Abstract
Background
Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) is a novel and noninvasive technique for the quantitative assessment of retinal microvascular perfusion. Since the retinal and cerebral small vessels share similar embryological origins, anatomical features, and physiological properties, altered retinal microvasculature might provide a new perspective on the mechanisms of cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD).
Objective
We aimed to evaluate retinal vessel density (VD) in patients with CSVD using OCTA and identify associations with cerebral magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) markers and cognitive function.
Methods
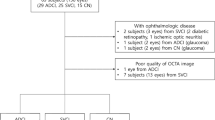
We prospectively recruited 47 CSVD patients and 30 healthy controls (HCs) to participate in the study. All participants underwent OCTA to evaluate retinal microvascular perfusion. The VDs of the macular region in the superficial retinal capillary plexus (SRCP), deep retinal capillary plexus (DRCP), and foveal avascular zone (FAZ) were determined, along with the VD of the optic nerve head (ONH) in the radial peripapillary capillary (RPC) network. Additionally, cerebral MRI and cognitive function tests were performed.
Results
In the macula area, the VD of the CSVD patients was significantly lower than HCs in the temporal quadrant of SRCP. In the ONH area, CSVD patients had lower VD than HCs in the peripapillary RPC network. According to multiple linear regression analysis, decreased VD of the macular SRCP was associated with white matter hyperintensity scores after adjustment for age, hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia. Furthermore, the VD of the macular SRCP was significantly correlated with CSVD patients’ cognitive function, especially global cognition, memory function, attention function, information processing, and executive function.
Conclusion
OCTA revealed a significant decrease in retinal microvascular perfusion in CSVD patients, and retinal hypoperfusion was related to MRI markers and cognitive function, suggesting that these parameters could have potential utility as early disease biomarkers.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pantoni L (2010) Cerebral small vessel disease: from pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol 9(7):689–701
Vermeer SE, Longstreth WJ, Koudstaal PJ (2007) Silent brain infarcts: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol 6(7):611–619
Debette S, Markus HS (2010) The clinical importance of white matter hyperintensities on brain magnetic resonance imaging: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 341(7767):288–288
Chen X, Wang J, Shan Y, Cai W, Liu S, Hu M, Liao S, Huang X, Zhang B, Wang Y, Lu Z (2019) Cerebral small vessel disease: neuroimaging markers and clinical implication. J Neurol 266(10):2347–2362
Montero-Odasso M, Hachinski V (2014) Preludes to brain failure: executive dysfunction and gait disturbances. Neurol Sci 35(4):601–604
Telgte AT et al (2018) Cerebral small vessel disease: from a focal to a global perspective. Nat Rev Neurol 14(7):387–398
Gorelick PB, Scuteri A, Black SE, Decarli C, Greenberg SM, Iadecola C, Launer LJ, Laurent S, Lopez OL, Nyenhuis D, Petersen RC, Schneider JA, Tzourio C, Arnett DK, Bennett DA, Chui HC, Higashida RT, Lindquist R, Nilsson PM, Roman GC, Sellke FW, Seshadri S, American Heart Association Stroke Council, Council on Epidemiology and Prevention, Council on Cardiovascular Nursing, Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention, and Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia (2011) Vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia. Stroke 42(9):2672–2713
Pantoni L, Garcia JH (1997) Pathogenesis of leukoaraiosis: a review. Stroke 28(3):652–659
London A, Benhar I, Schwartz M (2013) The retina as a window to the brain-from eye research to CNS disorders. Nat Rev Neurol 9(1):44–53
Hanff TC, Sharrett AR, Mosley TH, Shibata D, Knopman DS, Klein R, Klein BEK, Gottesman RF (2014) Retinal microvascular abnormalities predict progression of brain microvascular disease. Stroke 45(4):1012–1017
Mitchell P, Wang JJ, Wong TY, Smith W, Klein R, Leeder SR (2005) Retinal microvascular signs and risk of stroke and stroke mortality. Neurology 65(7):1005–1009
Cheung N, Mosley T, Islam A, Kawasaki R, Sharrett AR, Klein R, Coker LH, Knopman DS, Shibata DK, Catellier D, Wong TY (2010) Retinal microvascular abnormalities and subclinical magnetic resonance imaging brain infarct: a prospective study. Brain 133(7):1987–1993
Ikram MK, de Jong FJ, van Dijk EJ, Prins ND, Hofman A, Breteler MMB, de Jong PTVM (2006) Retinal vessel diameters and cerebral small vessel disease: the Rotterdam Scan Study. Brain 129(1):182–188
Hilal S, Ong YT, Cheung CY, Tan CS, Venketasubramanian N, Niessen WJ, Vrooman H, Anuar AR, Chew M, Chen C, Wong TY, Ikram MK (2014) Microvascular network alterations in retina of subjects with cerebral small vessel disease. Neurosci Lett 577:95–100
Dumitrascu OM, Demaerschalk BM, Valencia Sanchez C, Almader-Douglas D, O'Carroll CB, Aguilar MI, Lyden PD, Kumar G (2018) Retinal microvascular abnormalities as surrogate markers of cerebrovascular ischemic disease: a meta-analysis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 27(7):1960–1968
Spaide RF, Fujimoto JG, Waheed NK, Sadda SR, Staurenghi G (2018) Optical coherence tomography angiography. Prog Retin Eye Res 64:1–55
Lahme L, Esser EL, Mihailovic N, Schubert F, Lauermann J, Johnen A, Eter N, Duning T, Alnawaiseh M (2018) Evaluation of ocular perfusion in Alzheimer’s disease using optical coherence tomography angiography. J Alzheimers Dis 66(4):1745–1752
Bulut M, Kurtuluş F, Gözkaya O, Erol MK, Cengiz A, Akıdan M, Yaman A (2018) Evaluation of optical coherence tomography angiographic findings in Alzheimer’s type dementia. Br J Ophthalmol 102(2):233–237
Yoon SP, Thompson AC, Polascik BW, Calixte C, Burke JR, Petrella JR, Grewal DS, Fekrat S (2019) Correlation of OCTA and volumetric MRI in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina 50(11):709–718
Lanzillo R, Cennamo G, Criscuolo C, Carotenuto A, Velotti N, Sparnelli F, Cianflone A, Moccia M, Brescia Morra V (2018) Optical coherence tomography angiography retinal vascular network assessment in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 24(13):1706–1714
Feucht N, Maier M, Lepennetier G, Pettenkofer M, Wetzlmair C, Daltrozzo T, Scherm P, Zimmer C, Hoshi MM, Hemmer B, Korn T, Knier B (2019) Optical coherence tomography angiography indicates associations of the retinal vascular network and disease activity in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 25(2):224–234
Wang X, Jia Y, Spain R, Potsaid B, Liu JJ, Baumann B, Hornegger J, Fujimoto JG, Wu Q, Huang D (2014) Optical coherence tomography angiography of optic nerve head and parafovea in multiple sclerosis. Br J Ophthalmol 98(10):1368–1373
Cennamo G, Carotenuto A, Montorio D, Petracca M, Moccia M, Melenzane A, Tranfa F, Lamberti A, Spiezia AL, Servillo G, de Angelis M, Petruzzo M, Criscuolo C, Lanzillo R, Brescia Morra V (2020) Peripapillary vessel density as early biomarker in multiple sclerosis. Front Neurol 11:542
Lee JY, Kim JP, Jang H, Kim J, Kang SH, Kim JS, Lee J, Jung YH, Na DL, Seo SW, Oh SY, Kim HJ (2020) Optical coherence tomography angiography as a potential screening tool for cerebral small vessel diseases. Alzheimers Res Ther 12(1):73
Jia Y, Bailey ST, Hwang TS, McClintic SM, Gao SS, Pennesi ME, Flaxel CJ, Lauer AK, Wilson DJ, Hornegger J, Fujimoto JG, Huang D (2015) Quantitative optical coherence tomography angiography of vascular abnormalities in the living human eye. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(18):E2395–E2402
Di Maio LG et al (2020) Optical coherence tomography angiography findings in Huntington’s disease. Neurol Sci
Al-Sheikh M et al (2017) Impact of image quality on OCT angiography based quantitative measurements. Int J Retina Vitreous 3:13
Hiroki M, Miyashita K, Yoshida H, Hirai S, Fukuyama H (2003) Central retinal artery Doppler flow parameters reflect the severity of cerebral small-vessel disease. Stroke 34(7):e92–e94
Doubal FN, MacGillivray TJ, Patton N, Dhillon B, Dennis MS, Wardlaw JM (2010) Fractal analysis of retinal vessels suggests that a distinct vasculopathy causes lacunar stroke. Neurology 74(14):1102–1107
Mutlu U, Cremers LGM, de Groot M, Hofman A, Niessen WJ, van der Lugt A, Klaver CCW, Ikram MA, Vernooij MW, Ikram MK (2016) Retinal microvasculature and white matter microstructure. Neurology 87(10):1003–1010
McGrory S, Ballerini L, Doubal FN, Staals J, Allerhand M, Valdes-Hernandez MC, Wang X, MacGillivray T, Doney ASF, Dhillon B, Starr JM, Bastin ME, Trucco E, Deary IJ, Wardlaw JM (2019) Retinal microvasculature and cerebral small vessel disease in the Lothian Birth Cohort 1936 and Mild Stroke Study. Sci Rep 9(1):6320
Yu DY et al (1994) Intraretinal oxygen distribution in rats as a function of systemic blood pressure. Am J Phys 267(6 Pt 2):H2498–H2507
Chen M, Luo C, Zhao J, Devarajan G, Xu H (2019) Immune regulation in the aging retina. Prog Retin Eye Res 69:159–172
Khan U et al (2007) Risk factor profile of cerebral small vessel disease and its subtypes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78(7):702–706
Yamamoto Y, Akiguchi I, Oiwa K, Hayashi M, Kasai T, Ozasa K (2002) Twenty-four-hour blood pressure and MRI as predictive factors for different outcomes in patients with lacunar infarct. Stroke 33(1):297–305
Wardlaw JM, Sandercock PAG, Dennis MS, Starr J (2003) Is breakdown of the blood-brain barrier responsible for lacunar stroke, leukoaraiosis, and dementia? Stroke 34(3):806–812
Wong SM, Jansen JFA, Zhang CE, Hoff EI, Staals J, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Backes WH (2019) Blood-brain barrier impairment and hypoperfusion are linked in cerebral small vessel disease. Neurology 92(15):e1669–e1677
Kaur C, Foulds WS, Ling EA (2008) Blood-retinal barrier in hypoxic ischaemic conditions: basic concepts, clinical features and management. Prog Retin Eye Res 27(6):622–647
Patton N, Aslam T, MacGillivray T, Pattie A, Deary IJ, Dhillon B (2005) Retinal vascular image analysis as a potential screening tool for cerebrovascular disease: a rationale based on homology between cerebral and retinal microvasculatures. J Anat 206(4):319–348
Lenin R, Thomas SM, Gangaraju R (2018) Endothelial activation and oxidative stress in neurovascular defects of the retina. Curr Pharm Des 24(40):4742–4754
Deal JA, Sharrett AR, Rawlings AM, Gottesman RF, Bandeen-Roche K, Albert M, Knopman D, Selvin E, Wasserman BA, Klein B, Klein R (2018) Retinal signs and 20-year cognitive decline in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Neurology 90(13):e1158–e1166
Cheung CY, Ong SY, Ikram MK, Ong YT, Chen CP, Venketasubramanian N, Wong TY (2014) Retinal vascular fractal dimension is associated with cognitive dysfunction. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 23(1):43–50
Zhang YS, Zhou N, Knoll BM, Samra S, Ward MR, Weintraub S, Fawzi AA (2019) Parafoveal vessel loss and correlation between peripapillary vessel density and cognitive performance in amnestic mild cognitive impairment and early Alzheimer’s disease on optical coherence tomography angiography. PLoS One 14(4):e0214685
Jenkins AJ, Joglekar MV, Hardikar AA, Keech AC, O'Neal DN, Januszewski AS (2015) Biomarkers in diabetic retinopathy. Rev Diabet Stud 12(1–2):159–195
Criscuolo C, Cennamo G, Montorio D, Carotenuto A, Strianese A, Salvatore E, Tranfa F, Cennamo G, Lanzillo R, Brescia Morra V (2020) Assessment of retinal vascular network in amnestic mild cognitive impairment by optical coherence tomography angiography. PLoS One 15(6):e0233975
Campbell JP, Zhang M, Hwang TS, Bailey ST, Wilson DJ, Jia Y, Huang D (2017) Detailed vascular anatomy of the human retina by projection-resolved optical coherence tomography angiography. Sci Rep 7:42201
Zhu L, Zong Y, Yu J, Jiang C, He Y, Jia Y, Huang D, Sun X (2018) Reduced retinal vessel density in primary angle closure glaucoma. J Glaucoma 27(4):322–327
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (nos. 2016YFC1300604, 2016YFC1305904, and 2018YFC1314200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the Scientific Research Projects Approval Determination of Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. All the experiments were conducted with the consent of the patient and his/her family, and written informed consent was obtained in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wei, Q., Wu, X. et al. The vessel density of the superficial retinal capillary plexus as a new biomarker in cerebral small vessel disease: an optical coherence tomography angiography study. Neurol Sci 42, 3615–3624 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05038-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05038-z