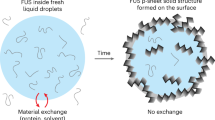
Abstract
Liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) or biomolecular condensation that leads to formation of membraneless organelles plays a critical role in many biochemical processes. Mechanism study of regulating LLPS is therefore central to the understanding of protein aggregation and disease-relevant process. We report a fused in sarcoma protein (FUS)-derived low complexity (LC) sequence that undergoes LLPS in the presence of metal ions. The LC protein was constructed by fusing a hexhistidine-tag to the N-terminal low complexity domain (the residues 1–165 in QGSY-rich segment) of FUS. Spontaneous condensation of the intrinsic disordered protein into coacervate droplets was observed in the presence of metal ions that chelate oligohistidine moieties to form protein matrix. We demonstrate the key role of metal ion-histidine coordination in governing LLPS behaviours and the fluidity of biomolecular condensates. By taking advantage of competitive binding using chelators, we show the possibility of regulating dynamic behaviors of disease-relevant protein droplets, and developing a potential approach towards controllable biological encapsulation/release.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koga, S.; Williams, D. S.; Perriman, A. W.; Mann, S. Peptide-nucleotide microdroplets as a step towards a membrane-free protocell model. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 720–724.
Qiao, Y.; Li, M.; Qiu, D.; Mann, S. Response-retaliation behavior in synthetic protocell communities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17758–17763.
Liu, Z.; Ji, Y.; Mu, W.; Liu, X.; Huang, L. Y.; Ding, T.; Qiao, Y. Coacervate microdroplets incorporating J-aggregates toward photoactive membraneless protocells. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 2536–2539.
Ji, Y.; Mu, W.; Wu, H.; Qiao, Y. Directing transition of synthetic protocell models via physicochemical cues-triggered interfacial dynamic covalent chemistry. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2101187.
Jia, L.; Ji, Z.; Ji, Y. M.; Zhou, C.; Xing, G. W.; Qiao, Y. Design and fluorescence localization of lipid-rich domains in multiphase coacervate droplets based on AIE-active molecules. ChemSystemsChem 2020, 3, e2000044.
Qiao, Y.; Li, M.; Booth, R.; Mann, S. Predatory behaviour in synthetic protocell communities. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 110–119.
Mu, W.; Ji, Z.; Zhou, M.; Wu, J.; Lin, Y.; Qiao, Y. Membrane-confined liquid-liquid phase separation toward artificial organelles. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf9000.
A. I. Oparin, A. S. The origin of life on the earth. Academic Press, New York, 1957.
Yin, Y.; Niu, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Mann, S.; Liang, D. Non-equilibrium behaviour in coacervate-based protocells under electric-field-induced excitation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10658.
Alberti, S.; Gladfelter, A.; Mittag, T. Considerations and challenges in studying liquid-liquid phase separation and biomolecular condensates. Cell 2019, 176, 419–434.
Iglesias-Artola, J. M.; Drobot, B.; Kar, M.; Fritsch, A. W.; Mutschler, H.; Dora Tang, T. Y.; Kreysing, M. Charge-density reduction promotes ribozyme activity in RNA-peptide coacervates via RNA fluidization and magnesium partitioning. Nat. Chem. 2022, 14, 1–10.
Weber, S. C.; Brangwynne, C. P. Inverse size scaling of the nucleolus by a concentration-dependent phase transition. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 641–646.
Gall, J. G. The centennial of the Cajal body. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 975–980.
Lamond, A. I.; Spector, D. L. Nuclear speckles: a model for nuclear organelles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 605–612.
Anderson, P.; Kedersha, N. Stress granules. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 397–398.
Decker, C. J.; Parker, R. P-bodies and stress granules: possible roles in the control of translation and mRNA degradation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a012286.
Shin, Y.; Brangwynne, C. P. Liquid phase condensation in cell physiology and disease. Science 2017, 357, eaaf4382.
Courtney, A. H.; Lo, W. L.; Weiss, A. TCR signaling: mechanisms of initiation and propagation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2018, 43, 108–123.
Gibson, B. A.; Doolittle, L. K.; Schneider, M. W.; Jensen, L. E.; Gamarra, N.; Henry, L.; Gerlich, D. W.; Redding, S.; Rosen, M. K. Organization of chromatin by intrinsic and regulated phase separation. Cell 2019, 179, 470–484.
Sabari, B. R.; Dall’Agnese, A.; Boija, A.; Klein, I. A.; Coffey, E. L.; Shrinivas, K.; Abraham, B. J.; Hannett, N. M.; Zamudio, A. V.; Manteiga, J. C. Coactivator condensation at super-enhancers links phase separation and gene control. Science 2018, 361, eaar3958.
Tang, T. D.; Hak, C. R. C.; Thompson, A. J.; Kuimova, M. K.; Williams, D.; Perriman, A. W.; Mann, S. Fatty acid membrane assembly on coacervate microdroplets as a step towards a hybrid protocell model. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 527–533.
Aumiller, W. M.; Keating, C. D. Phosphorylation-mediated RNA/peptide complex coacervation as a model for intracellular liquid organelles. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 129–137.
Mason, A. F.; Buddingh’, B. C.; Williams, D. S.; Van Hest, J. C. Hierarchical self-assembly of a copolymer-stabilized coacervate protocell. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17309–17312.
Love, C.; Steinkühler, J.; Gonzales, D. T.; Yandrapalli, N.; Robinson, T.; Dimova, R.; Tang, T. Y. D. Reversible pH-responsive coacervate formation in lipid vesicles activates dormant enzymatic reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 5950–5957.
Simon, J. R.; Eghtesadi, S. A.; Dzuricky, M.; You, L.; Chilkoti, A. Engineered ribonucleoprotein granules inhibit translation in protocells. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 66–75.
Peeples, W.; Rosen, M. K. Mechanistic dissection of increased enzymatic rate in a phase-separated compartment. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2021, 17, 693–702.
Abbas, M.; Lipiński, W. P.; Nakashima, K. K.; Huck, W. T.; Spruijt, E. A short peptide synthon for liquid-liquid phase separation. Nat. Chem. 2021, 13, 1046–1054.
Fung, H. Y. J.; Birol, M.; Rhoades, E. IDPs in macromolecular complexes: the roles of multivalent interactions in diverse assemblies. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2018, 49, 36–43.
Martin, E. W.; Mittag, T. Relationship of sequence and phase separation in protein low-complexity regions. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 2478–2487.
Murthy, A. C.; Tang, W. S.; Jovic, N.; Janke, A. M.; Seo, D. H.; Perdikari, T. M.; Mittal, J.; Fawzi, N. L. Molecular interactions contributing to FUS SYGQ LC-RGG phase separation and co-partitioning with RNA polymerase II heptads. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2021, 28, 923–935.
Wang, J.; Choi, J.-M.; Holehouse, A. S.; Lee, H. O.; Zhang, X.; Jahnel, M.; Maharana, S.; Lemaitre, R.; Pozniakovsky, A.; Drechsel, D. A molecular grammar governing the driving forces for phase separation of prion-like RNA binding proteins. Cell 2018, 174, 688–699.
Sreedharan, J.; Blair, I. P.; Tripathi, V. B.; Hu, X.; Vance, C.; Rogelj, B.; Ackerley, S.; Durnall, J. C.; Williams, K. L.; Buratti, E. TDP-43 mutations in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 2008, 319, 1668–1672.
Neumann, M.; Sampathu, D. M.; Kwong, L. K.; Truax, A. C.; Micsenyi, M. C.; Chou, T. T.; Bruce, J.; Schuck, T.; Grossman, M.; Clark, C. M. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 2006, 314, 130–133.
Gu, J.; Wang, C.; Hu, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, D.; Fang, Y.; Liu, C. Hsp70 chaperones TDP-43 in dynamic, liquid-like phase and prevents it from amyloid aggregation. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 1024–1027.
Guo, T.; Noble, W.; Hanger, D. P. Roles of tau protein in health and disease. Acta Neuropathologica 2017, 133, 665–704.
Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. Q.; Jia, C.; Lim, Y. J.; Feng, G.; Xu, E.; Long, H.; Kimura, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhao, C. Mechanistic basis for receptor-mediated pathological α-synuclein fibril cell-to-cell transmission in Parkinson’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2021, 118, e2011196118.
Sun, Y.; Hou, S.; Zhao, K.; Long, H.; Liu, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Su, X. D.; Li, D.; Liu, C. Cryo-EM structure of full-length a-synuclein amyloid fibril with Parkinson’s disease familial A53T mutation. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 360–362.
Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Gu, J.; Tong, Y.; Li, Y.; Gui, X.; Long, H.; Wang, C.; Zhao, C.; Lu, J. Hsp27 chaperones FUS phase separation under the modulation of stress-induced phosphorylation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 363–372.
Luo, F.; Gui, X.; Zhou, H.; Gu, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, M.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Liu, C. Atomic structures of FUS LC domain segments reveal bases for reversible amyloid fibril formation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 341–346.
Patel, A.; Lee, H. O.; Jawerth, L.; Maharana, S.; Jahnel, M.; Hein, M. Y.; Stoynov, S.; Mahamid, J.; Saha, S.; Franzmann, T. M. A liquid-to-solid phase transition of the ALS protein FUS accelerated by disease mutation. Cell 2015, 162, 1066–1077.
Masuda, A.; Takeda, J.-i.; Okuno, T.; Okamoto, T.; Ohkawara, B.; Ito, M.; Ishigaki, S.; Sobue, G.; Ohno, K. Position-specific binding of FUS to nascent RNA regulates mRNA length. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1045–1057.
Dini Modigliani, S.; Morlando, M.; Errichelli, L.; Sabatelli, M.; Bozzoni, I. An ALS-associated mutation in the FUS 3′-UTR disrupts a microRNA-FUS regulatory circuitry. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–7.
Levone, B. R.; Lenzken, S. C.; Antonaci, M.; Maiser, A.; Rapp, A.; Conte, F.; Reber, S.; Mechtersheimer, J.; Ronchi, A. E.; Mühlemann, O. FUS-dependent liquid-liquid phase separation is important for DNA repair initiation. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 220, e202008030.
Shelkovnikova, T. A.; Robinson, H. K.; Connor-Robson, N.; Buchman, V. L. Recruitment into stress granules prevents irreversible aggregation of FUS protein mislocalized to the cytoplasm. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 3383–3391.
Deng, H.; Gao, K.; Jankovic, J. The role of FUS gene variants in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 337–348.
Hofweber, M.; Dormann, D. Friend or foe—post-translational modifications as regulators of phase separation and RNP granule dynamics. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 7137–7150.
Kang, J.; Lim, L.; Song, J. ATP enhances at low concentrations but dissolves at high concentrations liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) of ALS/FTD-causing FUS. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 504, 545–551.
Fang, M. Y.; Markmiller, S.; Vu, A. Q.; Javaherian, A.; Dowdle, W. E.; Jolivet, P.; Bushway, P. J.; Castello, N. A.; Baral, A.; Chan, M. Y.; Linsley, J. W.; Linsley, D.; Mercola, M.; Finkbeiner, S.; Lecuyer, E.; Lewcock, J. W.; Yeo, G. W. Small-molecule modulation of TDP-43 recruitment to stress granules prevents persistent TDP-43 accumulation in ALS/FTD. Neuron 2019, 103, 802–819.
Babinchak, W. M.; Dumm, B. K.; Venus, S.; Boyko, S.; Putnam, A. A.; Jankowsky, E.; Surewicz, W. K. Small molecules as potent biphasic modulators of protein liquid-liquid phase separation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–15.
Guo, L.; Kim, H. J.; Wang, H.; Monaghan, J.; Freyermuth, F.; Sung, J. C.; O’Donovan, K.; Fare, C. M.; Diaz, Z.; Singh, N. Nuclear-import receptors reverse aberrant phase transitions of RNA-binding proteins with prion-like domains. Cell 2018, 173, 677–692.
Yang, L.; Gal, J.; Chen, J.; Zhu, H. Self-assembled FUS binds active chromatin and regulates gene transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2014, 111, 17809–17814.
Krainer, G.; Welsh, T. J.; Joseph, J. A.; Espinosa, J. R.; Wittmann, S.; de Csillery, E.; Sridhar, A.; Toprakcioglu, Z.; Gudiskyte, G.; Czekalska, M. A.; Arter, W. E.; Guillen-Boixet, J.; Franzmann, T. M.; Qamar, S.; George-Hyslop, P. S.; Hyman, A. A.; Collepardo-Guevara, R.; Alberti, S.; Knowles, T. P. J. Reentrant liquid condensate phase of proteins is stabilized by hydrophobic and non-ionic interactions. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–14.
Shi, C. Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, H.; Qu, D. H. Supramolecular adhesive materials from small-molecule self-assembly. SmartMat 2020, 1, e1012.
Mészáros, B.; Erdős, G.; Dosztányi, Z. IUPred2A: context-dependent prediction of protein disorder as a function of redox state and protein binding. Nucleic acids Res. 2018, 46, 329–337.
Qamar, S.; Wang, G.; Randle, S. J.; Ruggeri, F. S.; Varela, J. A.; Lin, J. Q.; Phillips, E. C.; Miyashita, A.; Williams, D.; Ströhl, F. FUS phase separation is modulated by a molecular chaperone and methylation of arginine cation-π interactions. Cell 2018, 173, 720–734.
Fvan Eldijk, M. B.; Schoonen, L.; Cornelissen, J. J.; Nolte, R. J.; van Hest, J. C. Metal ion-induced self-assembly of a multi-responsive block copolypeptide into well-defined nanocapsules. Small 2016, 12, 2476–2483.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22072159 and 22172007), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. buctrc202015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Notes
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., Lin, Y. & Qiao, Y. Regulating FUS Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation via Specific Metal Recognition. Chin J Polym Sci 40, 1043–1049 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-022-2763-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-022-2763-8