Abstract
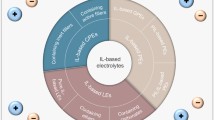
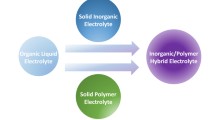
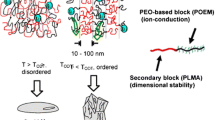
Ionic liquids (ILs) have appeared as the most promising electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries, owing to their unique high ionic conductivity, chemical stability and thermal stability properties. Poly(ionic liquid)s (PILs) with both IL-like characteristic and polymer structure are emerging as an alternative of traditional electrolyte. In this review, recent progresses on the applications of IL/PIL-based semi-solid state electrolytes, including gel electrolytes, ionic plastic crystal electrolytes, hybrid electrolytes and single-ion conducting electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu, J.; Yan, F.; Texter, J. Advanced applications of ionic liquids in polymer science. Prog. Polym. Sci.2009, 34, 431–448.
Qian, W.; Texter, J.; Yan, F. Frontiers in poly(ionic liquid)s: syntheses and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev.2017, 46, 1124–1159.
Etacheri, V.; Marom, R.; Elazari, R.; Salitra, G.; Aurbach, D. Challenges in the development of advanced Li-ion batteries: a review. Energy Environ. Sci.2011, 4, 3243–3262.
Tarascon, J.; Armand, M. Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature2001, 414, 359–367.
Scrosati, B. Recent advances in lithium ion battery materials. Electrochim. Acta2000, 45, 2461–2466.
Goodenough, J. B.; Kim, Y. Challenges for rechargeable batteries. J. Power Sources2011, 196, 6688–6694.
Cao, C.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Peng, C.; Li, Z.; Feng, W. A solid-state single-ion polymer electrolyte with ultrahigh ionic conductivity for dendrite-free lithium metal batteries. Energy Storage Mater.2019, 19, 401–407.
Cao, C.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Long, P.; An, H.; Qin, C.; Han, J.; Li, S.; Feng, W. A sulfonimide-based alternating copolymer as a single-ion polymer electrolyte for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A2017, 5, 22519–22526.
Cao, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Peng, C.; Li, Z.; Tang, L.; Feng, Y.; Feng, W. Electrolyte-solvent-modified alternating copolymer as a single-ion solid polymer electrolyte for high-performance lithium metal batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces2019, 11, 35683–35692.
Cheng, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, C. Z.; Wei, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q. A review of solid electrolyte interphases on lithium metal anode. Adv. Sci.2015, 3, 1–20.
Manthiram, A.; Yu, X.; Wang, S. Lithium battery chemistries enabled by solid-state electrolytes. Nat. Rev. Mater.2017, 2, 1–16.
Wu, Z.; Xie, Z.; Yoshida, A.; Wang, Z.; Hao, X.; Abudula, A.; Guan, G. Utmost limits of various solid electrolytes in all-solid-state lithium batteries: a critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev.2019, 109, 367–385.
Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Otaegui, L.; Singh, G.; Armand, M.; Rodriguez-Martinez, L. M. Estimation of energy density of Li-S batteries with liquid and solid electrolytes. J. Power Sources2016, 326, 1–5.
Eshetu, G. G.; Mecerreyes, D.; Forsyth, M.; Zhang, H.; Armand, M. Polymeric ionic liquids for lithium-based rechargeable batteries. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng.2019, 4, 294–309.
Ma, F.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, W.; Ma, X.; Sun, D.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; He, K. Solid polymer electrolyte based on polymerized ionic liquid for high performance all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng.2019, 7, 4675–4683.
Qiu, B.; Lin, B.; Yan, F. Ionic liquid/poly(ionic liquid)-based electrolytes for energy devices. Polym. Int.2013, 62, 335–337.
Shaplov, A. S.; Marcilla, R.; Mecerreyes, D. Recent advances in innovative polymer electrolytes based on poly(ionic liquid)s. Electrochim. Acta2015, 175, 18–34.
Park, J. Y.; Park, J. W.; Doh, C. H.; Ha, Y. C.; Lee, S. M.; Kim, S. Effect of solvated ionic liquids on the ion conducting property of composite membranes for lithium ion batteries. Res. Chem. Intermed.2018, 44, 6039–6051.
Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y. Nanoconfined ionic liquids. Chem. Rev.2017, 117, 6755–6833.
MacFarlane, D. R.; Forsyth, M.; Howlett, P. C.; Kar, M.; Passerini, S.; Pringle, J. M.; Ohno, H.; Watanabe, M.; Yan, F.; Zheng, W. Ionic liquids and their solid-state analogues as materials for energy generation and storage. Nat. Rev. Mater.2016, 1, 15005.
Forsyth, M.; Porcarelli, L.; Wang, X.; Goujon, N.; Mecerreyes, D. Innovative electrolytes based on ionic liquids and polymers for next-generation solid-state batteries. Acc. Chem. Res.2019, 52, 686–694.
Watanabe, M.; Thomas, M. L.; Zhang, S.; Ueno, K.; Yasuda, T.; Dokko, K. Application of ionic liquids to energy storage and conversion materials and devices. Chem. Rev.2017, 117, 7190–7239.
Tan, S.; Zeng, X.; Ma, Q.; Wu, X.; Guo, Y. Recent advancements in polymer-based composite electrolytes for rechargeable lithium batteries. Electrochem. Energy Rev.2018, 1, 113–138.
Xu, D.; Guo, J.; Yan, F. Porous ionic polymers: design, synthesis, and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci.2018, 79, 121–143.
Yin, K.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, L.; Tachibana, K.; Hirano, S. I. Polymer electrolytes based on dicationic polymeric ionic liquids: application in lithium metal batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A2015, 3, 170–178.
Di Noto, V.; Lavina, S.; Giffin, G. A.; Negro, E.; Scrosati, B. Polymer electrolytes: present, past and future. Electrochim. Acta2011, 57, 4–13.
Safa, M.; Chamaani, A.; Chawla, N.; El-Zahab, B. Polymeric ionic liquid gel electrolyte for room temperature lithium battery applications. Electrochim. Acta2016, 213, 587–593.
Li, Q.; Ardebili, H. Flexible thin-film battery based on solid-like ionic liquid-polymer electrolyte. J. Power Sources2016, 303, 17–21.
Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Wan, C. Review of gel-type polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources1999, 77, 183–197.
Ren, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Yan, F. Ionic liquid-based click-ionogels. Sci. Adv.2019, 5, eaax0648.
Sun, X. An investigation on ion solvation and ion association in a gel-type solid state polymer electrolyte. Solid State Ionics1996, 83, 79–85.
Guo, Q.; Han, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, W.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, C.; Xie, K. Thermo and electrochemical-stable composite gel polymer electrolytes derived from core-shell silica nanoparticles and ionic liquid for rechargeable lithium metal batteries. Electrochim. Acta2018, 288, 101–107.
Que, M.; Tong, Y.; Wei, G.; Yuan, K.; Wei, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Y. Safe and flexible ion gel based composite electrolyte for lithium batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A2016, 4, 14132–14140.
Singh, S. K.; Shalu; Balo, L.; Gupta, H.; Singh, V. K.; Tripathi, A. K.; Verma, Y. L.; Singh, R. K. Improved electrochemical performance of EMIMFSI ionic liquid based gel polymer electrolyte with temperature for rechargeable lithium battery. Energy2018, 150, 890–900.
Zhang, R.; Chen, Y.; Montazami, R. Ionic liquid-doped gel polymer electrolyte for flexible lithium-ion polymer batteries. Materials2015, 8, 2735–2748.
Li, Q.; Zhao, J.; Sun, B.; Lin, B.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Lu, J.; Yan, F. High-temperature solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells based on organic ionic plastic crystal electrolytes. Adv. Mater.2012, 24, 945.
Basile, A.; Hilder, M.; Makhlooghiazad, F.; Pozo-Gonzalo, C.; MacFarlane, D. R.; Howlett, P. C.; Forsyth, M. Ionic liquids and organic ionic plastic crystals: advanced electrolytes for safer high performance sodium energy storage technologies. Adv. Energy Mater.2018, 8, 1–20.
Cooper, E. I.; Angell, C. A. Ambient temperature plastic crystal fast ion conductors. Solid State Ionics1986, 18, 570–576.
Howlett, P. C.; Sunarso, J.; Shekibi, Y.; Wasser, E.; Jin, L.; MacFarlane, D. R.; Forsyth, M. On the use of organic ionic plastic crystals in all solid-state lithium metal batteries. Solid State Ionics2011, 204, 73–79.
Abu-Lebdeh, Y.; Abouimrane, A.; Alarco, P.; Armand, M. Ionic liquid and plastic crystalline phases of pyrazolium imide salts as electrolytes for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources2006, 154, 255–261.
Taniki, R.; Matsumoto, K.; Hagiwara, R.; Hachiya, K.; Morinaga, T.; Sato, T. Highly conductive plastic crystals based on fluorohydrogenate anions. J. Phys. Chem. B2013, 117, 955–960.
Tsunashima, K.; Sugiya, M. Physical and electrochemical properties of low-viscosity phosphonium ionic liquids as potential electrolytes. Electrochem. Commun.2001, 9, 2353–2358.
Jin, L.; Howlett, P. C.; Pringle, J. M.; Janikowski, J.; Armand, M.; MacFarlane, D. R.; Forsyth, M. An organic ionic plastic crystal electrolyte for rate capability and stability of ambient temperature lithium batteries. Energy Environ. Sci.2014, 7, 3352–3361.
Al-Masri, D.; Yunis, R.; Zhu, H.; Jin, L.; Bruce, P.; Hollenkamp, A.; Pringle, J. A new approach to very high lithium salt content quasi-solid state electrolytes for lithium metal batteries using plastic crystals. J. Mater. Chem. A2019, 7, 25389–25398.
Osada, I.; De Vries, H.; Scrosati, B.; Passerini, S. Ionic-liquid-based polymer electrolytes for battery applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.2016, 55, 500–513.
Eftekhari, A.; Saito, T. Synthesis and properties of polymerized ionic liquids. Eur. Polym. J.2017, 90, 245–272.
Pont, A. L.; Marcilla, R.; De Meatza, I.; Grande, H.; Mecerreyes, D. Pyrrolidinium-based polymeric ionic liquids as mechanically and electrochemically stable polymer electrolytes. J. Power Sources2009, 188, 558–563.
Appetecchi, G. B.; Kim, G. T.; Montanino, M.; Carewska, M.; Marcilla, R.; Mecerreyes, D.; de Meatza, I. Ternary polymer electrolytes containing pyrrolidinium-based polymeric ionic liquids for lithium batteries. J. Power Sources2010, 155, 3668–3675.
Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Yang, K.; Yang, L. Polymeric ionic liquid-ionic plastic crystal all-solid-state electrolytes for wide operating temperature range lithium metal batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A2011, 5, 21362–21369.
Tiyapiboonchaiya, C.; Pringle, J. M.; Sun, J.; Byrne, N.; Howlett, P. C.; MacFarlane, D. R.; Forsyth, M. The zwitterion effect in high-conductivity polyelectrolyte materials. Nat. Mater.2001, 3, 29–32.
Byrne, N.; Howlett, P. C.; MacFarlane, D. R.; Forsyth, M. The zwitterion effect in ionic liquids: towards practical rechargeable lithium-metal batteries. Adv. Mater.2005, 17, 2497–2501.
Lu, F.; Gao, X.; Wu, A.; Sun, N.; Shi, L.; Zheng, L. Lithium-containing zwitterionic poly(ionic liquid)s as polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C2017, 121, 17756–17763.
Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Du, B.; Peng, Z. Liquid-like poly(ionic liquid) as electrolyte for thermally stable lithium-ion battery. ACS Omega2018, 3, 10564–10571.
Li, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, J.; Yang, L.; Hirano, S. I. High-performance polymeric ionic liquid-silica hybrid ionogel electrolytes for lithium metal natteries. J. Mater. Chem. A2016, 4, 13822–13829.
Wang, S.; Shi, Q. X.; Ye, Y. S.; Xue, Y.; Wang, Y.; Peng, H. Y.; Xie, X. L.; Mai, Y. W. Constructing desirable ion-conducting channels within ionic liquid-based composite polymer electrolytes by using polymeric ionic liquid-functionalized 2D mesoporous silica nanoplates. Nano Energy2017, 33, 110–123.
Zhou, D.; Liu, R.; Zhang, J.; Qi, X.; He, Y. B.; Li, B.; Yang, Q. H.; Hu, Y. S.; Kang, F. In situ synthesis of hierarchical poly(ionic liquid)-based solid electrolytes for high-safety lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries. Nano Energy2017, 33, 45–54.
Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Piszcz, M.; Coya, E.; Rojo, T.; Rodriguez-Martinez, L. M.; Armand, M.; Zhou, Z. Single lithium-ion conducting solid polymer electrolytes: advances and perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev.2017, 46, 797–815.
Deng, K.; Han, D.; Ren, S.; Wang, S.; Xiao, M.; Meng, Y. Single-ion conducting artificial solid electrolyte interphase layers for dendrite-free and highly stable lithium metal anodes. J. Mater. Chem. A2019, 7, 13113–13119.
Bannister, D. J.; Davies, G. R.; Ward, I. M.; McIntyre, J. E. Ionic conductivities for poly(othylene oxide) complexes with lithium salts of monobasic and dibasic acids and blends of poly(ethylene oxide) with lithium salts of anionic polymers. Polymer1984, 25, 1291–1296.
Porcarelli, L.; Aboudzadeh, M. A.; Rubatat, L.; Nair, J. R.; Shaplov, A. S.; Gerbaldi, C.; Mecerreyes, D. Single-ion triblock copolymer electrolytes based on poly(ethylene oxide) and methacrylic sulfonamide blocks for lithium metal batteries. J. Power Sources2017, 364, 191–199.
Porcarelli, L.; Shaplov, A. S.; Salsamendi, M.; Nair, J. R.; Vygodskii, Y. S.; Mecerreyes, D.; Gerbaldi, C. Single-ion block copoly(ionic liquid)s as electrolytes for all-solid state lithium batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces2016, 8, 10350–10359.
Hovington, P.; Lagacé, M.; Guerfi, A.; Bouchard, P.; Mauger, A.; Julien, C. M.; Armand, M.; Zaghib, K. New lithium metal polymer solid state battery for an ultrahigh energy: nano C-LiFePO4 versus nano Li12V3O8. Nano Lett.2015, 15, 2671–2678.
Ma, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, C.; Zheng, L.; Cheng, P.; Nie, J.; Feng, W.; Hu, Y. S.; Li, H.; Huang, X. Single lithium-ion conducting polymer electrolytes based on a super-delocalized polyanion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.2016, 55, 2521–2525.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 21425417), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21835005 and U1862109), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, DZ., Ren, Yy., Hu, Y. et al. Ionic Liquid/Poly(ionic liquid)-based Semi-solid State Electrolytes for Lithium-ion Batteries. Chin J Polym Sci 38, 506–513 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-020-2390-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-020-2390-1