Abstract
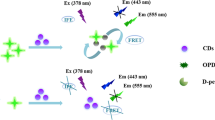
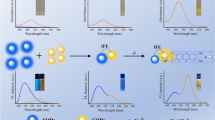
Two kinds of carbon dots with the maximum fluorescence peak of 492 nm (named as G-CDs) and 607 nm (named as R-CDs) were synthesized. In the presence of MoO42− ions, the fluorescence of R-CDs at 607 nm can be quenched, which can probably be assigned to their aggregation caused by MoO42−, while that of G-CDs at 492 nm remained unchanged. For the first time, a ratiometric fluorescence probe was developed for MoO42− ions detection. In the range 0.25 ~ 100 μM, the fluorescence ratio (F492/F607) of the probe was linearly related to MoO42− concentration, and the detection limit was 61.5 nM, which fully meets the minimum detection requirements of MoO42− ions in drinking water. On the other hand, when MoO42− was introduced, a significant fading phenomenon of R-CDs can be observed with the naked eye; thereby, the colorimetric method can also be proposed. Based on above, the ratiometric fluorometric/colorimetric dual-mode sensing method was established for MoO42− anion quantification. Compared with the traditional analysis methods, the results obtained by multimodal sensing can be mutually verified, which effectively improves the accuracy and reliability. The dual-mode assay proposed in this work provides an alternative scheme to meet the need of sensing target compounds in complex matrices.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Additional files.
References
Bhattacharya PT, Misra SR, Hussain M (2016) Nutritional aspects of essential trace elements in oral health and disease: an extensive review. Scientifica 2016:5464373
Prashanth L, Kattapagari KK, Chitturi RT, Baddam VRR, Prasad LK (2015) A review on role of essential trace elements in health and disease. J Dr NTR Univ Heal Sci 4:75–85
Johnson JL, Rajagopalan KV, Cohen HJ (1974) Molecular basis of the biological function of molybdenum: effect of tungsten on xanthine oxidase and sulfite oxidase in the rat. J Biol Chem 249:859–866
Barceloux DG, Barceloux D (1999) Molybdenum. J Toxicol-Clin Toxic 37:231–237
Huang C-Y, Lee NM, Lin S-Y, Liu C-Y (2002) Determination of vanadium, molybdenum and tungsten in complex matrix samples by chelation ion chromatography and on-line detection with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 466:161–174
Butler LRP, Mathews PM (1966) The determination of trace quantities of molybdenum by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Anal Chim Acta 36:319–327
Li Y, Jia W, Yang Z, Yang J, Chen Y, Yang J, Zhang W, Lu C, Wang X (2023) A fluorescent and colorimetric probe for MoO42- based on sulfur quantum dots nanozyme. J Alloy Compd 934:167926
Zhang C, Zhang M, Ma L, Li Y, Li L, Niu Y, Xu Y (2021) Environmental molybdate monitoring based on vanadium oxide quantum dots-derived fluorescent strategy. Microchem J 170:106702
Zhang Z, Chen Z, Chen L (2015) Ultrasensitive visual sensing of molybdate based on enzymatic-like etching of gold nanorods. Langmuir 31:9253–9259
Jiao Y, Gao Y, Meng Y, Lu W, Liu Y, Han H, Shuang S, Li L, Dong C (2019) One-step synthesis of label-free ratiometric fluorescence carbon dots for the detection of silver ions and glutathione and cellular imaging applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:16822–16829
Zeng H-H, Zhou Z-Y, Liu F, Deng J, Huang S-Y, Li G-P, Lai P-Q, Xie Y-P, Xiao W (2019) Design and synthesis of a vanadate-based ratiometric fluorescent probe for sequential recognition of Cu2+ ions and biothiols. Analyst 144:7368–7377
He Z, Sun Y, Zhang C, Zhang J, Liu S, Zhang K, Lan M (2023) Recent advances of solvent-engineered carbon dots: A review. Carbon 204:76–93
Liu J, Li R, Yang B (2020) Carbon dots: a new type of carbon-based nanomaterial with wide applications. ACS Central Sci 6:2179–2195
Xu Q, Kuang T, Liu Y, Cai L, Peng X, SreenivasanSreeprasad T, Zhao P, Yu Z, Li N (2016) Heteroatom-doped carbon dots: synthesis, characterization, properties, photoluminescence mechanism and biological applications. J Mater Chem B 4:7204–7219
Chao T, Wang J, Dong X, Ren J, Zhang H, Song R, Xie Z (2022) Defects and structural limitation-induced carbon dots-silica hybrid materials with ultralong room temperature phosphorescence. J Phys Chem Lett 13:9558–9563
Zhang T, Zhu J, Zhai Y, Wang H, Bai X, Dong B, Wang H, Song H (2017) A novel mechanism for red emission carbon dots: hydrogen bond dominated molecular states emission. Nanoscale 9:13042–13051
Wareing TC, Gentile P, Phan AN (2021) Biomass-based carbon dots: current development and future perspectives. ACS Nano 15:15471–15501
Xue S, Li P, Sun L, An L, Qu D, Wang X, Sun Z (2023) The formation process and mechanism of carbon dots prepared from aromatic compounds as precursors: a review. Small 19:2206180
Jiang K, Sun S, Zhang L, Lu Y, Wu A, Cai C, Lin H (2015) Red, green, and blue luminescence by carbon dots: full-color emission tuning and multicolor cellular imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed 54:5360–5363
Ding H, Yu S-B, Wei J-S, Xiong H-M (2016) Full-color light-emitting carbon dots with a surface-state-controlled luminescence mechanism. ACS Nano 10:484–491
Bhattacharya S, Phatake RS, NabhaBarnea S, Zerby N, Zhu J-J, Shikler R, Lemcoff NG, Jelinek R (2019) Fluorescent self-healing carbon dot/polymer gels. ACS Nano 13:1433–1442
Miao X, Qu D, Yang D, Nie B, Zhao Y, Fan H, Sun Z (2018) Synthesis of carbon dots with multiple color emission by controlled graphitization and surface functionalization. Adv Mater 30:1704740
Huang Z, Lin F, Hu M, Li C, Xu T, Chen C, Guo X (2014) Carbon dots with tunable emission, controllable size and their application for sensing hypochlorous acid. J Lumin 151:100–105
Wang Z, Yuan F, Li X, Li Y, Zhong H, Fan L, Yang S (2017) 53% Efficient red emissive carbon quantum dots for high color rendering and stable warm white-light-emitting diodes. Adv Mater 29:1702910
Hola K, Bourlinos AB, Kozak O, Berka K, Siskova KM, Havrdova M, Tucek J, Safarova K, Otyepka M, Giannelis EP, Zboril R (2014) Photoluminescence effects of graphitic core size and surface functional groups in carbon dots: COO- induced red-shift emission. Carbon 70:279–286
Tian Z, Zhang X, Li D, Zhou D, Jing P, Shen D, Qu S, Zboril R, Rogach AL (2017) Full-color inorganic carbon dot phosphors for white-light-emitting diodes. Adv Opt Mater 5:1700416
Yuan F, Wang Z, Li X, Li Y, Tan Za, Fan L, Yang S (2017) Bright multicolor bandgap fluorescent carbon quantum dots for electroluminescent light-emitting diodes. Adv Mater 29:1604436
Barhum H, Alon T, Attrash M, Machnev A, Shishkin I, Ginzburg P (2021) Multicolor phenylenediamine carbon dots for metal-ion detection with picomolar sensitivity. ACS Appl Nano Mater 4:9919–9931
Jia H, Wang Z, Yuan T, Yuan F, Li X, Li Y, Tan Za, Fan L, Yang S (2019) Electroluminescent warm white light-emitting diodes based on passivation enabled bright red bandgap emission carbon quantum dots. Adv Sci 6:1900397
Wang S, Cole IS, Zhao D, Li Q (2016) The dual roles of functional groups in the photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale 8:7449–7458
Chien C-T, Li S-S, Lai W-J, Yeh Y-C, Chen H-A, Chen IS, Chen L-C, Chen K-H, Nemoto T, Isoda S, Chen M, Fujita T, Eda G, Yamaguchi H, Chhowalla M, Chen C-W (2012) Tunable photoluminescence from graphene oxide. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:6662–6666
Yang Y, Peng K, Deng Y, Zhao Y, Ai J, Min X, Hu M, Huang S, Yu L (2022) Full-color-emission carbon quantum dots by controlling surface states in a system of solvent. J Lumin 243:118614
Zhu Z, Zhai Y, Li Z, Zhu P, Mao S, Zhu C, Du D, Belfiore LA, Tang J, Lin Y (2019) Red carbon dots: optical property regulations and applications. Mater Today 30:52–79
Jiang K, Hu S, Wang Y, Li Z, Lin H (2020) Photo-stimulated polychromatic room temperature phosphorescence of carbon dots. Small 16:2001909
Wang Z, Liu Y, Zhen S, Li X, Zhang W, Sun X, Xu B, Wang X, Gao Z, Meng X (2020) Gram-scale synthesis of 41% efficient single-component white-light-emissive carbonized polymer dots with hybrid fluorescence/phosphorescence for white light-emitting diodes. Adv Sci 7:1902688
Li H, Ye S, Guo J-Q, Kong J-T, Song J, Kang Z-H, Qu J-L (2019) The design of room-temperature-phosphorescent carbon dots and their application as a security ink. J Mater Chem C 7:10605–10612
Singaravelu CM, Deschanels X, Rey C, Causse J (2021) solid-state fluorescent carbon dots for fluorimetric sensing of Hg2+. ACS Appl Nano Mater 4:6386–6397
Lei X, Li D, Chen Y, Liu Q, Yan Q, Wang J, Han B, He G, An B (2022) RGB-multicolor fluorescent carbon dots by changing the reaction solvent type for white light-emitting diodes. New J Chem 46:4979–4982
Nguyen HA, Srivastava I, Pan D, Gruebele M (2020) Unraveling the fluorescence mechanism of carbon dots with sub-single-particle resolution. ACS Nano 14:6127–6137
Zheng Y, Arkin K, Hao J, Zhang S, Guan W, Wang L, Guo Y, Shang Q (2021) Multicolor carbon dots prepared by single-factor control of graphitization and surface oxidation for high-quality white light-emitting diodes. Adv Opt Mater 9:2100688
Wang J, Zheng J, Yang Y, Liu X, Qiu J, Tian Y (2022) Tunable full-color solid-state fluorescent carbon dots for light emitting diodes. Carbon 190:22–31
Bao L, Liu C, Zhang Z-L, Pang D-W (2015) Photoluminescence-tunable carbon nanodots: surface-state energy-gap tuning. Adv Mater 27:1663–1667
Bao L, Zhang Z-L, Tian Z-Q, Zhang L, Liu C, Lin Y, Qi B, Pang D-W (2011) Electrochemical tuning of luminescent carbon nanodots: from preparation to luminescence mechanism. Adv Mater 23:5801–5806
Hu S, Trinchi A, Atkin P, Cole I (2015) Tunable photoluminescence across the entire visible spectrum from carbon dots excited by white light. Angew Chem Int Ed 54:2970–2974
Pecora R (2000) Dynamic light scattering measurement of nanometer particles in liquids. J Nanopart Res 2:123–131
Zeng H-H, Wu H, Peng D, Liu F, Shi W-G, Qiu J-D (2018) Fast and selective detection of Cr(III) in environmental water samples using phosphovanadate Y(V0.2P0.8O4):Eu3+ fluorescence nanorods. ACS Sensors 3:1569–1575
Li Y, Liu K, Li W-J, Guo A, Zhao F-Y, Liu H, Ruan W-J (2015) Coordination polymer nanoarchitecture for nitroaromatic sensing by static quenching mechanism. J Phys Chem C 119:28544–28550
Zhai W, Wang C, Yu P, Wang Y, Mao L (2014) Single-layer MnO2 nanosheets suppressed fluorescence of 7-hydroxycoumarin: mechanistic study and application for sensitive sensing of ascorbic acid in vivo. Anal Chem 86:12206–12213
Madhu M, Chao C-M, Ke C-Y, Hsieh M-M, Tseng W-L (2022) Directed self-assembly of Ag+-deposited MoS2 quantum dots for colorimetric, fluorescent and fluorescence-lifetime sensing of alkaline phosphatase. Anal Bioanal Chem 414:1909–1919
Hoan BT, Van Huan P, Van HN, Nguyen DH, Tam PD, Nguyen KT, Pham V-H (2018) Luminescence of lemon-derived carbon quantum dot and its potential application in luminescent probe for detection of Mo6+ ions. Luminescence 33:545–551
Zhang J, Deng Y, Zhou Q, Qin P, Liu Y, Wang C (2017) Novel geochemistry-inspired method for the deep removal of vanadium from molybdate solution. J Hazard Mater 331:210–217
Li Z, Lu J, Wu S, Zhang G, Guan W, Zeng L, Li Q, Cao Z (2020) Sustainable extraction and complete separation of tungsten from ammonium molybdate solution by primary amine N1923. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:6914–6923
Yang C, Zhang J, Zhu X, Liu Y, Chen Y, Wang C (2020) Deep and efficient removal of vanadium from molybdate solution using magnetic γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 529:147060
Jelikić-Stankov M, Uskoković-Marković S, Holclajtner-Antunović I, Todorović M, Djurdjević P (2007) Compounds of Mo, V and W in biochemistry and their biomedical activity. J Trace Elem Med Bio 21:8–16
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2017) Molybdenum in natural waters: A review of occurrence, distributions and controls. Appl Geochem 84:387–432
Bolitschek J, Luidold S, O’Sullivan M (2018) A study of the impact of reduction conditions on molybdenum morphology. Int J Refract Met H 71:325–329
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21705083 and 22066019), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20202BABL203019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, HH., Huang, RX., Jiang, MQ. et al. Dual-mode sensing strategy based on carbon dots for sensitive and selective detection of molybdate ions. Microchim Acta 191, 187 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06275-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06275-7