stress granules after neuronal injury by arsenite stress or in vivo hippocampal electrode insertion. J Neurosci 26(9):2413–2418. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3680-05.2006
Sun C (2020) The SF3b complex: splicing and beyond. Cell Mol Life Sci 77(18):3583–3595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03493-z
Tajirika T, Tokumaru Y, Taniguchi K, Sugito N, Matsuhashi N, Futamura M, Yanagihara K, Akao Y, Yoshida K (2018) DEAD-Box protein RNA-helicase DDX6 regulates the expression of HER2 and FGFR2 at the post-transcriptional step in gastric cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci 19(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072005
Tassone F, de Rubeis S, Carosi C, la Fata G, Serpa G, Raske C, Willemsen R, Hagerman PJ, Bagni C (2011) Differential usage of transcriptional start sites and polyadenylation sites in FMR1 premutation alleles. Nucleic Acids Res 39(14):6172–6185. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr100
Taylor SC, Posch A (2014) The design of a quantitative Western Blot experiment. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/361590
Trajkovski M, Hausser J, Soutschek J, Bhat B, Akin A, Zavolan M, Heim MH, Stoffel M (2011) MicroRNAs 103 and 107 regulate insulin sensitivity. Nature 474(7353):649–653. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10112
Tsang HTH, Edwards TL, Wang X, Connell JW, Davies RJ, Durrington HJ, Cahir J, O’kane, J. Paul Luzio, and Evan Reid. (2009) The hereditary spastic paraplegia proteins NIPA1, spastin and spartin are inhibitors of mammalian BMP signalling. Hum Mol Genet 18(20):3805–3821. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddp324
Vanlerberghe C, Petit F, Malan V, Vincent-Delorme C, Bouquillon S, Boute O, Holder-Espinasse M et al (2015) 15q 11.2 microdeletion (BP1-BP2) and developmental delay, behaviour issues, epilepsy and congenital heart disease: a series of 52 patients. Eur J Med Genet 58(3):140–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmg.2015.01.002
Vessey JP, Schoderboeck L, Gingl E, Luzi E, Riefler J, di Leva F, Karra D, Thomas S, Kiebler MA, Macchi P (2010) Mammalian Pumilio 2 regulates dendrite morphogenesis and synaptic function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(7):3222–3227. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0907128107
Vessey JP, Vaccani A, Xie Y, Dahm R, Karra D, Kiebler MA, Macchi P (2006) Dendritic localization of the translational repressor Pumilio 2 and its contribution to dendritic stress granules. J Neurosci 26(24):6496–6508. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0649-06.2006
Wandrey F, Montellese C, Koos K, Badertscher L, Bammert L, Cook AG, Zemp I, Horvath P, Kutay U (2015) The NF45/NF90 heterodimer contributes to the biogenesis of 60S ribosomal subunits and influences nucleolar morphology. Mol Cell Biol 35(20):3491–3503. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.00306-15
Wang WX, Rajeev BW, Stromberg AJ, Ren N, Tang G, Huang Q, Rigoutsos I, Nelson PT (2008) The expression of microRNA miR-107 decreases early in Alzheimer’s disease and may accelerate disease progression through regulation of β-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1. J Neurosci 28(5):1213–1223. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5065-07.2008
Ware AP, Satyamoorthy K, Paul B (2022) CmirC: an integrated database of clustered MiRNAs co-localized with copy number variations in cancer. Functional and Integrative Genomics 22(6):1229–1241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-022-00909-w
Wilfred BR, Wang WX, Nelson PT (2007) Energizing MiRNA research: a review of the role of MiRNAs in lipid metabolism, with a prediction that MiR-103/107 regulates human metabolic pathways. Mol Genet Metab 91(3):209–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgme.2007.03.011
Wong D, Johnson SM, Young D, Iwamoto L, Sood S, Slavin TP (2013) Expanding the BP1-BP2 15q11.2 Microdeletion Phenotype: Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Congenital Cataracts. Case Rep Genet 2013:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/801094
Xu C, Xiuping F, Zhu S, Liu JJ (2016) Retrolinkin recruits the WAVE1 protein complex to facilitate BDNF-induced TrkB endocytosis and dendrite outgrowth. Mol Biol Cell 27(21):3342–3356. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E16-05-0326
Yang EW, Bahn JH, Hsiao EYH, Tan BX, Sun Y, Ting F, Zhou B et al (2019) Allele-specific binding of RNA-binding proteins reveals functional genetic variants in the RNA. Nat Commun 10(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09292-w
Yao C, Biesinger J, Wan J, Weng L, Xing Y, Xie X, Shi Y (2012) Transcriptome-wide analyses of CstF64-RNA interactions in global regulation of MRNA alternative polyadenylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(46):18773–18778. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1211101109
Zeng Y, Yi R, Cullen BR (2005) Recognition and cleavage of primary MicroRNA precursors by the nuclear processing enzyme Drosha. EMBO J 24(1):138–148. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600491
Zhang H, Wong JP, Ni G, Cano P, Dittmer DP, Damania B (2022a) Mitochondrial protein, TBRG4, modulates KSHV and EBV reactivation from latency. PLoS Pathogens 18(11). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1010990
Zhang Z, Cheng J, Wang S, Gao Y, Xian X, Li C, YanxiuWang (2022b) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of MhHEC2-like genes in Malus Halliana reveals it enhances Fe (iron) deficiency tolerance. Funct Integ Genom 22(6):1283–1295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-022-00917-w
Acknowledgements
We sincerely acknowledge Dr. Ajay Jajodia for the help with e-CLIP data analysis and for critically reading the manuscript. S.R.B. acknowledges fellowship from the research project SERB (EEQ/2018/000022), India, M.S. acknowledges junior research fellowship from the university grant commission (UGC) India. S.L.L.D acknowledges a fellowship from the institute (Ministry of Education, India).
Funding
Santosh Kumar acknowledges the research funding from SERB (EEQ/2018/000022), India, and ICMR (F. no.: 52/23/2020-BIO/BMS) research projects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Santosh Kumar did the conception of the study, analyzed the data, and critically reviewed and edited the manuscript. S.R.B. did the data collection, data analysis, experimentation, and manuscript writing. M.S. did the data analysis and manuscript writing. S.L.L.D drew the figures. S.K. helped in sample preparation. Santosh Kumar, S.M., and A.K. revised the article critically for important intellectual content.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent to publish
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Biswal, S.R., Singh, M., Dwibedy, S.L.L. et al. Deciphering the RNA-binding protein interaction with the mRNAs encoded from human chromosome 15q11.2 BP1-BP2 microdeletion region. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 174 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01105-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01105-0