Abstract
Background
Trigeminal schwannomas (TSs) with solitary extracranial location are rare, and surgical excision is challenging. In recent years, the endoscopic endonasal transmaxillary transpterygoid approach (EETPA) has been advocated as an effective strategy for TSs in the infratemporal fossa (ITF).
Method
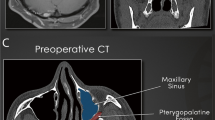
We describe the steps of the EETPA combined with the sublabial transmaxillary approach for the surgical excision of a giant mandibular schwannoma of the ITF. Indications, advantages, and approach-specific complications are also discussed. The main surgical steps are shown in an operative video.
Conclusion
A combined EETPA and sublabial transmaxillary approach represents a safe and effective option for the surgical excision of extracranial TSs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hofstetter CP, Singh A, Anand VK, Kacker A, Schwartz TH (2010) The endoscopic, endonasal, transmaxillary transpterygoid approach to the pterygopalatine fossa, infratemporal fossa, petrous apex, and the Meckel cave. J Neurosurg 113:967–974
Martinez-Perez R, Aref M, Ramakhrisnan V, Youssef AS (2021) Combined biportal unilateral endoscopic endonasal and endoscopic anterior transmaxillary approach for resection of lesions involving the infratemporal fossa. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 163:3439–3445
Martínez-Pérez R, Zachariah M, Li R, Silveira-Bertazzo G, Carrau RL, Prevedello DM (2020) Expanded endoscopic endonasal transpterygoid transmaxillary approach for a giant trigeminal schwannoma. Neurosurg Focus Video 2:V15
Park HH, Hong SD, Kim YH, Hong CK, Woo KI, Yun IS, Kong DS (2020) Endoscopic transorbital and endonasal approach for trigeminal schwannomas: a retrospective multicenter analysis (KOSEN-005). J Neurosurg 133:467–476
Pinheiro-Neto CD, Fernandez-Miranda JC, Prevedello DM, Carrau RL, Gardner PA, Snyderman CH (2013) Transposition of the pterygopalatine fossa during endoscopic endonasal transpterygoid approaches. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base 74:266–267
Pinheiro-Neto CD, Fernandez-Miranda JC, Rivera-Serrano CM, Paluzzi A, Snyderman CH, Gardner PA, Sennes LU (2012) Endoscopic anatomy of the palatovaginal canal (palatosphenoidal canal): a landmark for dissection of the vidian nerve during endonasal transpterygoid approaches. Laryngoscope 122:6–12
Ramina R, Mattei TA, Sória MG, da Silva Jr EB, Leal AG, Neto MC, Fernandes YB (2008) Surgical management of trigeminal schwannomas. Neurosurg Focus 25:E6
Raza SM, Donaldson AM, Mehta A, Tsiouris AJ, Anand VK, Schwartz TH (2014) Surgical management of trigeminal schwannomas: defining the role for endoscopic endonasal approaches. Neurosurg Focus 37:E17
Samii M, Migliori MM, Tatagiba M, Babu R (1995) Surgical treatment of trigeminal schwannomas. J Neurosurg 82:711–718
Yang L, Hu L, Zhao W, Zhang H, Liu Q, Wang D (2018) Endoscopic endonasal approach for trigeminal schwannomas: our experience of 39 patients in 10 years. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 275:735–741
Acknowledgements
We thank the Fondazione Beretta for their constant devotion to supporting brain cancer.
Funding
This work was supported in part by Joseph I. and Barbara Ashkins Endowed Professorship in surgery.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Approval was obtained from the ethics committee of the Mayo Clinic. The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in this study.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Ten key points
1. TSs represent between 0.07 and 0.36% of all intracranial tumors.
2. TSs with a solitary or predominantly extracranial component represent only 7–15% of all TSs.
3. EETPA, with or without a sublabial transmaxillary approach, has become a standard technique for the PPF, ITF, and upper PFS.
4. EETPA is mainly indicated for TSs involving the PPF or ITF with or without intracranial extension and for TSs stemming from Meckel’s cave.
5. Intraoperative neuromonitoring is useful to verify the physiological function of the motor root of V3 – which directs whether a nerve-sparing technique will be used.
6. In the case of ITF lesions, intraoperative neuronavigation is pivotal to direct the surgical corridor toward the lesion and reduce the risk of residual tumor.
7. TSs tend to displace the surrounding neurovascular structures, preserving a good plane of dissection.
8. Internal debulking of TS is key to safely dissect the capsule away from surrounding structures.
9. TS capsule must be carefully and completely dissected in order to avoid residual disease.
10. Hypoesthesia or anesthesia in the affected branch is a common occurrence after surgery, especially in large tumors.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Tumor - Schwannoma
Supplementary Information
Video 1 Surgical video of a step-by-step excision of a V3 trigeminal schwannoma of the infratemporal fossa through a combined EETPA and sublabial transmaxillary approach. Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 96782 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Agosti, E., Alexander, A.Y., Choby, G. et al. Combined endoscopic endonasal transpterygoid and sublabial transmaxillary approaches for a large infratemporal fossa trigeminal schwannoma. Acta Neurochir 164, 2525–2531 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-022-05327-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-022-05327-2