Abstract
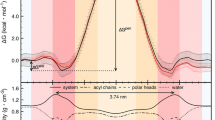
Cholesterol plays a crucial role in modulating the physicochemical properties of membranes, thus influencing the membrane transport of drugs. In this paper, the effects caused by cholesterol on the membrane transport of chlorzoxazone (CZX), a centrally acting muscle relaxant drug, were probed through molecular dynamics simulations. POPC was selected as the model lipid, and three different cholesterol concentrations (0%, 20%, and 50% CHOL) were considered. The outcomes reveal that the area per lipid of POPC decreases and the order parameter increases with enhanced concentration of CHOL. CZX prefers to localize at the interface between the headgroup region and the hydrophobic tail region of POPC, and the main energy barrier occurs in the hydrophobic region. The impact of CHOL on the free energy profile is correlated with concentration: low concentration facilitates CZX permeation, while high concentration hinders CZX permeation. Our findings coincide with experimental results, enhancing the mechanism understanding of how drug molecules are transported through membranes in the presence of CHOL.
Graphical abstract

• The effects caused by cholesterol (CHOL) on the membrane transport of chlorzoxazone (CZX) were studied.
• Low CHOL concentration facilitates CZX permeation, while high concentration hinders CZX permeation.
• Our findings improve the mechanism understanding of CHOL effects on CZX translocation across membrane.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting information file.
Code availability
GROMACS 5.0.
References
Seydel JK, Wiese M (2002) Drug-membrane interactions: analysis, drug distribution, modeling. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA
Tattrie NH, Bennet JR, Cyr R (1968) Maximum and minimum values for lecithin classes from various biological sources. Can J Biochem 46:819–824
Patrick JW, Gamez RC, Russell DH (2016) The influence of lipid bilayer physicochemical properties on gramicidin A conformer preferences. Biophys J 110(8):1826–1835
Favela-Rosales F, Carbajal-Tinoco MD, Ortega-Blake I (2014) Liquid-ordered phase formation in cholesterol-Popc bilayer: all-atom molecular dynamics simulations. Biophys J 106(2):80a
Cournia Z, Ullmann M, Smith JC (2007) Differential effects of cholesterol, ergosterol and lanosterol on a dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine membrane: a molecular dynamics simulation study. J Phys Chem B 111(7):1786–1801
Plesnar E, Subczynski WK, Pasenkiewicz-Gierula M (2012) Saturation with cholesterol increases vertical order and smoothes the surface of the phosphatidylcholine bilayer: a molecular simulation study. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1818:520–529
Pandit SA, Chiu S-W, Jakobsson E, Grama A, Scott HL (2008) Cholesterol packing around lipids with saturated and unsaturated chains. Langmuir 24(13):6858–6865
Pucadyil TJ, Chattopadhyay A (2006) Effect of cholesterol on lateral diffusion of fluorescent lipid probes in native hippocampal membranes. Chem Phys Lipids 43:11–21
Berka K, Paloncyova M, Anzenbacher P, Otyepka M (2013) Behavior of human cytochromes P450 on lipid membranes. J Phys Chem B 117:11556–11564
Berka K, Hendrychova T, Anzenbacher P, Otyepka M (2011) Membrane position of ibuprofen agrees with suggested access path entrance to cytochrome P450 2C9 active site. J Phys Chem A 115:11248–11255
Navrátilová V, Paloncýová M, Kajšová M, Berka K, Otyepk M (2015) Effect of cholesterol on the structure of membrane-attached cytochrome P450 3A4. J Chem Inf Model 55(3):628–635
Zhang L, Bennett WFD, Zheng T, Ouyang PK, Ouyang X, Qiu X, Luo A, Karttunen M, Chen P (2016) Effect of cholesterol on cellular uptake of cancer drugs pirarubicin and ellipticine. J Phys Chem B 120(12):3148–3156
Poojari C, Zak A, Dzieciuch-Rojek M, Bunker A, Kepczynski M, Róg T (2020) Cholesterol reduces partitioning of antifungal drug itraconazole into lipid bilayers. J Phys Chem B 124(11):2139–2148
Khajeh A, Modarress H (2014) Effect of cholesterol on behavior of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) in a DMPC lipid bilayer, a molecular dynamics study. Biophys Chem 187-188:43–50
Yamada A, Shimizu N, Hikima T, Takata M, Kobayashi T, Takahashi (2016) Effect of cholesterol on the interaction of cytochrome P450 substrate drug chlorzoxazone with the phosphatidylcholine bilayer. Biochem 55(28):3888–3898
Paloncyova M, Berka K, Otyepka M (2013) Molecular insight into affinities of drugs and their metabolites to lipid bilayers. J Phys Chem B 117:2403–2410
Martínez L, Andrade R, Birgin E, Martinez J (2009) PACKMOL: a package for building initial configurations for molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Chem 30:2157–2164
Ferreira TM, Coreta-Gomes F, Ollila OHS, Moreno MJ, Vaz WLC, Topgaard D (2013) Cholesterol and POPC segmental order parameters in lipid membranes: solid state 1H-13C NMR and MD simulation studies. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15(6):1976–1989
Hess B, Kutzner C, van der Spoel D, Lindahl E (2008) GROMACS 4: algorithms for highly efficient, load-balanced, and scalable molecular simulation. J Chem Theory Comput 4:435–447
Abraham MJ, Murtola T, Schulz R, Páll S, Smith JC, Hess B, Lindahl E (2015) GROMACS: high performance molecular simulations through muti-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 1-2:19–25
Schuettelkopf AW, Aalten DMF (2004) PRODRG-a tool for high-throughput crystallography of protein-ligand complexes. Acta Crystallogr D60:1355–1363
Kumar S, Rosenberg JM, Bouzida D, Swendsen RH, Kollman PA (1992) The weighted histogram analysis method for free-energy calculations on biomolecules: I. The method. J Comput Chem 13:1011–1021
Hub JS, de Groot BL, van der Spoel D (2010) g_wham–a free weighted histogram analysis implementation including robust error and autocorrelation estimates. J Chem Theory Comput 6:3713–3720
Lantzsch G, Binder H, Heerklotz H, Wendling M, Klose G (1996) Surface areas and packing constraints in POPC/C12EOn membranes. A time-resolved fluorescence study. Biophys Chem 58:289–302
Poger D, Mark AE (2010) On the validation of molecular dynamics simulations of saturated and cis-monounsaturated phosphatidylcholine lipid bilayers: a comparison with experiment. J Chem Theory Comput 6:325–336
Liu Y, Zhang D, Zhang Y, Tang Y, Xu L, He H, Wu J, Zheng J (2020) Molecular dynamics simulations of cholesterol effects on the interaction of hIAPP with lipid bilayer. J Phys Chem B 124(36):7830–7841
Leite NB, Mattins DB, Fazani VE, Vieira MR, Dos Santos Cabrera MP (2018) Cholesterol modulates curcumin partitioning and membrane effects. Biochim Bio Phys Acat-Biomembr 1860(11):2320–2328
Meng F, Wang H (2017) The permeability enhancing mechanism of menthol on skin lipids: a molecular dynamics simulation study. J Mol Model 23:279
Loura LMS, do Canto AMTM, Martins J (2013) Sensing hydration and behavior of pyrene in POPC and POPC/cholesterol bilayers: a molecular dynamics study. Biochim Biophys Acta 1828:1094–1101
Smondyrew AM, Berkowitz ML (1999) Structure of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine/cholesterol bilayer at low and high cholesterol concentrations: molecular dynamics simulation. Biophys J 77:2075–2089
Sun D, Lin X, Gu N (2014) Cholesterol affects C60 translocation across lipid bilayers. Soft Matter 13
Zocher F, van der Spoel D, Pohl P, Hub JS (2013) Local partition coefficients govern solute permeability of cholesterol-containing membranes. Biophys J 105:2760–2770
Jedlovszky P, Mezei M (2003) Effect of cholesterol on the properties of phospholipid membranes. 2. Free energy profile of small molecules. J Phys Chem B 107(22):5322–5332
Kang M, Loverde SM (2014) Molecular simulation of the concentration-dependent interaction of hydrophobic drugs with model cellular membranes. J Phys Chem B 118:11965–11972
Wang H, Meng F (2016) Concentration effect of cimetidine with POPC bilayer: a molecular dynamics simulation study. Mol Simul 42:1292–1297
Wang H, Meng F (2016) Molecular simulation study on concentration effects of rofecoxib with POPC bilayer. J Mol Graph Model 70:94–99
Acknowledgments
The calculations were performed using the TianHe-1(A) supercomputer at the National Supercomputing Center in Tianjin.
Funding
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Program of Tianjin (Grant Numbers 18ZXXYSY00040 and 19YFZCSY00620) and Tianjin 131 Talent Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F Meng conceived and designed the simulation. J Yuan performed the calculations and analysis. Both authors contributed to the first draft of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
N/A
Consent to participate
N/A
Consent for publication
N/A
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 737 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, J., Meng, F. Effects of cholesterol on chlorzoxazone translocation across POPC bilayer. J Mol Model 27, 146 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-021-04777-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-021-04777-2