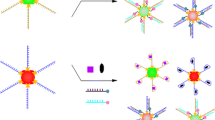
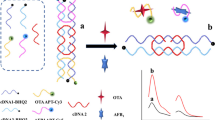
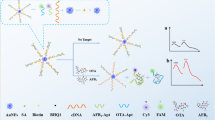
Abstract
A Fe/Zr bimetal-organic framework (ZrFe-MOF) is utilized to establish a ratiometric fluorescent aptasensor for the determination of tetrodotoxin (TTX). The multifunctional ZrFe-MOF possesses inherent fluorescence at 445 nm wavelength, peroxidase-mimetic activity, and specific recognition and adsorption capabilities for aptamers, owing to its organic ligand, and Fe and Zr nodes. The peroxidation of o-phenylenediamine (OPD) substrate generates fluorescent 2,3-diaminophenazine (OPDox) at 555 nm wavelength, thus quenching the inherent fluorescence of ZrFe-MOF because of the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) effect. TTX aptamers, which are absorbed on the material surface without immobilization or fluorescent labeling, inhibit the peroxidase-mimetic activity of ZrFe-MOF. It causes the decreased OPDox fluorescence at 555 nm wavelength and the inverse restoration of ZrFe-MOF fluorescence at 445 nm wavelength. With TTX, the aptamers specifically bind to TTX, triggering rigid complex release from ZrFe-MOF surface and reactivating its peroxidase-mimetic activity. Consequently, the two fluorescence signals exhibit opposite changes. Employing this ratiometric strategy, the determination of TTX is achieved with a detection limit of 0.027 ng/mL and a linear range of 0.05–500 ng/mL. This aptasensor also successfully determines TTX concentrations in puffer fish and clam samples, demonstrating its promising application for monitoring trace TTX in food safety.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Akopian AN, Sivilotti L, Wood JN (1996) A tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-gated sodium channel expressed by sensory neurons. Nature 379(6562):257–262. https://doi.org/10.1038/379257a0
Bane V, Lehane M, Dikshit M, O’Riordan A, Furey A (2014) Tetrodotoxin: chemistry, toxicity, source, distribution and detection. Toxins 6(2):693–755. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6020693
Li Y, Xu X, Liu L, Kuang H, Xu L, Xu C (2020) A gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of tetrodotoxin. Analyst 145(6):2143–2151. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0an00170h
Ling S, Chen QA, Zhang Y, Wang R, Jin N, Pang J, Wang S (2015) Development of ELISA and colloidal gold immunoassay for tetrodotoxin detetcion based on monoclonal antibody. Biosens Bioelectron 71:256–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.04.049
Rodriguez P, Alfonso A, Vale C, Alfonso C, Vale P, Tellez A, Botana LM (2008) First toxicity report of tetrodotoxin and 5,6,11-trideoxyTTX in the trumpet shell Charonia lampas lampas in Europe. Anal Chem 80(14):5622–5629. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac800769e
Chen L, Qiu J, Tang Y, Xu J, Huang S, Liu Y, Ouyang G (2017) Rapid in vivo determination of tetrodotoxin in pufferfish (fugu) muscle by solid-phase microextraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 171:179–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.04.078
Rey V, Botana AM, Antelo A, Alvarez M, Botana LM (2018) Rapid analysis of paralytic shellfish toxins and tetrodotoxins by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry using a porous graphitic carbon column. Food Chem 269:166–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.07.008
Liu S, Huo Y, Li G, Huang L, Wang T, Gao Z (2023) Aptamer-controlled reversible colorimetric assay: high-activity bimetallic organic frameworks for the efficient sensing of marine biotoxins. Chem Eng J 469:144027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.144027
Shen H, Zhang S, Fu Q, Xiao W, Wang S, Yu S, Xiao M, Bian H, Tang Y (2017) A membrane-based fluorescence-quenching immunochromatographic sensor for the rapid detection of tetrodotoxin. Food Control 81:101–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.06.001
Leonardo S, Kiparissis S, Rambla-Alegre M, Almarza S, Roque A, Andree KB, Christidis A, Flores C, Caixach J, Campbell K, Elliott CT, Aligizaki K, Diogène J, Campàs M (2019) Detection of tetrodotoxins in juvenile pufferfish Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) from the North Aegean Sea (Greece) by an electrochemical magnetic bead-based immunosensing tool. Food Chem 290:255–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.03.148
Dillon M, Zaczek-Moczydlowska MA, Edwards C, Turner AD, Miller PI, Moore H, McKinney A, Lawton L, Campbell K (2021) Current trends and challenges for rapid SMART diagnostics at point-of-site testing for marine toxins. Sensors 21(7):2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21072499
Wang Q, Yang Q, Wu W (2020) Ensuring seafood safe to spoon: a brief review of biosensors for marine biotoxin monitoring. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 62(9):2495–2507. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1854170
Zhao Y, Li L, Yan X, Wang L, Ma R, Qi X, Wang S, Mao X (2022) Emerging roles of the aptasensors as superior bioaffinity sensors for monitoring shellfish toxins in marine food chain. J Hazard Mater 421:126690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126690
Zhao L, Huang Y, Dong Y, Han X, Wang S, Liang X (2018) Aptamers and aptasensors for highly specific recognition and sensitive detection of marine biotoxins: recent advances and perspectives. Toxins 10(11):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110427
Mohan B, Priyanka SG, Chauhan A, Pombeiro AJL, Ren P (2023) Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) based luminescent and electrochemical sensors for food contaminant detection. J Hazard Mater 453:131324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131324
Yu K, Wei T, Li Z, Li J, Wang Z, Dai Z (2020) Construction of molecular sensing and logic systems based on site-occupying effect-modulated MOF–DNA interaction. J Am Chem Soc 142(51):21267–21271. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c10442
Xue W, Wang Y, Guo L, Zhang H (2023) Zr-MOF functionalized nanochannels: application to regenerative and sensitive electrochemical aptasensing platform. Sens Actuat B: Chem 381:133455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2023.133455
Rasheed T, Nabeel F (2019) Luminescent metal-organic frameworks as potential sensory materials for various environmental toxic agents. Coord Chem Rev 401:213065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2019.213065
Li G, Liu S, Huo Y, Zhou H, Li S, Lin X, Kang W, Li S, Gao Z (2022) “Three-in-one” nanohybrids as synergistic nanozymes assisted with exonuclease I amplification to enhance colorimetric aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of kanamycin. Anal Chim Acta 1222:340178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2022.340178
Luo L, Ou Y, Yang Y, Liu G, Liang Q, Ai X, Yang S, Nian Y, Su L, Wang J (2022) Rational construction of a robust metal-organic framework nanozyme with dual-metal active sites for colorimetric detection of organophosphorus pesticides. J Hazard Mater 423:127253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127253
Cai G, Yan P, Zhang L, Zhou H, Jiang H (2021) Metal–organic framework-based hierarchically porous materials: synthesis and applications. Chem Rev 121(20):12278–12326. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00243
Feng D, Gu Z, Li J, Jiang H, Wei Z, Zhou H (2012) Zirconium-metalloporphyrin PCN-222: mesoporous metal-organic frameworks with ultrahigh stability as biomimetic catalysts. Angew Chem Int Ed 51(41):10307–10310. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201204475
Kandiah M, Nilsen MH, Usseglio S, Jakobsen S, Olsbye U, Tilset M, Larabi C, Quadrelli EA, Bonino F, Lillerud KP (2010) Synthesis and stability of tagged UiO-66 Zr-MOFs. Chem Mater 22(24):6632–6640. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm102601v
Kulandaivel S, Chen HT, Lin CH, Yeh YC (2023) Exploring the potential of iron-based metal-organic frameworks as peroxidase nanozymes for glucose detection with various secondary building units. J Mater Chem B 11(43):10362–10368. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3tb00981e
Wang Y, Tang W, Li X, Wei D (2021) Improving the electrocatalytic activity of NiFe bimetal-organic framework toward oxygen evolution reaction by Zr doping. Electrochim Acta 381:138292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2021.138292
Peterson GW, Mahle JJ, DeCoste JB, Gordon WO, Rossin JA (2016) Extraordinary NO2 removal by the metal-organic framework UiO-66-NH2. Angew Chem Int Ed 55(21):6235–6238. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201601782
Amiripour F, Ghasemi S, Azizi SN (2022) Forster resonance energy transfer-based molecularly imprinted polymer/amine-functionalized metal-organic framework nanocomposite for trace level detection of 4-nitrophenol. Anal Chim Acta 1202:339638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2022.339638
Huo Y, Liu S, Gao Z, Ning B, Wang Y (2021) State-of-the-art progress of switch fluorescence biosensors based on metal-organic frameworks and nucleic acids. Microchim Acta 188(5):168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04827-9
Zhao M, Wang Y, Ma Q, Huang Y, Zhang X, Ping J, Zhang Z, Lu Q, Yu Y, Xu H, Zhao Y, Zhang H (2015) Ultrathin 2D metal-organic framework nanosheets. Adv Mater 27(45):7372–7378. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201503648
Sun X, Wang Y, Zhang L, Liu S, Zhang M, Wang J, Ning B, Peng Y, He J, Hu Y, Gao Z (2020) CRISPR-Cas9 triggered two-step isothermal amplification method for E. coli O157:H7 detection based on a metal–organic framework platform. Anal Chem 92(4):3032–3041. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04162
Liu S, Huo Y, Deng S, Li G, Li S, Huang L, Ren S, Gao Z (2022) A facile dual-mode aptasensor based on AuNPs@MIL-101 nanohybrids for ultrasensitive fluorescence and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection of tetrodotoxin. Biosens Bioelectron 201:113891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113891
Kalimuthu P, Kim Y, Subbaiah MP, Kim D, Jeon BH, Jung J (2022) Comparative evaluation of Fe-, Zr-, and La-based metal-organic frameworks derived from recycled PET plastic bottles for arsenate removal. Chemosphere 294:133672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133672
Zhang M, Wang Y, Wu P, Wang W, Cheng Y, Huang L, Bai J, Peng Y, Ning B, Gao Z, Liu B (2020) Development of a highly sensitive detection method for TTX based on a magnetic bead-aptamer competition system under triple cycle amplification. Anal Chim Acta 1119:18–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.04.050
Luengo C, Brigante M, Antelo J, Avena M (2006) Kinetics of phosphate adsorption on goethite: comparing batch adsorption and ATR-IR measurements. J Coll Interf Sci 300(2):511–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2006.04.015
Dou X, Xu S, Jiang Y, Ding Z, Xie J (2023) Aptamers-functionalized nanoscale MOFs for saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin sensing in sea foods through FRET. Spectrochim Acta, Part A 284:121827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2022.121827
Fu J, Zhou S, Zhao P, Wu X, Tang S, Chen S, Yang Z, Zhang Z (2022) A dual-response ratiometric fluorescence imprinted sensor based on metal-organic frameworks for ultrasensitive visual detection of 4-nitrophenol in environments. Biosens Bioelectron 198:113848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113848
Shen Y, Wei Y, Zhu C, Cao J, Han D-M (2022) Ratiometric fluorescent signals-driven smartphone-based portable sensors for onsite visual detection of food contaminants. Coord Chem Rev 458:214442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214442
Long F, Zhang M, Yuan J, Du J, Ma A, Pan J (2020) A simple, versatile, and automated pulse-diffusion-focusing strategy for sensitive milliliter-level-injection HILIC-MS/MS analysis of hydrophilic toxins. J Hazard Mater 392:122318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122318
Zhou Y, Li Y, Lu S, Ren H, Li Z, Zhang Y, Pan F, Liu W, Zhang J, Liu Z (2010) Gold nanoparticle probe-based immunoassay as a new tool for tetrodotoxin detection in puffer fish tissues. Sens Actuat B: Chem 146(1):368–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2010.02.049
Reverté L, Campàs M, Yakes BJ, Deeds JR, Katikou P, Kawatsu K, Lochhead M, Elliott CT, Campbell K (2017) Tetrodotoxin detection in puffer fish by a sensitive planar waveguide immunosensor. Sens Actuat B: Chem 253:967–976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.06.181
Reverté L, Campbell K, Rambla-Alegre M, Elliott CT, Diogène J, Campàs M (2017) Immunosensor array platforms based on self-assembled dithiols for the electrochemical detection of tetrodotoxins in puffer fish. Anal Chim Acta 989:95–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.07.052
Zhang Y, Fan Y, Wu J, Wang X, Liu Y (2016) An amperometric immunosensor based on an ionic liquid and single-walled carbon nanotube composite electrode for detection of tetrodotoxin in pufferfish. J Agric Food Chem 64(36):6888–6894. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.6b02426
Shkembi X, Skouridou V, Svobodova M, Leonardo S, Bashammakh AS, Alyoubi AO, Campàs M, O’Sullivan CK (2021) Hybrid antibody–aptamer assay for detection of tetrodotoxin in pufferfish. Anal Chem 93(44):14810–14819. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c03671
Gu H, Duan N, Xia Y, Hun X, Wang H, Wang Z (2018) Magnetic separation-based multiple SELEX for effectively selecting aptamers against saxitoxin, domoic acid, and tetrodotoxin. J Agric Food Chem 66(37):9801–9809. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b02771
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFA0910200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sha Liu: methodology, investigation, validation, data curation, formal analysis, writing—original draft; Yapeng Huo: data curation, formal analysis, conceptualization, writing—original draft; Zhiyong Hu: investigation, validation, writing—original draft; Gaofang Cao: methodology, project administration, writing—original/reviewing and editing, supervision; Zhixian Gao: conceptualization, project administration, writing—original/reviewing and editing, funding acquisition, supervision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Huo, Y., Hu, Z. et al. A label-free ratiometric fluorescent aptasensor based on a peroxidase-mimetic multifunctional ZrFe-MOF for the determination of tetrodotoxin. Microchim Acta 191, 57 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06118-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06118-x