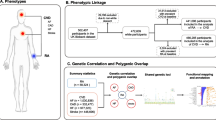
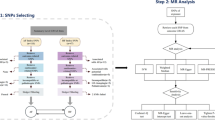
Abstract
Background
It has been proved that rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients have high incidence of atrial fibrillation (AF). Nevertheless, whether they have causal relevance is uncertain. This study aimed to explore and verify the authenticity of causal relationship between RA and AF using Mendelian randomization (MR).
Methods
The genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary data from Biobank Japan Project (BBJ) (RA, 4199 cases and 208,254 controls) were regarded as exposure data and the GWAS data from European Bio-informatics Institute database (EBI) (AF, 15,979 cases and 102,776 controls) as outcome data. The causal effect was appraised by the inverse variance weighted (IVW) method, MR-Egger regression, and weighted median estimator. MR-robust adjusted profile score (MR-RAPS) method was delivered to examine the robustness of causal relationship and MR Pleiotropy Residual Sum and Outlier (MR-PRESSO) method to control horizontal (directional) pleiotropy.
Results
The results indicated that RA increased the risk of AF (IVW, the odds ratio (OR) = 1.060; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.028 to 1.092; p = 1.411 × 10−4; weighted median, OR = 1.046, 95% CI, 1.002 to 1.093, p = 0.047). The MR analysis also showed this causal effect through all four IVW methods with various statistical algorithms. Both MR-RAPS and MR-PRESSO supported the causality of RA and AF. Also, the MR-PRESSO result indicated the absence of apparent pleiotropy.
Conclusion
There is a causal association between RA and AF. RA patients are genetically more vulnerable to AF. This study may contribute to further exploring early clinical prevention and fundamental mechanism of AF in patients with RA.
Key Points • We provided some genetic evidence for the causal link between rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and atrial fibrillation (AF) with multiple Mendelian randomization (MR) methods. • RA patients were genetically more vulnerable to AF. • This study partly shed light on latent fundamental mechanisms underlying RA-induced AF and inspired future studies on RA-AF relationship. |






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets applied in this study are readily accessible from the online repositories. This article contains the names of the repositories as well as the accession number.
References
Klareskog L, Catrina AI, Paget S (2009) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 373:659–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60008-8
England BR, Thiele GM, Anderson DR, Mikuls TR (2018) Increased cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis: mechanisms and implications. BMJ 361:k1036. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k1036
Sodergren A, Stegmayr B, Lundberg V, Ohman ML, Wallberg-Jonsson S (2007) Increased incidence of and impaired prognosis after acute myocardial infarction among patients with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 66:263–266. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2006.052456
Meune C, Touze E, Trinquart L, Allanore Y (2010) High risk of clinical cardiovascular events in rheumatoid arthritis: levels of associations of myocardial infarction and stroke through a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Cardiovasc Dis 103:253–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acvd.2010.03.007
Jang SY, Kang KW, Jo M, Park M (2021) Risk of new-onset acute coronary syndrome and atrial fibrillation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with a risk-set and propensity score-matched cohort - a nationwide cohort study. Circ J 85:194–200. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.CJ-20-0825
Lazzerini PE, Capecchi PL, Laghi-Pasini F (2017) Systemic inflammation and arrhythmic risk: lessons from rheumatoid arthritis. Eur Heart J 38:1717–1727. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehw208
Joseph PG, Healey JS, Raina P et al (2021) Global variations in the prevalence, treatment, and impact of atrial fibrillation in a multi-national cohort of 153 152 middle-aged individuals. Cardiovasc Res 117:1523–1531. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvaa241
Du X, Guo L, Xia S, Du J, Anderson C, Arima H, Huffman M, Yuan Y, Zheng Y, Wu S, Guang X, Zhou X, Lin H, Cheng X, Dong J, Ma C (2021) Atrial fibrillation prevalence, awareness and management in a nationwide survey of adults in China. Heart 107:535–541. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2020-317915
Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N et al (2021) Corrigendum to: 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): the Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 42:4194. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab648
Bacani AK, Crowson CS, Roger VL, Gabriel SE, Matteson EL (2015) Increased incidence of atrial fibrillation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed Res Int 2015:809514. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/809514
Kim SC, Liu J, Solomon DH (2014) The risk of atrial fibrillation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 73:1091–1095. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203343
Lindhardsen J, Ahlehoff O, Gislason GH, Madsen OR, Olesen JB, Svendsen JH, Torp-Pedersen C, Hansen PR (2012) Risk of atrial fibrillation and stroke in rheumatoid arthritis: Danish nationwide cohort study. BMJ 344:e1257. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.e1257
Ungprasert P, Srivali N, Kittanamongkolchai W (2017) Risk of incident atrial fibrillation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Rheum Dis 20:434–441. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.12820
Tan JS, Liu NN, Guo TT, Hu S, Hua L (2021) Genetic predisposition to COVID-19 may increase the risk of hypertension disorders in pregnancy: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Pregnancy Hypertens 26:17–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preghy.2021.08.112
Lawlor DA (2016) Commentary: two-sample Mendelian randomization: opportunities and challenges. Int J Epidemiol 45:908–915. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyw127
Richmond RC, Hemani G, Tilling K, Davey Smith G, Relton CL (2016) Challenges and novel approaches for investigating molecular mediation. Hum Mol Genet 25:R149–R156. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddw197
Christophersen IE, Rienstra M, Roselli C et al (2017) Large-scale analyses of common and rare variants identify 12 new loci associated with atrial fibrillation. Nat Genet 49:946–952. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3843
Kamat MA, Blackshaw JA, Young R, Surendran P, Burgess S, Danesh J, Butterworth AS, Staley JR (2019) PhenoScanner V2: an expanded tool for searching human genotype-phenotype associations. Bioinformatics 35:4851–4853. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz469
Ma M, Zhi H, Yang S, Yu EY, Wang L (2022) Body mass index and the risk of atrial fibrillation: a Mendelian randomization study. Nutrients 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091878
Pierce BL, Burgess S (2013) Efficient design for Mendelian randomization studies: subsample and 2-sample instrumental variable estimators. Am J Epidemiol 178:1177–1184. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwt084
Au Yeung SL, Luo S, Schooling CM (2018) The impact of glycated hemoglobin (HbA(1c)) on cardiovascular disease risk: a Mendelian randomization study using UK Biobank. Diabetes Care 41:1991–1997. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc18-0289
Hemani G, Tilling K, Davey Smith G (2017) Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data. PLoS Genet 13:e1007081. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1007081
Burgess S, Davey Smith G, Davies NM et al (2023) Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations: update for summer 2023. Wellcome Open Res 4:186. https://doi.org/10.12688/wellcomeopenres.15555.3
Smith GD, Ebrahim S (2003) 'Mendelian randomization': can genetic epidemiology contribute to understanding environmental determinants of disease? Int J Epidemiol 32:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyg070
Burgess S, Thompson SG (2017) Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur J Epidemiol 32:377–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-017-0255-x
Spiller W, Davies NM, Palmer TM (2019) Software application profile: mrrobust—a tool for performing two-sample summary Mendelian randomization analyses. Int J Epidemiol 48:684–690. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyy195
Tan JS, Liu NN, Guo TT, Hu S, Hua L (2021) Genetically predicted obesity and risk of deep vein thrombosis. Thromb Res 207:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2021.08.026
Burgess S, Davey Smith G, Davies NM, Dudbridge F, Gill D, Glymour MM, Hartwig FP, Holmes MV, Minelli C, Relton CL, Theodoratou E (2019) Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations. Wellcome Open Res 4:186. https://doi.org/10.12688/wellcomeopenres.15555.2
Kaltoft M, Langsted A, Nordestgaard BG (2020) Obesity as a causal risk factor for aortic valve stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 75:163–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2019.10.050
Broadbent JR, Foley CN, Grant AJ, Mason AM, Staley JR, Burgess S (2020) MendelianRandomization v0.5.0: updates to an R package for performing Mendelian randomization analyses using summarized data. Wellcome Open Res 5:252. https://doi.org/10.12688/wellcomeopenres.16374.2
Verbanck M, Chen CY, Neale B, Do R (2018) Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet 50:693–698. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0099-7
Wang M, Chao C, Mei K, Di D, Qian Y, Wang B, Zhang X (2023) Relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and cardiovascular comorbidity, causation or co-occurrence: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Cardiovasc Med 10:1099861. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2023.1099861
Cupido AJ, Asselbergs FW, Natarajan P, Group CIW, Ridker PM, Hovingh GK, Schmidt AF (2022) Dissecting the IL-6 pathway in cardiometabolic disease: a Mendelian randomization study on both IL6 and IL6R. Br J Clin Pharmacol 88:2875–2884. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.15191
Rosa M, Chignon A, Li Z, Boulanger MC, Arsenault BJ, Bosse Y, Theriault S, Mathieu P (2019) A Mendelian randomization study of IL6 signaling in cardiovascular diseases, immune-related disorders and longevity. NPJ Genom Med 4:23. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41525-019-0097-4
Dai H, Wang X, Yin S, Zhang Y, Han Y, Yang N, Xu J, Sun L, Yuan Y, Sheng L, Gong Y, Li Y (2017) Atrial fibrillation promotion in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis. J Am Heart Assoc 6. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.117.007320
Wang X, Fan H, Wang Y, Yin X, Liu G, Gao C, Li X, Liang B (2021) Elevated peripheral T helper cells are associated with atrial fibrillation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol 12:744254. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.744254
Wang Q, Shi Q, Lu J, Wang Z, Hou J (2022) Causal relationships between inflammatory factors and multiple myeloma: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Int J Cancer 151:1750–1759. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.34214
Yang C, Pring M, Wear MA, Huang M, Cooper JA, Svitkina TM, Zigmond SH (2005) Mammalian CARMIL inhibits actin filament capping by capping protein. Dev Cell 9:209–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2005.06.008
Liang Y, Niederstrasser H, Edwards M, Jackson CE, Cooper JA (2009) Distinct roles for CARMIL isoforms in cell migration. Mol Biol Cell 20:5290–5305. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e08-10-1071
Takahashi N, Coluccio A, Thorball CW, Planet E, Shi H, Offner S, Turelli P, Imbeault M, Ferguson-Smith AC, Trono D (2019) ZNF445 is a primary regulator of genomic imprinting. Genes Dev 33:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.320069.118
Mackay DJ, Callaway JL, Marks SM, White HE, Acerini CL, Boonen SE, Dayanikli P, Firth HV, Goodship JA, Haemers AP, Hahnemann JM, Kordonouri O, Masoud AF, Oestergaard E, Storr J, Ellard S, Hattersley AT, Robinson DO, Temple IK (2008) Hypomethylation of multiple imprinted loci in individuals with transient neonatal diabetes is associated with mutations in ZFP57. Nat Genet 40:949–951. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.187
Shi H, Li S, Geng Y, Fan H, Zhang R, Zhang Y, Pan J, Song G, Ge L, Xie T, Wang L (2022) Euphorbia factor L3 ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis by suppressing the inflammatory response by targeting Rac family small GTPase 1. Bioengineered 13:10984–10997. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2066761
Berntsson J, Smith JG, Johnson LSB, Soderholm M, Borne Y, Melander O, Orho-Melander M, Nilsson J, Engstrom G (2019) Increased vascular endothelial growth factor D is associated with atrial fibrillation and ischaemic stroke. Heart 105:553–558. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2018-313684
Chang JH, Cheng CC, Lu YY, Chung CC, Yeh YH, Chen YC, Higa S, Chen SA, Chen YJ (2021) Vascular endothelial growth factor modulates pulmonary vein arrhythmogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1/NOS pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 911:174547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174547
Mezache L, Struckman HL, Greer-Short A, Baine S, Gyorke S, Radwanski PB, Hund TJ, Veeraraghavan R (2020) Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes atrial arrhythmias by inducing acute intercalated disk remodeling. Sci Rep 10:20463. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-77562-5
Igarashi Y, Nochioka K, Sakata Y, Tamai T, Ohkouchi S, Irokawa T, Ogawa H, Hayashi H, Fujihashi T, Yamanaka S, Shiroto T, Miyata S, Hata J, Yamada S, Ninomiya T, Yasuda S, Kurosawa H, Shimokawa H (2021) Risk prediction for new-onset atrial fibrillation using the Minnesota code electrocardiography classification system. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc 34:100762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcha.2021.100762
Murakami T, Takahata Y, Hata K, Ebina K, Hirose K, Ruengsinpinya L, Nakaminami Y, Etani Y, Kobayashi S, Maruyama T, Nakano H, Kaneko T, Toyosawa S, Asahara H, Nishimura R (2022) Semaphorin 4D induces articular cartilage destruction and inflammation in joints by transcriptionally reprogramming chondrocytes. Sci Signal 15:eabl5304. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.abl5304
Qian K, Zheng XX, Wang C, Huang WG, Liu XB, Xu SD, Liu DK, Liu MY, Lin CS (2021) beta-sitosterol inhibits rheumatoid synovial angiogenesis through suppressing VEGF signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol 12:816477. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.816477
Alipour P, Senkevich K, Ross JP, Spiegelman D, Manousaki D, Dion PA, Rouleau GA (2022) Investigation of the causal relationship between ALS and autoimmune disorders: a Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med 20:382. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-022-02578-9
Ishigaki K, Sakaue S, Terao C et al (2022) Multi-ancestry genome-wide association analyses identify novel genetic mechanisms in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet 54:1640–1651. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-022-01213-w
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the financial support from Medical Health Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Provincial Health Commission (Grant Number: 2021KY1072) for checking the R code and the whole process of our entire MR analysis. And we also sincerely appreciate the guidance to our analysis from “Bio-informatics and Clinical Medicine” (WeChat Subscription).
Funding
This study is supported by The Medical Health Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Provincial Health Commission (Grant No. 2021KY1072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Ethics approval
Ethical approval was not applicable in this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rong, Jc., Chen, Xd., Jin, Nk. et al. Exploring the causal association of rheumatoid arthritis with atrial fibrillation: a Mendelian randomization study. Clin Rheumatol 43, 29–40 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06804-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06804-4