Abstract
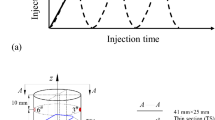
Traditional grouting technology only provides a bonding effect to surrounding rock fissures. Here, a new expansive grout was prepared using a high-efficiency soundless crush agent as the expansion source to provide an extrusion effect in the early stage of hydration development. Expansion and uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) tests under three expansion constraint conditions were designed to analyze the expansion behavior and mechanical properties of the expansive grout. The results show that the expansion development of the grout mostly occurred within 24–72 h after final setting; greater restrictions in the constraint conditions produced a smaller volume expansion ratio and a greater compressive strength. The volume expansion ratio and UCS of expansive grout are considerable; volume expansion occurs rapidly, while the strength increases, indicating good application prospects in grouting reinforcement engineering.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atteyeh SN, Debra FL, Iman Zolanvari SM (2020) Selective demolition of masonry unit walls with a soundless chemical demolition agent. Constr Build Mater 248:118635
Celik F, Akcuru O (2020) Rheological and workability effects of bottom ash usage as a mineral additive on the cement based permeation grouting method. Constr Build Mater 263:120186
Das R, Singh TN (2020) Effect of rock bolt support mechanism on tunnel deformation in jointed rockmass: a numerical approach. Undergr Space 06:001
De Silva VRS, Ranjith PG, Perear MSA, Wu B, Rathnaweera TD (2017) Investigation of the mechanical, microstructural and mineralogical morphology of soundless cracking demolition agents during the hydration process. Mater Charact 130:9–24
De Silva VRS, Ranjith PG, Perear MSA, Wu B (2019) The effect of saturation conditions on fracture performance of different soundless cracking demolition agents (SCDAs) in geological reservoir rock formations. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 62:157–170
Debra FL, Atteyeh SN (2018) Impact of thermal transfer on hydration heat of a Soundless Chemical Demolition Agent. Constr Build Mater 187:348–359
Garcia Calvo JL, Pedrosa F, Carballosa P, Revuelta D (2020) Evaluation of the sealing effectiveness of expansive cement grouts through a novel water penetration test. Constr Build Mater 251:118974
Huang SB, Yao N, Ye YC, Cui XZ (2019) Strength and failure characteristics of rocklike material containing a large-opening crack under uniaxial compression: experimental and numerical studies. Int J Geomech 19(8):1–15
Lee JS, Sagong M, Park J, Choi YI (2020) Experimental analysis of penetration grouting in umbrella arch method for tunnel reinforcement. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 13:104346
Liu C, Pan LF, Liu H, Tong HW, Yang YB, Chen W (2020a) Experimental and numerical investigation on mechanical properties of grouted-sleeve splices. Constr Build Mater 260:120441
Liu LP, Xie MJ, He Y, Li YY, Wei AH, Cui XM, Shi CJ (2020b) Expansion behavior and microstructure change of alkali-activated slag grouting material in carbonate environment. Constr Build Mater 262:120593
Liu SW, He DY, Fu MX (2020c) Experimental investigation of surrounding-rock anchoring synergistic component for bolt support in tunnels. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 104:103531
Omid S, Hakan S, Seyed Rahman T (2013) Numerical and analytical analyses of the effects of different joint and grout properties on the rock mass groutability. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 38:11–25
Parth P, Ol R, Moneeb G, Maria CG, van Oort E (2020) Shrinkage behavior of Portland and geopolymer cements at elevated temperature and pressure. J Pet Sci Eng 195:107884
Rikard G, Hakan S (2009) Fracture dilation during grouting. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 24:126–135
Rikard G, Hakan S (2010) Fracture–fracture interaction during grouting. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 25:199–204
Van ND, Chol H, Hama Y (2019) Modeling early age hydration reaction and predicting compressive strength of cement paste mixed with expansive additives. Constr Build Mater 223:994–1007
Wang YL, Tang JX, Dai ZY, Yi T (2018) Experimental study on mechanical properties and failure modes of low-strength rock samples containing different fissures under uniaxial compression. Eng Fract Mech 197:1–20
Wang Q, Qin Q, Jiang B, Yu HC, Pan R, Li SC (2019) Study and engineering application on the bolt-grouting reinforcement effect in underground engineering with fractured surrounding rock. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 84:237–247
Yao N, Ye YC, Hu B, Wang WQ, Wang QH (2019) Particle flow code modeling of the mechanical behavior of layered rock under uniaxial compression. Arch Min Sci 64(1):181–196
Yao N, Chen JW, Hu NY, Ye YC, Xiao YH, Huang Y (2021) Experimental study on expansion mechanism and characteristics of expansive grout. Constr Build Mater 268:121574
Zhang ZD, Scherer GW (2020) Measuring chemical shrinkage of ordinary Portland cement pastes with high water-to-cement ratios by adding cellulose nanofibrils. Cem Concr Compos 111:103625
Zhang JP, Liu LM, Li QH, Peng W, Zhang FT, Cao JZ, Wang H (2019a) Development of cement-based self-stress composite grouting material for reinforcing rock mass and engineering application. Constr Build Mater 201:314–327
Zhang WQ, Zhang XX, Xu SX, Wang ZY, Li W (2019b) Experimental study on properties of a new type of grouting material for the reinforcement of fractured seam floor. J Mater Res Technol 8(6):5171–5281
Zhang X, Wang MN, Wang ZL, Li JW, Zhao SG, Tong JJ, Liu DG (2020a) Stability analysis model for a tunnel face reinforced with bolts and an umbrella arch in cohesive-frictional soils. Comput Geotech 124:103635
Zhang YG, Li LF, Xi YP, Hubler M (2020b) Experimental and theoretical study of the restrained shrinkage cracking of early age well cement. Constr Build Mater 262:120368
Zheng Y, Chen CX, Liu TT, Song DR, Meng F (2019) Stability analysis of anti-dip bedding rock slopes locally reinforced by rock bolts. Eng Geol 251:229–237
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51804224) and the Key Research and Development Plan of Hubei Province (No. 2020BCA082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, N., Deng, X., Wang, Q. et al. Experimental investigation of expansion behavior and uniaxial compression mechanical properties of expansive grout under different constraint conditions. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80, 5609–5621 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02190-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02190-w