Abstract
Objective
Dickkopf-1 (Dkk-1), a regulatory molecule of the Wnt pathway, is elevated and leads to bone resorption in patients with RA. This study is aimed to investigate the contribution of Dkk-1 to synovial inflammation and synovial fibroblast-mediated angiogenesis in RA.
Methods
The expression of Dkk-1 in RA synovial fibroblasts (RASF) and osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts (OASF) was detected by real-time PCR and ELISA, respectively. RASF were stimulated with different pro-inflammatory factors. The expression of angiogenic factors, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and MMPs in RASF was analyzed by real-time PCR when Dkk-1 was inhibited or overexpressed. Meanwhile, the concentrations of MCP-1, IL-6, IL-8, and MMP-3 in the cell culture supernatant were assessed by ELISA. The effects of Dkk-1 on the MAPK signaling pathway were evaluated by western blot. Matrigel tube formation assay was employed to reveal the direct and indirect effects of Dkk-1 on synovial angiogenesis.
Results
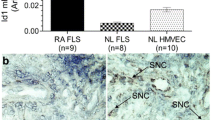
Dkk-1 expression was elevated in synovial fluids and synovial fibroblasts of RA patients. Treatment with various pro-inflammatory cytokines significantly promoted DKK-1 expression in RASF. The production of potent angiogenic factors, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and MMPs in RASF was elevated, whereas the reverse results were found in the inhibitor groups. Silenced Dkk-1expression in RASF dampened capillary tube organization in both direct and indirect manners, resulting in restrained ERK, JNK, and p38 signaling pathway activation.
Conclusion
We concluded that Dkk-1 exacerbated the inflammation, cartilage erosion, and angiogenesis mediated by synovial fibroblasts in RA. Modulation of DKK-1 expression may facilitate development of novel strategies to control RA.
Key points • Dkk-1 expression was elevated in synovial fluids and synovial fibroblasts of RA patients. • Treatment with various pro-inflammatory cytokines significantly promoted DKK-1 expression. • Silenced Dkk-1expression in RASF dampened capillary tube organization. |





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Falconer J, Murphy AN, Young SP et al (2018) Review: synovial cell metabolism and chronic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 70(7):984–999. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.40504
Leblond A, Allanore Y, Avouac J (2017) Targeting synovial neoangiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev 16(6):594–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2017.04.005
Volin MV, Koch AE (2011) Interleukin-18: a mediator of inflammation and angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Interferon Cytokine Res 31(10):745–751. https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.2011.0050
SR Pickens MV Volin AM Mandelin AM, 2nd et al. (2010) IL-17 contributes to angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 184 (6):3233–3241. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0903271
Ganesan R, Rasool M (2017) Fibroblast-like synoviocytes-dependent effector molecules as a critical mediator for rheumatoid arthritis: current status and future directions. Int Rev Immunol 36(1):20–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/08830185.2016.1269175
Cici D, Corrado A, Rotondo C, Cantatore FP (2019) Wnt signaling and biological therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis. Int J Mol Sci 20 (22). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225552
Fassio A, Adami G, Gatti D et al (2019) Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis results in acute changes of bone modulators. Int Immunopharmacol 67:487–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.12.050
Diller M, Hasseli R, Hülser ML et al (2019) Targeting activated synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis by peficitinib. Front Immunol 10:541. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00541
Korb-Pap A, Bertrand J, Sherwood J, Pap T (2016) Stable activation of fibroblasts in rheumatic arthritis-causes and consequences. Rheumatology (Oxford, England) 55(suppl 2):ii64–ii67. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kew347
Skalska U, Prochorec-Sobieszek M, Kontny E (2016) Osteoblastic potential of infrapatellar fat pad-derived mesenchymal stem cells from rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients. Int J Rheum Dis 19(6):577–585. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185x.12368
Choe JY, Hun Kim J, Park KY et al (2016) Activation of dickkopf-1 and focal adhesion kinase pathway by tumour necrosis factor alpha induces enhanced migration of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 55(5):928–938. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kev422
Miao CG, Yang YY, He X et al (2013) Wnt signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis, with special emphasis on the different roles in synovial inflammation and bone remodeling. Cell Signal 25(10):2069–2078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.04.002
Katoh M, Katoh M (2007) STAT3-induced WNT5A signaling loop in embryonic stem cells, adult normal tissues, chronic persistent inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis and cancer (Review). Int J Mol Med 19(2):273–278
Aicher A, Kollet O, Heeschen C et al (2008) The Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-1 mobilizes vasculogenic progenitor cells via activation of the bone marrow endosteal stem cell niche. Circ Res 103(8):796–803. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.107.172718
Li M, Cai H, Yang Y et al (2016) Perichondrium mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the growth of breast cancer cells via the DKK-1/Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol Rep 36(2):936–944. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2016.4853
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31(3):315–324. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780310302
Recommendations for the medical management of osteoarthritis of the hip and knee: 2000 update. American College of Rheumatology Subcommittee on Osteoarthritis Guidelines (2000). Arthritis and rheumatism 43 (9):1905–1915. https://doi.org/10.1002/1529-0131(200009)43:9<1905::Aid-anr1>3.0.Co;2-p
Zeng S, Wang K, Huang M et al (2017) Halofuginone inhibits TNF-α-induced the migration and proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Int Immunopharmacol 43:187–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2016.12.016
Diarra D, Stolina M, Polzer K et al (2007) Dickkopf-1 is a master regulator of joint remodeling. Nat Med 13(2):156–163. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1538
Alten R, Maleitzke T (2013) Tocilizumab: a novel humanized anti-interleukin 6 (IL-6) receptor antibody for the treatment of patients with non-RA systemic, inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Ann Med 45(4):357–363. https://doi.org/10.3109/07853890.2013.771986
van Oosterhout M, Levarht EWN, Sont JK et al (2005) Clinical efficacy of infliximab plus methotrexate in DMARD naive and DMARD refractory rheumatoid arthritis is associated with decreased synovial expression of TNF alpha and IL18 but not CXCL12. Ann Rheum Dis 64(4):537–543. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2004.024927
Yeremenko N, Zwerina K, Rigter G et al (2015) Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 differentially regulate Dkk-1 in the inflamed arthritic joint. Arthritis Rheumatol 67(8):2071–2075. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39183
Sun M, Rethi B, Krishnamurthy A et al (2019) Anticitrullinated protein antibodies facilitate migration of synovial tissue-derived fibroblasts. Ann Rheum Dis 78(12):1621–1631. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214967
Ruaro B, Casabella A, Paolino S et al (2018) Dickkopf-1 (Dkk-1) serum levels in systemic sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis patients: correlation with the Trabecular Bone Score (TBS). Clin Rheumatol 37(11):3057–3062. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4322-9
Ma Y, Zhang X, Wang M et al (2018) The serum level of Dickkopf-1 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Immunopharmacol 59:227–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.04.019
Li M, Liu X, Zhang Y et al (2016) Upregulation of Dickkopf1 by oscillatory shear stress accelerates atherogenesis. J Mol Med (Berl) 94(4):431–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-015-1369-9
Jia Q, Wang T, Wang X et al (2019) Astragalin suppresses inflammatory responses and bone destruction in mice with collagen-induced arthritis and in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Front Pharmacol 10:94–94. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00094
Elshabrawy HA, Chen Z, Volin MV et al (2015) The pathogenic role of angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Angiogenesis 18(4):433–448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-015-9477-2
Wang C-h, Yao H, Chen L-n et al (2012) CD147 induces angiogenesis through a vascular endothelial growth factor and hypoxia-inducible transcription factor 1α-mediated pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 64(6):1818–1827. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.34341
Villalvilla A, Gomez R, Roman-Blas JA et al (2014) SDF-1 signaling: a promising target in rheumatic diseases. Expert Opin Ther Targets 18(9):1077–1087. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728222.2014.930440
Guo J, Du J, Fei D et al (2018) miR-152 inhibits rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblast proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting ADAM10. Int J Mol Med 42(1):643–650. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3636
Kim H-R, Kim K-W, Kim B-M et al (2015) The effect of vascular endothelial growth factor on osteoclastogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 10(4):e0124909–e0124909. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124909
Seror R, Boudaoud S, Pavy S et al (2016) Increased Dickkopf-1 in recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis is a new biomarker of structural severity. Data from the ESPOIR Cohort. Sci Rep 6:18421. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18421
Funding
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81771678, 81801617), Peking University People’s Hospital Research and Development Funds (RDH 2020–03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Concept and design: Xuewu Zhang, Yanying Liu, and Zhanguo Li.
Definition of intellectual content: Xuewu Zhang and Yanying Liu.
Literature search: Wenjie Bian and Yuqin Yang.
Experimental studies: Li Zheng and Fanlei Hu.
Supplementary experiments: Yanying Liu and Linqi Zhang.
Data acquisition: Lianjie Shi and Fanlei Hu.
Statistical analysis: Yingni Li and Wenjie Bian.
Manuscript preparation: Li Zheng and Fanlei Hu.
Manuscript editing and manuscript review: Xiaoxu Ma and Lianjie Shi.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All the experiment for involving humans was in accordance to guidelines of national Declaration of Helsinki in the manuscript.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed with publication.
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, L., Hu, F., Bian, W. et al. Dickkopf-1 perpetuated synovial fibroblast activation and synovial angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 40, 4279–4288 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-05766-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-05766-9