Abstract
Objectives
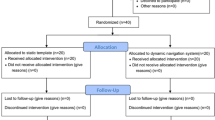
This study aimed to compare implant positioning accuracy and patient-centered results between static and dynamic computer-assisted implant surgery (s-CAIS and d-CAIS) in edentulous jaws.
Material and methods
The current study retrospectively evaluated a total of 110 implants placed in 22 fully edentulous patients via s-CAIS or d-CAIS (n = 11). The accuracy of implant positioning was assessed by measuring the implant’s angular deviation and deviation at the platform and apex from the preoperative design postoperatively. Patient-centered results, including preoperative and intraoperative patient-reported experiences and postoperative patient-reported outcomes, were extracted from the medical records. The nested t test and chi‐square test were used to compare accuracy and patient-centered results between s-CAIS and d-CAIS postoperatively.
Results
The implants in the s-CAIS group showed significantly smaller angular deviation (2.32 ± 1.23°) than those in the d-CAIS group (3.87 ± 2.75°). In contrast, the platform and apical deviation were significantly larger in s-CAIS (1.56 ± 1.19 mm and 1.70 ± 1.09 mm, respectively) than d-CAIS (1.02 ± 0.45 mm and 1.00 ± 0.51 mm, respectively). Furthermore, the implants in the s-CAIS group deviated significantly (p < 0.001) more toward the coronal direction than those in the d-CAIS group. Notably, all patients in the s-CAIS group reported an obvious foreign body sensation during surgery, representing a significant difference from the d-CAIS group.
Conclusions
Compared to s-CAIS, d-CAIS is a reliable technique for the placement of multiple implants in fully edentulous patients with less linear deviation and less foreign body sensation.
Trial registration.
The retrospective study was registered on the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry on August 8th, 2022, with registration number No. ChiCTR2200062484.
Clinical relevance
Despite the increasing use of computer- assisted implant surgery in fully edentulous patients, clinical evidence comparing implant positioning accuracy and patient-centered results between static and dynamic CAIS systems is scarce. Our study demonstrated that compared to s-CAIS, d-CAIS is a reliable technique for the placement of multiple implants in fully edentulous patients with less linear deviation.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Nickenig HJ, Wichmann M, Terheyden H, Kreppel M (2016) Oral health-related quality of life and implant therapy: A prospective multicenter study of preoperative, intermediate, and posttreatment assessment. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 44:753–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2016.02.014
Cabanes-Gumbau G, Agustin-Panadero R, Revilla-Leon M, Zubizarreta-Macho A (2021) Prosthetically-Driven Full-Mouth Implant-Supported Prostheses Using Guided Surgical Implant Planning with Composite Resin Markers: A Case Report. J Prosthodont 30:561–568. https://doi.org/10.1111/jopr.13367
Buser D, Bornstein MM, Weber HP, Grutter L, Schmid B, Belser UC (2008) Early implant placement with simultaneous guided bone regeneration following single-tooth extraction in the esthetic zone: a cross-sectional, retrospective study in 45 subjects with a 2- to 4-year follow-up. J Periodontol 79:1773–1781. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2008.080071
Cooper, L. F. . (2015). Prosthodontic complications related to non-optimal dental implant placement. Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York
Chen ST ,Buser D (2015) Esthetic complications due to implant malpositions: Etiology, prevention, and treatment. Wiley, New York
Kiatkroekkrai P, Takolpuckdee C, Subbalekha K, Mattheos N, Pimkhaokham A (2020) Accuracy of implant position when placed using static computer-assisted implant surgical guides manufactured with two different optical scanning techniques: a randomized clinical trial. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 49:377–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2019.08.019
Arisan V, Karabuda CZ, Mumcu E, Ozdemir T (2013) Implant positioning errors in freehand and computer-aided placement methods: a single-blind clinical comparative study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 28:190–204. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.2691
Smitkarn P, Subbalekha K, Mattheos N, Pimkhaokham A (2019) The accuracy of single-tooth implants placed using fully digital-guided surgery and freehand implant surgery. J Clin Periodontol 46:949–957. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13160
Tahmaseb A, Wismeijer D, Coucke W, Derksen W (2014) Computer technology applications in surgical implant dentistry: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 29(Suppl):25–42. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.2014suppl.g1.2
D'haese J, Ackhurst J, Wismeijer D, De Bruyn H, Tahmaseb A (2017) Current state of the art of computer-guided implant surgery. Periodontol 2000 73:121–133. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12175
Block MS, Emery RW, Cullum DR, Sheikh A (2017) Implant Placement Is More Accurate Using Dynamic Navigation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 75:1377–1386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2017.02.026
Aydemir CA, Arisan V (2020) Accuracy of dental implant placement via dynamic navigation or the freehand method: A split-mouth randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 31:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.13563
Gargallo-Albiol J, Barootchi S, Salomo-Coll O, Wang HL (2019) Advantages and disadvantages of implant navigation surgery. A systematic review. Ann Anat 225:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aanat.2019.04.005
Raico Gallardo YN, da Silva-Olivio IRT, Mukai E, Morimoto S, Sesma N, Cordaro L (2017) Accuracy comparison of guided surgery for dental implants according to the tissue of support: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res 28:602–612. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12841
Pessoa R, Siqueira R, Li J, Saleh I, Meneghetti P, Bezerra F, Wang HL, Mendonca G (2022) The Impact of Surgical Guide Fixation and Implant Location on Accuracy of Static Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery. J Prosthodont 31:155–164. https://doi.org/10.1111/jopr.13371
Chackartchi T, Romanos GE, Parkanyi L, Schwarz F, Sculean A (2022) Reducing errors in guided implant surgery to optimize treatment outcomes. Periodontol 2000 88:64–72. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12411
Pettersson A, Komiyama A, Hultin M, Nasstrom K, Klinge B (2012) Accuracy of virtually planned and template guided implant surgery on edentate patients. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 14:527–537. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2010.00285.x
Marliere DAA, Demetrio MS, Picinini LS, Oliveira RG, Netto H (2018) Accuracy of computer-guided surgery for dental implant placement in fully edentulous patients: A systematic review. Eur J Dent 12:153–160. https://doi.org/10.4103/ejd.ejd_249_17
Emery RW, Merritt SA, Lank K, Gibbs JD (2016) Accuracy of dynamic navigation for dental implant placement - model based evaluation. J Oral Implantol 42(5):399–405. https://doi.org/10.1563/aaid-joi-D-16-00025
McGrath C, Lam O, Lang N (2012) An evidence-based review of patient-reported outcome measures in dental implant research among dentate subjects. J Clin Periodontol 39(Suppl 12):193–201. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2011.01841.x
Kunavisarut C, Santivitoonvong A, Chaikantha S, Pornprasertsuk-Damrongsri S, Joda T (2022) Patient-reported outcome measures comparing static computer-aided implant surgery and conventional implant surgery for single-tooth replacement: A randomized controlled trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 33:278–290. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.13886
Kingsley C, Patel S (2017) Patient-reported outcome measures and patient-reported experience measures. BJA Educ 17:137–144. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjaed/mkw060
Youk SY, Lee JH, Park JM, Heo SJ, Roh HK, Park EJ, Shin IH (2014) A survey of the satisfaction of patients who have undergone implant surgery with and without employing a computer-guided implant surgical template. J Adv Prosthodont 6:395–405. https://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2014.6.5.395
Fernandes S, Fond G, Zendjidjian X, Michel P, Baumstarck K, Lancon C, Berna F, Schurhoff F, Aouizerate B, Henry C, Etain B, Samalin L, Leboyer M, Llorca PM, Coldefy M, Auquier P, Boyer L (2019) The Patient-Reported Experience Measure for Improving qUality of care in Mental health (PREMIUM) project in France: study protocol for the development and implementation strategy. Patient Prefer Adherence 13:165–177. https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S172100
Block MS, Emery RW, Lank K, Ryan J (2017) Implant Placement Accuracy Using Dynamic Navigation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 32:92–99. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.5004
Behneke A, Burwinkel M, Behneke N (2012) Factors influencing transfer accuracy of cone beam CT-derived template-based implant placement. Clin Oral Implants Res 23:416–423. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02337.x
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Buchner A, Lang AG (2009) Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav Res Methods 41:1149–1160. https://doi.org/10.3758/BRM.41.4.1149
Steenberghe D, Glauser R, Blombäck U, Andersson M, Schutyser F, Pettersson A, Wendelhag I (2010) A computed tomographic scan-derived customized surgical template and fixed prosthesis for flapless surgery and immediate loading of implants in fully edentulous maxillae: a prospective multicenter study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 7:s111–s120
Stubinger S, Buitrago-Tellez C, Cantelmi G (2014) Deviations between placed and planned implant positions: an accuracy pilot study of skeletally supported stereolithographic surgical templates. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 16:540–551. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12019
Hua F (2022) Dental patient-reported outcomes update 2022. J Evid-Based Dent Pract. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebdp.2022.101802
Engkawong S, Mattheos N, Pisarnturakit PP, Pimkhaokham A, Subbalekha K (2021) Comparing patient-reported outcomes and experiences among static, dynamic computer-aided, and conventional freehand dental implant placement: A randomized clinical trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 23:660–670. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.13030
Van Assche N, Vercruyssen M, Coucke W, Teughels W, Jacobs R, Quirynen M (2012) Accuracy of computer-aided implant placement. Clin Oral Implants Res 23(Suppl 6):112–123. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02552.x
Somogyi-Ganss E, Holmes HI, Jokstad A (2015) Accuracy of a novel prototype dynamic computer-assisted surgery system. Clin Oral Implants Res 26:882–890. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12414
Yimarj P, Subbalekha K, Dhanesuan K, Siriwatana K, Mattheos N, Pimkhaokham A (2020) Comparison of the accuracy of implant position for two-implants supported fixed dental prosthesis using static and dynamic computer-assisted implant surgery: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 22:672–678. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12949
Sittikornpaiboon P, Arunjaroensuk S, Kaboosaya B, Subbalekha K, Mattheos N, Pimkhaokham A (2021) Comparison of the accuracy of implant placement using different drilling systems for static computer-assisted implant surgery: A simulation-based experimental study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 23:635–643. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.13032
Wei SM, Zhu Y, Wei JX, Zhang CN, Shi JY, Lai HC (2021) Accuracy of dynamic navigation in implant surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res 32:383–393. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.13719
Verhamme LM, Meijer GJ, Boumans T, de Haan AF, Berge SJ, Maal TJ (2015) A clinically relevant accuracy study of computer-planned implant placement in the edentulous maxilla using mucosa-supported surgical templates. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 17:343–352. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12112
Stumpel LJ (2012) Deformation of stereolithographically produced surgical guides: an observational case series report. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 14:442–453. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2010.00268.x
D’Haese J, Van De Velde T, Elaut L, De Bruyn H (2012) A prospective study on the accuracy of mucosally supported stereolithographic surgical guides in fully edentulous maxillae. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 14:293–303. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2009.00255.x
Jorba-Garcia A, Gonzalez-Barnadas A, Camps-Font O, Figueiredo R, Valmaseda-Castellon E (2021) Accuracy assessment of dynamic computer-aided implant placement: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Investig 25:2479–2494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-021-03833-8
Mediavilla Guzman A, Riad Deglow E, Zubizarreta-Macho A, Agustin-Panadero R, Hernandez Montero S (2019) Accuracy of computer-aided dynamic navigation compared to computer-aided static navigation for dental implant placement: an in vitro study. J Clin Med 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122123
Feng Y, Yao Y, Yang X (2022) Effect of a dynamic navigation device on the accuracy of implant placement in the completely edentulous mandible: An in vitro study. J Prosthet Dent. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prosdent.2021.12.012
Sondergaard K, Hosseini M, Storgard Jensen S, Spin-Neto R, Gotfredsen K (2021) Fully versus conventionally guided implant placement by dental students: A randomized controlled trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 32:1072–1084. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.13802
Sakamoto T, Fukuda K, Saita N, Koukita Y, Yamashita S, Koizumi J, Ichinohe T (2016) Autonomic nervous activity of patients with gagging problems during dental mirror insertion. Spec Care Dentist 36:80–84. https://doi.org/10.1111/scd.12148
Eachempati P, Kumbargere Nagraj S, Kiran Kumar Krishanappa S, George RP, Soe HHK, Karanth L (2019) Management of gag reflex for patients undergoing dental treatment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011116.pub3
Pimkhaokham A, Jiaranuchart S, Kaboosaya B, Arunjaroensuk S, Subbalekha K, Mattheos N (2022) Can computer-assisted implant surgery improve clinical outcomes and reduce the frequency and intensity of complications in implant dentistry? A critical review. Periodontol 2000 90(1):197–223. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12458
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Mr. Xiaogang Qiu and Mr. Peijian Huang for their assistance in software acquisition and image analysis.
Funding
This study was supported by the Wuhan University Specific Fund for Major School-level Internationalization Initiatives (WHU-GJZDZX-RC07) and an ITI research grant (1721–2022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shuang Fu performed data analysis and wrote the manuscript. Wei Sun designed the experiment and performed clinical operations. Jingxian Zhu collected the data and assisted with data analysis. Bin Huang assisted with clinical operations and data collection. Wei Ji conceived the idea, designed the experiment, supervised the project and wrote the manuscript. Bin Shi supervised the project and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the content of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Approval of the study was obtained from the Ethics Committee of the School & Hospital of Stomatology, Wuhan University (No. 2022B44).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Shuang Fu and Wei Sun contributed equally as first authors.
Wei Ji and Bin Shi share equal senior authorships.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, S., Sun, W., Zhu, J. et al. Accuracy and patient-centered results of static and dynamic computer-assisted implant surgery in edentulous jaws: a retrospective cohort study. Clin Oral Invest 27, 5427–5438 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-023-05161-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-023-05161-5