Abstract
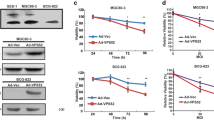
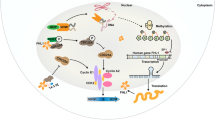
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is insidious and highly malignant with extremely poor prognosis and drug resistance to current chemotherapies. Therefore, there is a critical need to investigate the molecular mechanism underlying PDAC progression to develop promising diagnostic and therapeutic interventions. In parallel, vacuolar protein sorting (VPS) proteins, involved in the sorting, transportation, and localization of membrane proteins, have gradually attracted the attention of researchers in the development of cancers. Although VPS35 has been reported to promote carcinoma progression, the specific molecular mechanism is still unclear. Here, we determined the impact of VPS35 on the tumorigenesis of PDAC and explored the underlying molecular mechanism. We performed a pan-cancer analysis of 46 VPS genes using RNAseq data from GTEx (control) and TCGA (tumor) and predicted potential functions of VPS35 in PDAC by enrichment analysis. Furthermore, cell cloning experiments, gene knockout, cell cycle analysis, immunohistochemistry, and other molecular and biochemical experiments were used to validate the function of VPS35. Consequently, VPS35 was found overexpressed in multiple cancers and correlated with the poor prognosis of PDAC. Meanwhile, we verified that VPS35 could modulate the cell cycle and promote tumor cell growth in PDAC. Collectively, we provide solid evidence that VPS35 facilitates the cell cycle progression as a critical novel target in PDAC clinical therapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets presented in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
16 May 2024
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-024-01383-2
Notes
Cancer Research UK, (2022). Pancreatic cancer mortality statistics. http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/cancer-info/cancerstats/types/pancreas/mortality [Accessed December 13, 2022].
References
Adamska A, Domenichini A, Falasca M (2017) Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: current and evolving therapies. Int J Mol Sci 18:1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071338
An CH, Kim YR, Kim HS et al (2012) Frameshift mutations of vacuolar protein sorting genes in gastric and colorectal cancers with microsatellite instability. Hum Pathol 43:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2010.03.015
Bonifacino JS, Hurley JH (2008) Retromer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20:427–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2008.03.009
Chen Z, Peng P, Zhang X et al (2021) Advanced pediatric diffuse pontine glioma murine models pave the way towards precision medicine. Cancers 13:1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051114
Chen T, Tu Y, Lv D et al (2022) Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 72 homolog (VPS72) binding to lysine acetyltransferase 5 (KAT5) promotes the proliferation, invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathway. Bioengineered 13:9197–9210. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2056692
Choy RW-Y, Park M, Temkin P et al (2014) Retromer mediates a discrete route of local membrane delivery to dendrites. Neuron 82:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.02.018
Dursun A, Yalnizoglu D, Gerdan OF et al (2017) A probable new syndrome with the storage disease phenotype caused by the VPS33A gene mutation. Clin Dysmorphol 26:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCD.0000000000000149
Dyczynski M, Yu Y, Otrocka M et al (2018) Targeting autophagy by small molecule inhibitors of vacuolar protein sorting 34 (Vps34) improves the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to sunitinib. Cancer Lett 435:32–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.07.028
Ediriweera MK, Tennekoon KH, Samarakoon SR (2019) Role of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in ovarian cancer: biological and therapeutic significance. Semin Cancer Biol 59:147–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.05.012
Furukawa T, Kuboki Y, Tanji E et al (2011) Whole-exome sequencing uncovers frequent GNAS mutations in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Sci Rep 1:161. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00161
Goel S, Bergholz JS, Zhao JJ (2022) Targeting CDK4 and CDK6 in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 22:356–372. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-022-00456-3
Grossberg AJ, Chu LC, Deig CR et al (2020) Multidisciplinary standards of care and recent progress in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. CA Cancer J Clin 70:375–403. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21626
Hidalgo M, Cascinu S, Kleeff J et al (2015) Addressing the challenges of pancreatic cancer: future directions for improving outcomes. Pancreatology 15:8–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2014.10.001
Horning AM, Wang Y, Lin C-K et al (2018) Single-cell RNA-seq reveals a subpopulation of prostate cancer cells with enhanced cell-cycle-related transcription and attenuated androgen response. Cancer Res 78:853–864. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1924
Hua H, Kong Q, Zhang H et al (2019) Targeting mTOR for cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol 12:71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0754-1
Jiang D, Hu B, Wei L et al (2015) High expression of vacuolar protein sorting 4B (VPS4B) is associated with accelerated cell proliferation and poor prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract 211:240–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2014.11.013
Kent LN, Leone G (2019) The broken cycle: E2F dysfunction in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 19:326–338. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-019-0143-7
Kent LN, Bae S, Tsai S-Y et al (2017) Dosage-dependent copy number gains in E2f1 and E2f3 drive hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Invest 127:830–842. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI87583
Kim LC, Cook RS, Chen J (2017) mTORC1 and mTORC2 in cancer and the tumor microenvironment. Oncogene 36:2191–2201. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.363
Lan W, Bian B, Xia Y et al (2018) E2F signature is predictive for the pancreatic adenocarcinoma clinical outcome and sensitivity to E2F inhibitors, but not for the response to cytotoxic-based treatments. Sci Rep 8:8330. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-26613-z
Laviano A, Meguid MM, Inui A et al (2005) Therapy insight: cancer anorexia-cachexia syndrome–when all you can eat is yourself. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2:158–165. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncponc0112
Liu Y, Lv L, Xue Q et al (2013) Vacuolar protein sorting 4B, an ATPase protein positively regulates the progression of NSCLC via promoting cell division. Mol Cell Biochem 381:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1699-2
Malumbres M, Barbacid M (2009) Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer 9:153–166. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2602
Montemagno C, Cassim S, De Leiris N et al (2021) Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: the dawn of the era of nuclear medicine? Int J Mol Sci 22:6413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126413
Morita E, Colf LA, Karren MA et al (2010) Human ESCRT-III and VPS4 proteins are required for centrosome and spindle maintenance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:12889–12894. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1005938107
Mossmann D, Park S, Hall MN (2018) mTOR signalling and cellular metabolism are mutual determinants in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 18:744–757. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-018-0074-8
Oshi M, Newman S, Tokumaru Y et al (2020) High G2M pathway score pancreatic cancer is associated with worse survival, particularly after margin-positive (R1 or R2) resection. Cancers (basel) 12:2871. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102871
Popova NV, Jücker M (2021) The role of mTOR signaling as a therapeutic target in cancer. Int J Mol Sci 22:1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041743
Rahman AA, Morrison BE (2019) Contributions of VPS35 mutations to Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 401:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.01.006
Sanderson LE, Lanko K, Alsagob M et al (2021) Bi-allelic variants in HOPS complex subunit VPS41 cause cerebellar ataxia and abnormal membrane trafficking. Brain 144:769–780. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awaa459
Schmidt O, Teis D (2012) The ESCRT machinery. Curr Biol 22:R116-120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2012.01.028
Seaman MNJ (2012) The retromer complex - endosomal protein recycling and beyond. J Cell Sci 125:4693–4702. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.103440
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O et al (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1239303
Small SA, Kent K, Pierce A et al (2005) Model-guided microarray implicates the retromer complex in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 58:909–919. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.20667
Sørensen CS, Syljuåsen RG, Falck J et al (2003) Chk1 regulates the S phase checkpoint by coupling the physiological turnover and ionizing radiation-induced accelerated proteolysis of Cdc25A. Cancer Cell 3:247–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00048-5
Stark GR, Taylor WR (2004) Analyzing the G2/M checkpoint. Methods Mol Biol 280:51–82. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-788-2:051
Tang J, Ji L, Wang Y et al (2015) Cell adhesion down-regulates the expression of vacuolar protein sorting 4B (VPS4B) and contributes to drug resistance in multiple myeloma cells. Int J Hematol 102:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-015-1783-3
Tsika E, Glauser L, Moser R et al (2014) Parkinson’s disease-linked mutations in VPS35 induce dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Hum Mol Genet 23:4621–4638. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddu178
Vermeulen K, Van Bockstaele DR, Berneman ZN (2003) The cell cycle: a review of regulation, deregulation and therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Prolif 36:131–149. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2184.2003.00266.x
Wang G, Li Y, Zhu H et al (2020) Circ-PRKDC Facilitates the progression of colorectal cancer through miR-198/DDR1 regulatory axis. Cancer Manag Res 12:12853–12865. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S273484
Williams ET, Chen X, Moore DJ (2017) VPS35, the retromer complex and Parkinson’s disease. JPD 7:219–233. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-161020
Wu P, Zhou D, Wang Y et al (2019) Identification and validation of alternative splicing isoforms as novel biomarker candidates in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 41:1929–1937. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6947
Xu Z, Zhang F, Bai C et al (2017) Sophoridine induces apoptosis and S phase arrest via ROS-dependent JNK and ERK activation in human pancreatic cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36:124. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0590-5
Yu G, Wang L-G, Han Y, He Q-Y (2012) clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 16:284–287. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2011.0118
Zanazzi G, Liechty BL, Pendrick D, et al 2020 Diffuse midline glioma with novel potentially targetable FGFR2-VPS35 fusion Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud 6 a005660 https://doi.org/10.1101/mcs.a005660
Zhang G, Tang X, Liang L et al (2020) DNA and RNA sequencing identified a novel oncogene VPS35 in liver hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 39:3229–3244. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-1215-6
Zhang B, Ma Y, Niu H, Liu Z (2022) Overexpression of VPS16 correlates with tumor progression and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 607:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.03.139
Zhao T, Sun Q, del Rincon SV et al (2014) Gallotannin imposes S phase arrest in breast cancer cells and suppresses the growth of triple-negative tumors in vivo. PLoS One 9:e92853. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0092853
Zhou M, Wiener H, Su W et al (2016) VPS35 binds farnesylated N-Ras in the cytosol to regulate N-Ras trafficking. J Cell Biol 214:445–458. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201604061
Zimprich A, Benet-Pagès A, Struhal W et al (2011) A mutation in VPS35, encoding a subunit of the retromer complex, causes late-onset Parkinson disease. Am J Hum Genet 89:168–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.06.008
Acknowledgements
We appreciated the generosity of Professor Cun Wang in providing the plasmid. We thanked the public databases TCGA, GTEx, and GEO for data collection.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no.82273228 and no. 82173153).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HL, MM, and HN initiated the concept and reviewed the manuscript. YG, LQ, HP, YL, HW, SH, and SZ performed the experiments. HL analyzed the RNAseq data. SJ, JL, XZ, and XY supervised this study. YG and LQ wrote the draft of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the manuscript revision and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University (approval number RA-2021–295).
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Yanzhi Gai and Liheng Qian contributed equally to this work.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-024-01383-2
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gai, Y., Qian, L., Jiang, S. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Vacuolar protein sorting 35 (VPS35) acts as a tumor promoter via facilitating cell cycle progression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 90 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01020-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01020-4