Abstract
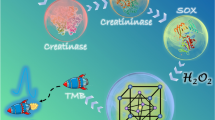
Mn3O4 nanozyme with good oxidase-like activity was successfully synthesized. The prepared Mn3O4 nanozyme can directly and effectively catalyze the oxidation of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) to generate green–blue-colored ox-TMB. Creatinine exhibits distinct inhibition effect on Mn3O4 nanozyme-catalyzed TMB colorimetric reaction system, leading to obvious color fading and absorbance intensity decrease of the reaction system. Furthermore, interference from uric acid can be effectively eliminated by regulating the pH of TMB-Mn3O4 colorimetric reaction system to pH 2.0. Then, a simple and bioenzyme-free colorimetric assay for the determination of creatinine was developed based on TMB-Mn3O4 colorimetric reaction. The linear detection range is from 100 to 800 μM and from 1 to 20 mM. The lowest limit of detection is 35.3 μM. Satisfied results are obtained for the determination of creatinine in real urine and sweat samples. This work provides the synthesis of a good oxidase-like nanozyme Mn3O4 and presents the fabrication of an effective nanozyme-based bioenzyme-free colorimetric assay for the determination of creatinine.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supplementary Information.
References
Levey AS, Inker LA, Coresh J (2015) Chronic kidney disease in older people. JAMA 314:557–558
Kellum JA, Romagnani P, Ashuntantang G, Ronco C, Zarbock A, Anders HJ (2021) Acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers 7:52
Kashani K, Rosner MH, Ostermann M (2020) Creatinine: from physiology to clinical application. Eur J Intern Med 72:9–14
Cánovas R, Cuartero M, Crespo GA (2019) Modern creatinine (bio)sensing: challenges of point-of-care platforms. Biosens Bioelectron 130:110–124
Fakrogha PE, Ntuen N, Oko-Jaja R, Duru U, Harry AM, David-West M, Amadi O, Nonju TI, Owhonda G, Ohiri J, Alasia DD, Izuchukwu AD, Erekosima I, Lewis D, Wokoma FS, Emem-Chioma PC, Poulikakos D (2022) Evaluation and use of point-of-care creatinine for detection of acute kidney injury in nigeria. Kidney Int Rep 7:1439–1440
Li Y, Luo L, Nie M, Davenport A, Li Y, Li B, Choy K-L (2022) A graphene nanoplatelet-polydopamine molecularly imprinted biosensor for ultratrace creatinine detection. Biosens Bioelectron 216:114638
An JN, Kim J-K, Lee H-S, Kim SG, Kim HJ, Song YR (2022) Serum cystatin C to creatinine ratio is associated with sarcopenia in non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease. Kidney Res Clin Pract 41:580–590
Hanif S, John P, Gao W, Saqib M, Qi L, Xu G (2016) Chemiluminescence of creatinine/H2O2/Co2+ and its application for selective creatinine detection. Biosens Bioelectron 75:347–351
Karn-orachai K, Ngamaroonchote A (2021) Role of polyelectrolyte multilayers over gold film for selective creatinine detection using Raman spectroscopy. Appl Surf Sci 546:149092
Yen T-A, Dahal KS, Lavine B, Hassan Z, Gamagedara S (2018) Development and validation of high performance liquid chromatographic method for determination of gentisic acid and related renal cell carcinoma biomarkers in urine. J Microchem 137:85–89
Jen JF, Hsiao S-L, Liu K-H (2002) Simultaneous determination of uric acid and creatinine in urine by an eco-friendly solvent-free high performance liquid chromatographic method. Talanta 58:711–717
Chiou WL, Pu FS, Prueksaritanont T (1983) Creatinine. XIII: micro high-performance liquid chromatographic assay of creatinine in biological fluids using fixed- or variable-wavelength UV detector. J Chromatogr A 277:436–438
Lad U, Khokhar S, Kale GM (2008) Electrochemical creatinine biosensors. Anal Chem 80:7910–7917
Corba A, Sierra AF, Blondeau P, Giussani B, Riu J, Ballester P, Andrade FJ (2022) Potentiometric detection of creatinine in the presence of nicotine: molecular recognition, sensing and quantification through multivariate regression. Talanta 246:123473
Saidi T, Moufid M, Zaim O, El Bari N, Bouchikhi B (2018) Voltammetric electronic tongue combined with chemometric techniques for direct identification of creatinine level in human urine. Measurement 115:178–184
Li J, Li Z, Dou Y, Su J, Shi J, Zhou Y, Wang L, Song S, Fan C (2021) A nano-integrated microfluidic biochip for enzyme-based point-of-care detection of creatinine. ChemComm 57:4726–4729
Liang L, Xiong Y, Duan Y, Zuo W, Liu L, Ye F, Zhao S (2022) Colorimetric detection of creatinine based on specifically modulating the peroxidase-mimicking activity of Cu-Fenton system. Biosens Bioelectron 206:114121
Lewińska I, Speichert M, Granica M, Tymecki Ł (2021) Colorimetric point-of-care paper-based sensors for urinary creatinine with smartphone readout. Sens Actuators B Chem 340:129915
He Y, Zhang X, Yu H (2015) Gold nanoparticles-based colorimetric and visual creatinine assay. Microchim Acta 182:2037–2043
Sergeyeva TA, Gorbach LA, Piletska EV, Piletsky SA, Brovko OO, Honcharova LA, Lutsyk OD, Sergeeva LM, Zinchenko OA, El’skaya AV, (2013) Colorimetric test-systems for creatinine detection based on composite molecularly imprinted polymer membranes. Anal Chim Acta 770:161–168
Cheng J, Guo J, Li X, Guo J (2023) A smartphone-connected point-of-care photochemical biosensor for the determination of whole blood creatinine by differential optical signal readout. Biosens Bioelectron 235:115410
Tseng CC, Yang RJ, Ju WJ, Fu LM (2018) Microfluidic paper-based platform for whole blood creatinine detection. Chem Eng J 348:117–124
Piéroni L, Delanaye P, Boutten A, Bargnoux A-S, Rozet E, Delatour V, Carlier M-C, Hanser A-M, Cavalier E, Froissart M, Cristol J-P (2011) A multicentric evaluation of IDMS-traceable creatinine enzymatic assays. Clin Chim Acta 412:2070–2075
Junge W, Wilke B, Halabi A, Klein G (2004) Determination of reference intervals for serum creatinine, creatinine excretion and creatinine clearance with an enzymatic and a modified Jaffé method. Clin Chim Acta 344:137–148
Wang X, Hu Y, Wei H (2016) Nanozymes in bionanotechnology: from sensing to therapeutics and beyond. Inorg Chem Front 3:41–60
Gupta A, Das R, Yesilbag Tonga G, Mizuhara T, Rotello VM (2018) Charge-switchable nanozymes for bioorthogonal imaging of biofilm-associated infections. ACS Nano 12:89–94
Liang M, Yan X (2019) Nanozymes: from new concepts, mechanisms, and standards to applications. Acc Chem Res 52:2190–2200
Wu J, Li S, Wei H (2018) Multifunctional nanozymes: enzyme-like catalytic activity combined with magnetism and surface plasmon resonance. Nanoscale Horiz 3:367–382
Jiang D, Ni D, Rosenkrans ZT, Huang P, Yan X, Cai W (2019) Nanozyme: new horizons for responsive biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev 48:3683–3704
Ai Y, Hu ZN, Liang X, Hb S, Xin H, Liang Q (2021) Recent advances in nanozymes: from matters to bioapplications. Adv Funct Mater 32:2110432
Zhang XD, Huang YM (2015) Evaluation of the antioxidant activity of phenols and tannic acid determination with Mn3O4 nano-octahedrons as an oxidase mimic. Anal Methods 7:8640–8646
Huang L, Qin S, Xu Y, Cheng S, Yang J, Wang Y (2023) Enzyme-free colorimetric detection of uric acid on the basis of MnO2 nanosheets-mediated oxidation of 3, 3′, 5, 5′- tetramethylbenzidine. Microchem J 190:108719
Yang W, Fei J, Xu W, Jiang H, Sakran M, Hong J, Zhu W, Zhou X (2022) A biosensor based on the biomimetic oxidase Fe3O4@MnO2 for colorimetric determination of uric acid. Colloids Surf B 212:112347
Wang JJ, Wang JL, Zhou P, Tao H, Wang XL, Wu YG (2020) Oligonucleotide-induced regulation of the oxidase-mimicking activity of octahedral Mn3O4 nanoparticles for colorimetric detection of heavy metals. Microchim Acta 187:1–11
Guan J, Xiong Y, Wang M, Liu Q, Chen X (2024) A novel functionalized CdTe@MOFs based fluorometric and colorimetric biosensor for dual-readout assay of creatinine. Sens Actuators B-Chem 399:134842
Kai K, Yoshida Y, Kageyama H, Saito G, Ishigaki T, Furukawa Y, Kawamata J (2008) Room-temperature synthesis of manganese oxide monosheets. J Am Chem Soc 130:15938–15943
Singh N, Savanur MA, Srivastava S, D’Silva P, Mugesh G (2017) A redox modulatory Mn3O4 nanozyme with multi-enzyme activity provides efficient cytoprotection to human cells in a parkinson’s disease model. Angew Chem Int Ed 56:14267–14271
Cao S, Han N, Han J, Hu Y, Fan L, Zhou C, Guo R (2016) Mesoporous hybrid shells of carbonized polyaniline/Mn2O3 as non-precious efficient oxygen reduction reaction catalyst. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:6040–6050
Moses Ezhil Raj A, Victoria SG, Jothy VB, Ravidhas C, Wollschläger J, Suendorf M, Neumann M, Jayachandran M, Sanjeeviraja C (2010) XRD and XPS characterization of mixed valence Mn3O4 hausmannite thin films prepared by chemical spray pyrolysis technique. Appl Surf Sci 256:2920–2926
Liu Y, Li H, Guo B, Wei L, Chen B, Zhang Y (2017) Gold nanoclusters as switch-off fluorescent probe for detection of uric acid based on the inner filter effect of hydrogen peroxide-mediated enlargement of gold nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 91:734–740
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by NSAF (Grant No. U2230117), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (PA2022GDSK0044) and the Undergraduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (X202310359291).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
The experimental protocol was approved by the Research Ethics committee of Hefei University of Technology, China (Project No. U2230117).
Informed consent
All participants provided written informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Shen, N., Xi, Y. et al. Bioenzyme-free colorimetric assay for creatinine determination based on Mn3O4 nanoparticles catalyzed oxidation of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine. Microchim Acta 191, 44 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06129-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06129-8