Abstract
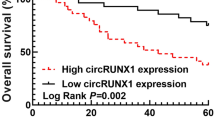
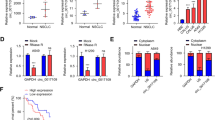
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) represents the subtype of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), with the high morbidity over the world. Mounting studies have highlighted the important roles of circular RNAs (circRNA) in cancers, including LUAD. This study mainly focused on revealing the role of circGRAMD1B and its relevant regulatory mechanism in LUAD cells. RT-qPCR and Western blot were conducted to detect the expression of target genes. Function assays were performed to determine the effect of related genes on migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of LUAD cells. Mechanism analyses were conducted to figure out the specific mechanism with regard to circGRAMD1B and its downstream molecules as well. Based on the experimental results, circGRAMD1B was upregulated in LUAD cells and promoted the migration, invasion, and EMT of LUAD cells. Mechanically, circGRAMD1B sponged miR-4428 to upregulate the expression of SOX4. In addition, SOX4 activated the expression of MEX3A at the transcriptional level, thereby modulating PI3K/AKT pathway to facilitate LUAD cell malignant behaviors. In conclusion, circGRAMD1B is discovered to modulate miR-4428/SOX4/MEX3A axis to further activate PI3K/AKT pathway, finally boosting migration, invasion, and EMT of LUAD cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Chen T, Yang Y (2019) [Role of circular RNA in diagnosis, development and durg resistance of lung cancer]. Zhongguo fei ai za zhi = Chin J Lung Cancer 22:532–536
Chen L, Nan A, Zhang N, Jia Y, Li X, Ling Y, Dai J, Zhang S, Yang Q, Yi Y, Jiang Y (2019) Circular RNA 100146 functions as an oncogene through direct binding to miR-361-3p and miR-615-5p in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer 18:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0943-0
Chen R, Xu X, Qian Z, Zhang C, Niu Y, Wang Z, Sun J, Zhang X, Yu Y (2019) The biological functions and clinical applications of exosomes in lung cancer. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences : CMLS 76:4613–4633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03233-y
Dai X, Guo X, Liu J, Cheng A, Peng X, Zha L, Wang Z (2019) Circular RNA circGRAMD1B inhibits gastric cancer progression by sponging miR-130a-3p and regulating PTEN and p21 expression. Aging 11:9689–9708. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102414
Dams RV, Yuan Y, Robinson CG, Lee P (2020) Immunotherapy and radiation therapy for non-small cell lung cancer-a stimulating partnership. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 41:360–368. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-3399578
Fu Y, Huang L, Tang H, Huang R (2020) hsa_circRNA_012515 is highly expressed in NSCLC patients and affects its prognosis. Cancer Manag Res 12:1877–1886. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.S245525
Gao N, Ye B (2020) Circ-SOX4 drives the tumorigenesis and development of lung adenocarcinoma via sponging miR-1270 and modulating PLAGL2 to activate WNT signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int 20:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-1065-x
Guan Y, Ren M, Guo D, He Y (2020) Research progress on lung cancer screening. Zhongguo fei ai za zhi = Chinese Journal of Lung Cancer 23:954–960. https://doi.org/10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2020.101.37
Hanieh H, Ahmed EA, Vishnubalaji R, Alajez NM (2020) SOX4: epigenetic regulation and role in tumorigenesis. Semin Cancer Biol 67:91–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.06.022
Howlader N, Forjaz G, Mooradian MJ, Meza R, Kong CY, Cronin KA, Mariotto AB, Lowy DR, Feuer EJ (2020) The effect of advances in lung-cancer treatment on population mortality. N Engl J Med 383:640–649. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1916623
Huang Q, Guo H, Wang S, Ma Y, Chen H, Li H, Li J, Li X, Yang F, Qiu M, Zhao S, Wang J (2020) A novel circular RNA, circXPO1, promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression by interacting with IGF2BP1. Cell Death Dis 11:1031. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03237-8
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J (2019) The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet 20:675–691. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-019-0158-7
Lei B, Tian Z, Fan W, Ni B (2019) Circular RNA: a novel biomarker and therapeutic target for human cancers. Int J Med Sci 16:292–301. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.28047
Lei M, Zheng G, Ning Q, Zheng J, Dong D (2020) Translation and functional roles of circular RNAs in human cancer. Mol Cancer 19:30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-1135-7
Li S, Sun X, Miao S, Lu T, Wang Y, Liu J, Jiao W (2018) hsa_circ_0000729, a potential prognostic biomarker in lung adenocarcinoma. Thoracic Cancer 9:924–930. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.12761
Li L, Liu J, Xue H, Li C, Liu Q, Zhou Y, Wang T, Wang H, Qian H, Wen T (2020) A TGF-β-MTA1-SOX4-EZH2 signaling axis drives epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tumor metastasis. Oncogene 39:2125–2139. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-1132-8
Liang J, Li H, Han J, Jiang J, Wang J, Li Y, Feng Z, Zhao R, Sun Z, Lv B, Tian H (2020) Mex3a interacts with LAMA2 to promote lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell Death Dis 11:614. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-02858-3
Liu M, Wang P, Sui X, Ding F, Liu L, Gao Z, Cheng Z (2020) Circular RNA circABCC4 regulates lung adenocarcinoma progression via miR-3186-3p/TNRC6B axis. J Cell Biochem 121:4226–4238. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29627
Moreno CS (2020) SOX4: The unappreciated oncogene. Semin Cancer Biol 67:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.08.027
Peng P, Zhang B, Huang J, Xing C, Liu W, Sun C, Guo W, Yao S, Ruan W, Ning G, Kong X, Feng S (2020) Identification of a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network to explore the effects of circRNAs on pathogenesis and treatment of spinal cord injury. Life Sci 257:118039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118039
Qu Y, Cheng B, Shao N, Jia Y, Song Q, Tan B, Wang J (2020) Prognostic value of immune-related genes in the tumor microenvironment of lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma. Aging 12:4757–4777. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102871
Rajai N, Ghanbari A, Yoosefi M, Mohebi F, Mohajer B, Sheidaei A, Gohari K, Masinaei M, Haghshenas R, Kompani F, Vaezi M, Farzadfar F (2020) National and subnational trends in incidence and mortality of lung cancer in Iran from 1990 to 2016. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 16:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajco.13303
Relli V, Trerotola M, Guerra E, Alberti S (2019) Abandoning the notion of non-small cell lung cancer. Trends Mol Med 25:585–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2019.04.012
Sayeeram D, Katte TV, Bhatia S, Jai Kumar A, Kumar A, Jayashree G, Rachana DS, Nalla Reddy HV, Arvind Rasalkar A, Malempati RL, Reddy SD (2020) Identification of potential biomarkers for lung adenocarcinoma. Heliyon 6:e05452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05452
Sun GZ, Zhao TW (2019) Lung adenocarcinoma pathology stages related gene identification. Math Biosci Eng : MBE 17:737–746. https://doi.org/10.3934/mbe.2020038
Wang Y (2021) circ-ANXA7 facilitates lung adenocarcinoma progression via miR-331/LAD1 axis. Cancer Cell Int 21:85. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-021-01791-5
Wang Q, Li M, Yang M, Yang Y, Song F, Zhang W, Li X, Chen K (2020) Analysis of immune-related signatures of lung adenocarcinoma identified two distinct subtypes: implications for immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Aging 12:3312–3339. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102814
Xue YB, Ding MQ, Xue L, Luo JH (2019) CircAGFG1 sponges miR-203 to promote EMT and metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer by upregulating ZNF281 expression. Thorac Cancer 10:1692–1701. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.13131
Xu Z, Wu Z, Xu J, Zhang J, Yu B (2020) Identification of hub driving genes and regulators of lung adenocarcinoma based on the gene Co-expression network. Biosci Rep 30;40(4). https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20200295
Yao Y, Hua Q, Zhou Y, Shen H (2019) CircRNA has_circ_0001946 promotes cell growth in lung adenocarcinoma by regulating miR-135a-5p/SIRT1 axis and activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother = Biomed Pharmacotherapie 111:1367–1375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.120
Zhang SB, Lin SY, Liu M, Liu CC, Ding HH, Sun Y, Ma C, Guo RX, Lv YY, Wu SL, Xu T, Xin WJ (2019) CircAnks1a in the spinal cord regulates hypersensitivity in a rodent model of neuropathic pain. Nat Commun 10:4119. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12049-0
Zhang P, Xue XF, Ling XY, Yang Q, Yu Y, Xiao J, Wang ZN (2020) CircRNA_010763 promotes growth and invasion of lung cancer through serving as a molecular sponge of miR-715 to induce c-Myc expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24:7310–7319. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202007_21892
Zhang SJ, Ma J, Wu JC, Hao ZZ, Zhang YN, Zhang YJ (2020) CircRNA EPB41L2 inhibits tumorigenicity of lung adenocarcinoma through regulating CDH4 by miR-211–5p. Europ Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24:3749–3760. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202004_20839
Zhu J, Zhang X, Gao W, Hu H, Wang X, Hao D (2019) lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network in lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Mol Med Rep 20:3160–3174. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10569
Acknowledgements
All supports from participants in this research were undeniable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xingjun Liu administrated the whole research. Yi Wang and Guixing Zhou performed the experiments. Jinbo Zhou and Zhongmin Tian completed the figures. The paper was written by Jie Xu.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Wang, Y., Zhou, G. et al. circGRAMD1B contributes to migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma cells via modulating the expression of SOX4. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 75 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-00972-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-00972-x