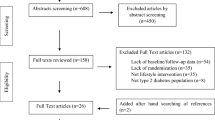
Abstract
Previous studies have suggested that taurine has hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects on experimental diabetic models. Therefore, this clinical trial was designed to explore the impacts of taurine supplementation on glycemic control and lipid profile in the patients with T2DM. This study was conducted on 45 patients with T2DM in Tabriz Sheikhor-raees Polyclinic and Imam-Reza Hospital Endocrine Center. Subjects were randomly divided into taurine and placebo groups. Accordingly, the taurine group (n = 23) received taurine 3000 mg/daily and the placebo group (n = 22) took crystalline microcellulose/daily for the duration of 8 weeks. At baseline and after the trial completion, fasting blood samples were obtained from the patients to assess the glycemic indicators and lipid profile. Independent t test, paired t test, Pearson’s correlation, and analysis of covariance was used for analysis. At the end of the study, levels of FBS (p = 0.01), insulin (p = 0.01), HOMA-IR (p = 0.003), TC (p = 0.013), and LDL-C (p = 0.041) significantly decreased in the taurine group compared to the placebo group. In addition, there was no significant changes in HbA1c, triglyceride, HDL-C, anthropometric indicators or dietary intakes by passing 8 weeks from the intervention. In conclusion, the findings of the current study indicated that taurine supplementation (3000 mg/day) for 8 weeks could improve the glycemic indexes and lipid profiles including TC and LDL-C in the patients with T2DM.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Akt:
-
Protein kinase B
- ALX:
-
Alloxan
- AMPK:
-
5′ AMP-activated protein kinase
- Apo A-I:
-
Apolipoprotein A I
- Apo B:
-
Apolipoprotein B
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- FBS:
-
Fasting blood sugar
- HbA1c:
-
Hemoglobin A1C
- HDL-C:
-
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- HOMA-IR:
-
Homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance
- IPAQ:
-
International physical activity questionnaire
- IRβ:
-
Insulin receptor Β-subunit
- LDL-C:
-
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- Lp(a):
-
Lipoprotein (a)
- OLETF:
-
Otsuka long evans tokushima fatty
- STZ:
-
Streptozotocin
- TC:
-
Total cholesterol
- TG:
-
Triglyceride
- UCP1:
-
Uncoupling protein 1
References
Association AD (2015) Standards of medical care in diabetes—2015 abridged for primary care providers. Clin Diabetes 33(2):97
Atlas D (2015) International diabetes federation. IDF diabetes atlas, 7th edn. International Diabetes Federation, Brussels
Borck PC, Vettorazzi JF, Branco RCS, Batista TM, Santos-Silva JC, Nakanishi VY, Boschero AC, Ribeiro RA, Carneiro EM (2018) Taurine supplementation induces long-term beneficial effects on glucose homeostasis in ob/ob mice. Amino Acids 50(6):765–774
Bouckenooghe T, Remacle C, Reusens B (2006) Is taurine a functional nutrient? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 9(6):728–733
Brøns C, Spohr C, Storgaard H, Dyerberg J, Vaag A (2004) Effect of taurine treatment on insulin secretion and action, and on serum lipid levels in overweight men with a genetic predisposition for type II diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Nutr 58(9):1239
Buonani C, Rossi FE, Diniz TA, Fortaleza AC, Viezel J, Picolo MR, Fernandes RA, Freitas Júnior IF (2019) Concurrent training and taurine improve lipid profile in postmenopausal women. Rev Bras Med Esporte 25(2):121–126
Camargo RL, Branco RCS, de Rezende LF, Vettorazzi JF, Borck PC, Boschero AC, Carneiro EM (2015) The effect of taurine supplementation on glucose homeostasis: the role of insulin-degrading enzyme. Adv Exp Med Biol 803:715–24
Cao P-j, Jin Y-j, Li M-e, Zhou R, Yang M-z (2016) PGC-1α may associated with the anti-obesity effect of taurine on rats induced by arcuate nucleus lesion. Nutr Neurosci 19(2):86–93
Carneiro EM, Latorraca MQ, Araujo E, Beltrá M, Oliveras MJ, Navarro M, Berná G, Bedoya FJ, Velloso LA, Soria B (2009) Taurine supplementation modulates glucose homeostasis and islet function. J Nutr Biochem 20(7):503–511
Chang KJ (1999) The effects of taurine and??-alanine on blood glucose and blood lipid concentrations in insulin-treated diabetic rats. Korean J Community Nutr 4(1):103
Chauncey KB, Tenner TE, Lombardini JB, Jones BG, Brooks ML, Warner RD, Davis RL, Ragain RM (2003) The effect of taurine supplementation on patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Adv Exp Med Biol 526:91–6
Chen W, Guo J-X, Chang P (2012) The effect of taurine on cholesterol metabolism. Mol Nutr Food Res 56(5):681–690
Cho N, Shaw J, Karuranga S, Huang Y, da Rocha FJ, Ohlrogge A, Malanda B (2018) IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 138:271–281
Contreras C, González-García I, Seoane-Collazo P, Martínez-Sánchez N, Liñares-Pose L, Rial-Pensado E, Fernø J, Tena-Sempere M, Casals N, Diéguez C (2017) Reduction of hypothalamic endoplasmic reticulum stress activates browning of white fat and ameliorates obesity. Diabetes 66(1):87–99
Das J, Vasan V, Sil PC (2012) Taurine exerts hypoglycemic effect in alloxan-induced diabetic rats, improves insulin-mediated glucose transport signaling pathway in heart and ameliorates cardiac oxidative stress and apoptosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 258(2):296–308
Foda D, Farrag E, Metwally N, Maghraby A, Farrag A, Rawi S (2016) Protective and therapeutic impact of taurine on some biochemical, immunological and histological parameters in diabetic rats. J Appl Pharm Sci 6:45–54
Franconi F, Bennardini F, Mattana A, Miceli M, Ciuti M, Mian M, Gironi A, Anichini R, Seghieri G (1995) Plasma and platelet taurine are reduced in subjects with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: effects of taurine supplementation. Am J Clin Nutr 61(5):1115–1119
Fukuyama N, Homma K, Wakana N, Kudo K, Suyama A, Ohazama H, Tsuji C, Ishiwata K, Eguchi Y, Nakazawa H (2007) Validation of the Friedewald equation for evaluation of plasma LDL-cholesterol. J Clin Biochem Nutr 43(1):1–5
Gomez R, Caletti G, Arbo BD, Hoefel AL, Schneider R Jr, Hansen AW, Pulcinelli RR, Freese L, Bandiera S, Kucharski LC (2018) Acute intraperitoneal administration of taurine decreases the glycemia and reduces food intake in type 1 diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother 103:1028–1034
Hy C, Wallis M, Tiralongo E (2007) Use of complementary and alternative medicine among people living with diabetes: literature review. J Adv Nurs 58(4):307–319
Ito T, Schaffer SW, Azuma J (2012) The potential usefulness of taurine on diabetes mellitus and its complications. Amino Acids 42(5):1529–1539
Jong CJ, Azuma J, Schaffer S (2012) Mechanism underlying the antioxidant activity of taurine: prevention of mitochondrial oxidant production. Amino Acids 42(6):2223–2232
Kim KS, Kim JY, Lee BG, You JS, Chang KJ, Chung H, Yoo MC, Yang H-I, Kang J-H, Hwang YC (2012) Taurine ameliorates hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia by reducing insulin resistance and leptin level in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty (OLETF) rats with long-term diabetes. Exp Mol Med 44(11):665
Lin S, Yang J, Wu G, Liu M, Luan X, Lv Q, Zhao H, Hu J (2010) Preventive effect of taurine on experimental type II diabetic nephropathy. J Biomed Sci 17(1):S46
Maddison R, Mhurchu CN, Jiang Y, Vander Hoorn S, Rodgers A, Lawes CM, Rush E (2007) International physical activity questionnaire (IPAQ) and New Zealand physical activity questionnaire (NZPAQ): a doubly labelled water validation. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 4(1):62
Marcinkiewicz J, Kontny E (2014) Taurine and inflammatory diseases. Amino Acids 46(1):7–20
Mirmiran P, Bahadoran Z, Azizi F (2014) Functional foods-based diet as a novel dietary approach for management of type 2 diabetes and its complications: a review. World J Diabetes 5(3):267
Moloney MA, Casey RG, O'Donnell DH, Fitzgerald P, Thompson C, Bouchier-Hayes DJ (2010) Two weeks taurine supplementation reverses endothelial dysfunction in young male type 1 diabetics. Diabetes Vasc Disease Res 7(4):300–310
Murakami S (2015) Role of taurine in the pathogenesis of obesity. Mol Nutr Food Res 59(7):1353–1363
Nakaya Y, Minami A, Harada N, Sakamoto S, Niwa Y, Ohnaka M (2000) Taurine improves insulin sensitivity in the Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty rat, a model of spontaneous type 2 diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr 71(1):54–58
Nardelli TR, Ribeiro RA, Balbo SL, Vanzela EC, Carneiro EM, Boschero AC, Bonfleur ML (2011) Taurine prevents fat deposition and ameliorates plasma lipid profile in monosodium glutamate-obese rats. Amino Acids 41(4):901–908
Nishimura N, Umeda C, Oda H, Yokogoshi H (2002) The effect of taurine on plasma cholesterol concentration in genetic type 2 diabetic GK rats. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 48(6):483–490
Ozougwu J, Obimba K, Belonwu C, Unakalamba C (2013) The pathogenesis and pathophysiology of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Physiol Pathophysiol 4(4):46–57
Papatheodorou K, Papanas N, Banach M, Papazoglou D, Edmonds M (2016) Complications of diabetes 2016. J Diabetes Res 2016:6989453
Park E-J, Bae JH, Kim S-Y, Lim J-G, Baek W-K, Kwon TK, Suh S-i, Park J-W, Lee I-K, Ashcroft FM (2004) Inhibition of ATP-sensitive K+ channels by taurine through a benzamido-binding site on sulfonylurea receptor 1. Biochem Pharmacol 67(6):1089–1096
Ribeiro RA, Santos-Silva JC, Vettorazzi JF, Cotrim BB, Mobiolli DD, Boschero AC, Carneiro EM (2012) Taurine supplementation prevents morpho-physiological alterations in high-fat diet mice pancreatic β-cells. Amino Acids 43(4):1791–1801
Ribeiro RA, Bonfleur ML, Batista TM, Borck PC, Carneiro EM (2018) Regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism by the pancreatic and extra-pancreatic actions of taurine. Amino Acids 50(11):1511–1524
Ripps H, Shen W (2012) Taurine: a “very essential” amino acid. Mol Vis 18:2673
Rosa FT, Freitas EC, Deminice R, Jordao AA, Marchini JS (2014) Oxidative stress and inflammation in obesity after taurine supplementation: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur J Nutr 53(3):823–830
Sak D, Erdenen F, Müderrisoglu C, Altunoglu E, Sozer V, Gungel H, Guler PA, Sak T, Uzun H (2019) The relationship between plasma taurine levels and diabetic complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomolecules 9(3):96
Saleh AAS (2012) Effects of taurine and/or ginseng and their mixture on lipid profile and some parameters indicative of myocardial status in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. J Basic Appl Zool 65(5):267–273
Santos-Silva JC, Ribeiro RA, Vettorazzi JF, Irles E, Rickli S, Borck PC, Porciuncula PM, Quesada I, Nadal A, Boschero AC (2015) Taurine supplementation ameliorates glucose homeostasis, prevents insulin and glucagon hypersecretion, and controls β, α, and δ-cell masses in genetic obese mice. Amino Acids 47(8):1533–1548
Schaffer S, Azuma J, Takahashi K, Mozaffari M (2003) Why is taurine cytoprotective? Adv Exp Med Biol 526:307–21
Schuller-Levis GB, Park E (2003) Taurine: new implications for an old amino acid. FEMS Microbiol Lett 226(2):195–202
Shari FH, Dawood H, Hassan JK, ALJazeari QA, Najm MA, Salahuddin A, Al-Salman H (2019) To study the effect of taurine on the effects of vital bones and regulate the level of glucose in type II diabetes. Int J Res Pharm Sci 10(3):2545–2551
Spohr C, Brøns C, Winther K, Dyerberg J, Vaag A (2005) No effect of taurine on platelet aggregation in men with a predisposition to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Platelets 16(5):301–305
Vettorazzi JF, Ribeiro RA, Santos-Silva JC, Borck PC, Batista TM, Nardelli TR, Boschero AC, Carneiro EM (2014) Taurine supplementation increases K ATP channel protein content, improving Ca 2+ handling and insulin secretion in islets from malnourished mice fed on a high-fat diet. Amino Acids 46(9):2123–2136
You JS, Chang KJ (1998) Effects of taurine supplementation on lipid peroxidation, blood glucose and blood lipid metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Adv Exp Med Biol 442:163–168
Zheng Y, Ceglarek U, Huang T, Wang T, Heianza Y, Ma W, Bray GA, Thiery J, Sacks FM, Qi L (2016) Plasma taurine, diabetes genetic predisposition, and changes of insulin sensitivity in response to weight-loss diets. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 101(10):3820–3826
Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB (2018) Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol 14(2):88
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all members of the present study group for their ideas, suggestions, participation and support. This study is a part of a thesis proposal for Ph.D. degree. The thesis proposal was approved by Medical Ethics Committee of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences (IR.TBZMED.REC.1397.682). Moreover, the authors acknowledge TBZMED for their financial support.
Funding
This study was funded by Vice Chancellor for Research at Nutrition Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VM: Contributed to the study conception, design and data collection and drafting the manuscript. MA: Participated in study design, revising the paper and approving the version of the manuscript being submitted. FE: Contributed to the interpretation of data, revising the paper critically and giving final approval. RM: Participated in study design, revising the paper and approving the version of the manuscript being submitted.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All the study procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research ethics committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Written informed consents were obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Handling Editor S. W. Schaffer.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maleki, V., Alizadeh, M., Esmaeili, F. et al. The effects of taurine supplementation on glycemic control and serum lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Amino Acids 52, 905–914 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-020-02859-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-020-02859-8