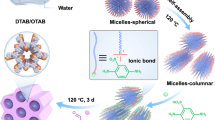
Abstract
Two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks (COFs) with specific morphologies including nanofibers and nanoplates are highly desired in both nanoscience research and practical applications. Thus far, however, morphology engineering for COFs remains challenging because the mechanism underlying the morphology formation and evolution of COFs is not well understood. Herein, we propose a strategy of surfactant mediation coupled with acid adjustment to engineer the morphology of a β-ketoenamine-linked COF, TpPa, during solvothermal synthesis. The surfactants function as stabilizers that can encapsulate monomers and prepolymers to create micelles, enabling the formation of fiber-like and plate-like morphologies of TpPa rather than irregularly shaped aggregates. It is also found that acetic acid is important in regulating such morphologies, as the amino groups inside the prepolymers can be precisely protonated by acid adjustment, leading to an inhibited ripening process for the creation of specific morphologies. Benefitting from the synergistic enhancement of surfactant mediation and acid adjustment, TpPa nanofibers with a diameter down to ∼20 nm along with a length of up to a few microns and TpPa nanoplates with a thickness of ∼18 nm are created. Our work sheds light on the mechanism underlying the morphology formation and evolution of TpPa, providing some guidance for exquisite control over the growth of COFs, which is of great significance for their practical applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, Z. F.; Zhang, S. N.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z. J.; Ma, S. Q. Covalent organic frameworks for separation applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 708–735.
Zhao, X. J.; Pachfule, P.; Thomas, A. Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) for electrochemical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 6871–6913.
Esrafili, A.; Wagner, A.; Inamdar, S.; Acharya, A. P. Covalent organic frameworks for biomedical applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2002090.
Zhu, D.; Xu, G.; Barnes, M.; Li, Y.; Tseng, C. P.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J. J.; Zhu, Y.; Khalil, S.; Rahman, M. M.; Verduzco, R.; Ajayan, P. M. Covalent organic frameworks for batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100505.
Iqbal, R.; Badshah, A.; Ma, Y. J.; Zhi, L. J. An electrochemically stable 2D covalent organic framework for high-performance organic supercapacitors. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 38, 558–564.
Gropp, C.; Canossa, S.; Wuttke, S.; Gandara, F.; Li, Q.; Gagliardi, L.; Yaghi, O. M. Standard practices of reticular chemistry. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 1255–1273.
Sun, D. W.; Huang, L. J.; Pu, H. B.; Ma, J. Introducing reticular chemistry into agrochemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 1070–1110.
Zhu, Y.; Shao, P.; Hu, L.; Sun, C.; Li, J.; Feng, X.; Wang, B. Construction of interlayer conjugated links in 2D covalent organic frameworks via topological polymerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 7897–7902.
Haase, F.; Lotsch, B. V. Solving the COF trilemma: towards crystalline, stable and functional covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 8469–8500.
Kandambeth, S.; Dey, K.; Banerjee, R. Covalent organic frameworks: chemistry beyond the structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 1807–1822.
Smith, B. J.; Overholts, A. C.; Hwang, N.; Dichtel, W. R. Insight into the crystallization of amorphous imine-linked polymer networks to 2D covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 3690–3693.
Huang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X. J.; Wang, J. Y.; Wu, Q.; Liu, X. K. Solvothermal synthesis of microporous, crystalline covalent organic framework nanofibers and their colorimetric nanohybrid structures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8845–8854.
Guan, Q.; Wang, G. B.; Zhou, L. L.; Li, W. Y.; Dong, Y. B. Nanoscale covalent organic frameworks as theranostic platforms for oncotherapy: synthesis, functionalization, and applications. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 3656–3733.
Tao, S.; Xu, H.; Xu, Q.; Hijikata, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Irle, S.; Jiang, D. Hydroxide anion transport in covalent organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 8970–8975.
Geng, K.; He, T.; Liu, R.; Dalapati, S.; Tan, K. T.; Li, Z.; Tao, S.; Gong, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Jiang, D. Covalent organic frameworks: design, synthesis, and functions. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8814–8933.
Liu, R.; Tan, K. T.; Gong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Xie, S.; He, T.; Lu, Z.; Yang, H.; Jiang, D. Covalent organic frameworks: an ideal platform for designing ordered materials and advanced applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 120–242.
Liu, W.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Pan, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, K.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, R.; Jiang, J. A scalable general synthetic approach toward ultrathin imine-linked two-dimensional covalent organic framework nanosheets for photocatalytic CO2 reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 17431–17440.
Zhao, W.; Wang, T. P.; Wu, J. L.; Pan, R. P.; Liu, X. Y.; Liu, X. K. Monolithic covalent organic framework aerogels through framework crystallization induced self-assembly: heading towards framework materials synthesis over all length scales. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 37, 1045–1052.
Das, G.; Benyettou, F.; Sharma, S. K.; Sharama, S. K.; Prakasam, T.; Gandara, F.; de la Pena-O’Shea, V. A.; Saleh, N.; Pasricha, R.; Jagannathan, R.; Olson, M. A.; Olson, A. Covalent organic nanosheets for bioimaging. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 8382–8387.
Peng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Lai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Tan, C.; Yang, N.; Shao, F.; Han, Y.; Zhang, H. Ultrathin two-dimensional covalent organic framework nanosheets: preparation and application in highly sensitive and selective DNA detection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 8698–8704.
Liu, Y. Y.; Li, X. C.; Wang, S.; Cheng, T.; Yang, H.; Liu, C.; Gong, Y.; Lai, W. Y.; Huang, W. Self-templated synthesis of uniform hollow spheres based on highly conjugated three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5561.
Wang, Y.; Xie, M.; Lan, J.; Yuan, L.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Peng, J.; Chai, Z.; Gibson, J. K.; Zhai, M.; Shi, W. Radiation controllable synthesis of robust covalent organic framework conjugates for efficient dynamic column extraction of 99TcO4−. Chem 2020, 6, 2796–2809.
Gole, B.; Stepanenko, V.; Rager, S.; Grüne, M.; Medina, D. D.; Bein, T.; Würthner, F.; Beuerle, F. Microtubular self-assembly of covalent organic frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 846–850.
Zhang, Z.; Shi, X. S.; Wang, R.; Xiao, A.; Wang, Y. Ultra-permeable polyamide membranes harvested by covalent organic framework nanofiber scaffolds: a two-in-one strategy. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 9077–9083.
Sun, Q.; Aguila, B.; Perman, J.; Earl, L. D.; Abney, C. W.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, H.; Nguyen, N.; Wojtas, L.; Ma, S. Postsynthetically modified covalent organic frameworks for efficient and effective mercury removal. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2786–2793.
Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B.; Tan, X.; Shao, D.; Shi, J.; Tan, D.; Liu, L.; Feng, J.; Han, B.; Yang, G.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, J. Room-temperature synthesis of covalent organic framework (COF-LZU1) nanobars in CO2/water solvent. ChemSusChem, 2018, 11, 3576–3580.
Yamada, H.; Urata, C.; Higashitamori, S.; Aoyama, Y.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kuroda, K. Critical roles of cationic surfactants in the preparation of colloidal mesostructured silica nanoparticles: control of mesostructure, particle size, and dispersion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 3491–3500.
Yang, H.; Coombs, N.; Ozin, G. A. Morphogenesis of shapes and surface patterns in mesoporous silica. Nature 1977, 386, 692–695.
Li, K.; Lin, S.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Gu, J. Aqueous-phase synthesis of mesoporous Zr-based MOFs templated by amphoteric surfactants. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3439–3443.
Alizadeh, S.; Nematollahi, D. Electrochemically assisted self-assembly technique for the fabrication of mesoporous metal-organic framework thin films: composition of 3D hexagonally packed crystals with 2D honeycomb-like mesopores. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 4753–4761.
Zhang, S.; Wu, X.; Ma, C.; Li, Y.; You, J. Cationic surfactant modified 3D COF and its application in the adsorption of UV filters and alkylphenols from food packaging material migrants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 3663–3669.
Sahabudeen, H.; Qi, H.; Ballabio, M.; Polozij, M.; Olthof, S.; Shivhare, R.; Jing, Y.; Park, S.; Liu, K.; Zhang, T.; Ma, J.; Rellinghaus, B.; Mannsfeld, S.; Heine, T.; Bonn, M.; Canovas, E.; Zheng, Z.; Kaiser, U.; Dong, R.; Feng, X. Highly crystalline and semiconducting imine-based two-dimensional polymers enabled by interfacial synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 6028–6036.
Poyraz, A. S.; Albayrak, C.; Dag, Ö. The effect of cationic surfactant and some organic/inorganic additives on the morphology of mesostructured silica templated by pluronics. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 115, 548–555.
Liang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, C.; Lee, K. R.; Hung, W. S.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Elimelech, M.; Jin, J.; Lin, S. Polyamide nanofiltration membrane with highly uniform sub-nanometre pores for sub-1 A precision separation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2015.
Franco, C.; Rodriguez-San-Miguel, D.; Sorrenti, A.; Sevim, S.; Pons, R.; Platero-Prats, A. E.; Pavlovic, M.; Szilagyi, I.; Ruiz Gonzalez, M. L.; Gonzalez-Calbet, J. M.; Bochicchio, D.; Pesce, L.; Pavan, G. M.; Imaz, I.; Cano-Sarabia, M.; Maspoch, D.; Pane, S.; de Mello, A. J; Zamora, F.; Puigmarti-Luis, J. Biomimetic synthesis of sub-20 nm covalent organic frameworks in water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 3540–3547.
Kandambeth, S.; Mallick, A.; Lukose, B. V.; Mane, M.; Heine, T.; Banerjee, R. Construction of crystalline 2D covalent organic frameworks with remarkable chemical (acid/base) stability via a combined reversible and irreversible route. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19524–19527.
Kong, D. Y.; Chen, Z. L. Covalent organic framework TpPa-1 as stationary phase for capillary electrochromatographic separation of drugs and food additives. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 2912–2918.
Li, Y.; Pei, B.; Chen, J.; Bing, S.; Hou, L.; Sun, Q.; Xu, G.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, L. Hollow nanosphere construction of covalent organic frameworks for catalysis: (Pd/C)@TpPa COFs in Suzuki coupling reaction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 591, 273–280.
Pérez-Carvajal, J.; Boix, G.; Imaz, I.; Maspoch, D. The Imine-based COF TpPa-1 as an efficient cooling adsorbent that can be regenerated by heat or light. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1901535.
Shi, X. S.; Ma, D. W.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y. Table-salt enabled interface-confined synthesis of covalent organic framework (COF) nanosheets. Chem. Sci. 2019, 11, 989–996.
Hu, X.; Jian, J.; Fang, Z.; Zhong, L.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, M.; Ren, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Yu, D. Hierarchical assemblies of conjugated ultrathin COF nanosheets for high-sulfur-loading and long-lifespan lithium-sulfur batteries: fully-exposed porphyrin matters. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 22, 40–47.
Tan, J.; Namuangruk, S.; Kong, W.; Kungwan, N.; Guo, J.; Wang, C. Manipulation of amorphous-to-crystalline transformation: towards the construction of covalent organic framework hybrid microspheres with NIR photothermal conversion ability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13979–13984.
Martin-Illan, J. A.; Rodriguez-San-Miguel, D.; Franco, C.; Imaz, I.; Maspoch, D.; Puigmarti-Luis, J.; Zamora, F. Green synthesis of imine-based covalent organic frameworks in water. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 6704–6707.
Sasmal, H. S.; Halder, A.; Kunjattu H. S.; Dey, K.; Nadol, A.; Ajithkumar, T. G.; Bedadur, P. R.; Banerjee, R. Covalent self-assembly in two dimensions: connecting covalent organic framework nanospheres into crystalline and porous thin films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 20371–20379.
Nguyen, H. L.; Gropp, C.; Yaghi, O. M. Reticulating 1D ribbons into 2D covalent organic frameworks by imine and imide linkages. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2771–2776.
Dong, W. L.; Li, S. Y.; Yue, J. Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, D.; Wan, L. J. Fabrication of bilayer tetrathiafulvalene integrated surface covalent organic frameworks. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 17356–17359.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21921006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Notes
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Electronic Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, GH., Zhang, Z., Yin, CC. et al. Morphology Engineering for Covalent Organic Frameworks (COFs) by Surfactant Mediation and Acid Adjustment. Chin J Polym Sci 40, 338–344 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-022-2676-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-022-2676-6