Abstract
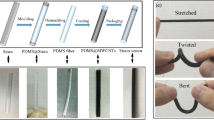
Although there has been rapid advancement in piezoelectric sensors, challenges still remain in developing wearable piezoelectric sensors by a one-step, continuous and environmentally friendly method. In this work, a 1D flexible coaxial piezoelectric fiber was directly fabricated by melt extrusion molding, whose core and sheath layer are respectively slender steel wire (i.e., electrode) and PVDF (i.e., piezoelectric layer). Moreover, such 1D flexible coaxial piezoelectric fiber possesses short response time and high sensitivity, which can be used as a self-powered sensor for bending and vibration sensing. More interestingly, such 1D flexible coaxial piezoelectric fiber (1D-PFs) can be further endowed with 3D helical structure. Moreover, a wearable and washable motion monitoring system can be constructed via braiding such 3D helical piezoelectric fiber (3D-PF) into commercial textiles. This work paves a new way for developing 1D and 3D piezoelectric fibers through a one-step, continuous and environmentally friendly method, showing potential applications in the field of sensing and wearable electronics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
He, X.; Zi, Y.; Guo, H.; Zheng, H.; Xi, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C.; Wang, Z. L. A highly stretchable fiber-based triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered wearable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604378.
Ning, C.; Dong, K.; Cheng, R.; Yi, J.; Ye, C.; Peng, X.; Sheng, F.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z. L. Flexible and stretchable fiber-shaped triboelectric nanogenerators for biomechanical monitoring and human-interactive sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2006679.
Dong, K.; Deng, J.; Ding, W.; Wang, A. C.; Wang, P.; Cheng, C.; Wang, Y. C.; Jin, L.; Gu, B.; Sun, B. Versatile core-sheath yarn for sustainable biomechanical energy harvesting and real-time human-interactive sensing. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1801114.
Song, Y.; Mukasa, D.; Zhang, H.; Gao, W. Self-powered wearable biosensors. Acc. Mater. Res. 2021, 2, 184–197.
Chen, S.; Huang, T.; Zuo, H.; Qian, S.; Guo, Y.; Sun, L.; Lei, D.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, B.; He, C. A single integrated 3D-printing process customizes elastic and sustainable triboelectric nanogenerators for wearable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1805108.
Wang, Z. L.; Wu, W. Nanotechnology-enabled energy harvesting for self-powered micro-/nanosystems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 11700–11721.
Ma, J.; Cui, Z.; Du, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, C.; Hou, C.; Zhu, N. Wearable fiber-eased supercapacitors enabled by additive-free aqueous MXene inks for self-powering healthcare sensors. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 1535–1544.
Pang, C.; Lee, G. Y.; Kim, T. I.; Kim, S. M.; Kim, H. N.; Ahn, S. H.; Suh, K. Y. A flexible and highly sensitive strain-gauge sensor using reversible interlocking of nanofibres. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 795–801.
Bai, P.; Zhu, G.; Jing, Q.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Su, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z. L. Membrane-based self-powered triboelectric sensors for pressure change detection and Its uses in security surveillance and healthcare monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5807–5813.
Peng, X.; Dong, K.; Ye, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wang Z. L. A breathable, biodegradable, antibacterial, and self-powered electronic skin based on all-nanofiber triboelectric nanogenerators. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba9624.
Wu, N.; Cheng, X.; Zhong, Q.; Zhong, J.; Li, W.; Wang, B.; Hu, B.; Zhou, J. Cellular polypropylene piezoelectret for human body energy harvesting and health monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4788–4794.
Garcia, C.; Trendafilova, I.; Guzman de Villoria, R.; Sanchez del Rio, J. Self-powered pressure sensor based on the triboelectric effect and its analysis using dynamic mechanical analysis. Nano Energy 2018, 50, 401–409.
Yang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, K.; Ma, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ji, H.; Qiu, J. PVDF-based composition-gradient multilayered nanocomposites for flexible high-performance piezoelectric nanogenerators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 11045–11054.
Xue, L.; Fan, W.; Yu, Y.; Dong, K.; Liu, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, W.; Lei, R.; Rong, K. A novel strategy to fabricate core-sheath structure piezoelectric yarns for wearable energy harvesters. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2021, 3, 239–250.
Song, J.; Chen, S.; Sun, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Xuan, H.; Guan, Q.; You, Z. Mechanically and electronically robust transparent organohydrogel fibers. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906994.
Scheffler, S.; Poulin, P. Piezoelectric fibers: processing and challenges. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 16961–16982.
Jeong, K.; Kim, D. H.; Chung, Y. S.; Hwang, S. K.; Hwang, H. Y.; Kim, S. S. Effect of processing parameters of the continuous wet spinning system on the crystal phase of PVDF fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45712.
Tascan, M.; Nohut, S. Effects of process parameters on the properties of wet-spun solid PVDF fibers. Text. Res. J. 2014, 84, 2214–2225.
Chapron, D.; Rault, F.; Talbourdet, A.; Lemort, G.; Cochrane, C.; Bourson, P.; Devaux, E.; Campagne, C. In-situ raman monitoring of the poly(vinylidene fluoride) crystalline structure during a melt-spinning process. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2021, 52, 1073–1079.
Lund, A.; Jonasson, C.; Johansson, C.; Haagensen, D.; Hagström, B. Piezoelectric polymeric bicomponent fibers produced by melt spinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 126, 490–500.
Ponnamma, D.; Chamakh, M. M.; Alahzm, A. M.; Salim, N.; Hameed, N.; AlMaadeed, M. A. A. Core-shell nanofibers of polyvinylidene fluoride-based nanocomposites as piezoelectric nanogenerators. Polymers (Basel) 2020, 12, 2344.
Luo, G.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, L.; Teh, K. S.; Jiang, Z. The radial piezoelectric response from three-dimensional electrospun PVDF micro wall structure. Materials 2020, 13, 1368.
Yang, Z.; Deng, J.; Chen, X.; Ren, J.; Peng, H. A highly stretchable, fiber-shaped supercapacitor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 13453–13457.
Zhao, Z.; Yan, C.; Liu, Z.; Fu, X.; Peng, L. M.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, Z. Machine-washable textile triboelectric nanogenerators for effective human respiratory monitoring through loom weaving of metallic yarns. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 10267–10274.
Dong, K.; Wang, Y. C.; Deng, J.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, S. L.; Zou, H.; Gu, B.; Sun, B.; Wang, Z. L. A highly stretchable and washable all-yarn-based self-charging knitting power textile composed of fiber triboelectric nanogenerators and supercapacitors. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9490–9499.
Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Lian, M.; Zheng, G.; Dai, K.; Guo, Z.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Continuous fabrication of polymer microfiber bundles with interconnected microchannels for oil/water separation. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 9, 77–81.
Zhao, L. J. Elastic behavior of LDPE/HEPE blend melts in capillary extrusion. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 78, 759–765.
Pokharel, P.; Bae, H.; Lim, J. G.; Lee, K. Y.; Choi, S. Effects of titanate treatment on morphology and mechanical properties of graphene nanoplatelets/high density polyethylene nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42073.
Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Ji, Y.; Dai, K.; Mi, L.; Zhang, D.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Microribbon structured polyvinylidene fluoride with high-performance piezoelectricity for sensing application. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 2411–2419.
Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, H.; Qin, W.; Liao, Y.; Yu, Q.; Cheng, H. Stretchable piezoelectric energy harvesters and self-powered sensors for wearable and implantable devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 168, 112569.
Lu, X.; Qu, H.; Skorobogatiy, M. Piezoelectric micro- and nanostructured fibers fabricated from thermoplastic nanocomposites using a fiber drawing technique: comparative study and potential applications. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2103–2114.
Lu, L.; Yang, B.; Zhai, Y.; Liu, J. Electrospinning core-sheath piezoelectric microfibers for self-powered stitchable sensor. Nano Energy 2020, 76, 104966.
Martins, R. S.; Gonçalves, R.; Azevedo, T.; Rocha, J. G.; Nόbrega, J. M.; Carvalho, H.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Piezoelectric coaxial filaments produced by coextrusion of poly(vinylidene fluoride) and electrically conductive inner and outer layers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40710.
Lin, J.; Malakooti, M. H.; Sodano, H. A. Thermally stable poly(vinylidene fluoride) for high-performance printable piezoelectric devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 21871–21882.
Karan, S. K.; Mandal, D.; Khatua, B. B. Self-powered flexible Fedoped RGO/PVDF nanocomposite: an excellent material for a piezoelectric energy harvester. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10655–10666.
Martins, P.; Lopes, A. C.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): determination, processing and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 683–706.
Deng, W.; Yang, T.; Jin, L.; Yan, C.; Huang, H.; Chu, X.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, D.; Tian, G.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, W. Cowpea-structured PVDF/ZnO nanofibers based flexible self-powered piezoelectric bending motion sensor towards remote control of gestures. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 516–525.
Peng, F.; Liu, D.; Zhao, W.; Zheng, G.; Ji, Y.; Dai, K.; Mi, L.; Zhang, D.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Facile fabrication of triboelectric nanogenerator based on low-cost thermoplastic polymeric fabrics for large-area energy harvesting and self-powered sensing. Nano Energy 2019, 65, 104068.
Wei, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, T. A fully hydrophobic ionogel enables highly efficient wearable underwater sensors and communicators. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 2761–2770.
Zhang, Y.; Gao, M.; Gao, C.; Zheng, G.; Ji, Y.; Dai, K.; Mi, L.; Zhang, D.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Facile preparation of micropatterned thermoplastic surface for wearable capacitive sensor. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2023, 232, 109863.
Su, T.; Liu, N.; Lei, D.; Wang, L.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Su, J.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y. Flexible MXene/bacterial cellulose film sound detector based on piezoresistive sensing mechanism. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 8461–8471.
Woo, J.; Lee, H.; Yi, C.; Lee, J.; Won, C.; Oh, S.; Jekal, J.; Kwon, C.; Lee, S.; Song, J.; et al. Ultrastretchable helical conductive fibers using percolated Ag nanoparticle networks encapsulated by elastic polymers with high durability in omnidirectional deformations for wearable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910026.
Chen, S.; Sun, L.; Zhou, X.; Guo, Y.; Song, J.; Qian, S.; Liu, Z.; Guan, Q.; Meade Jeffries, E.; Liu, W. Mechanically and biologically skinlike elastomers for bio-integrated electronics. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1107.
Sun, L.; Huang, H.; Ding, Q.; Guo, Y.; Sun, W.; Wu, Z.; Qin, M.; Guan, Q.; You, Z. Highly transparent, stretchable, and self-healable ionogel for multifunctional sensors, triboelectric nanogenerator, and wearable fibrous electronics. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 98–107.
Yan, T.; Zhou, H.; Niu, H.; Shao, H.; Wang, H.; Pan, Z.; Lin, T. Highly sensitive detection of subtle movement using a flexible strain sensor from helically wrapped carbon yarns. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 10049–10058.
Xiong, J.; Cui, P.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Parida, K.; Lin, M. F.; Lee, P. S. Skin-touch-actuated textile-based triboelectric nanogenerator with black phosphorus for durable biomechanical energy harvesting. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4280.
Fan, W. J.; He, Q.; Meng, K. Y.; Tan, X. L.; Zhou, Z. H.; Zhang, G. Q.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z. L. Machine-knitted washable sensor array textile for precise epidermal physiological signal monitoring. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay2840.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.51873199) and Program for Innovative Research Team (in Science and Technology) in University (No.20IRTSTHN002) Furthermore, we also express our great thanks to Shiyanjia Lab for the support of SEM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no interest conflict.
Electronic Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gui, SS., Da, BX., Peng, F. et al. One-step and Continuous Fabrication of Coaxial Piezoelectric Fiber for Sensing Application. Chin J Polym Sci 41, 1778–1785 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-023-2960-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-023-2960-0