Abstract
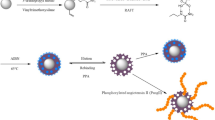
A new general approach called in situ digestion-assisted multi-template imprinting is proposed for preparation of phospho-specific molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. Through the novel templating strategy and controllable imprinting process, imprinted nanoparticles specific to the intact phosphoprotein and its phosphopeptides were synthesized. The prepared imprinted nanoparticles exhibited excellent specificity (cross reactivity < 10%), high affinity (10−6 M), high efficiency (47.5%), and good generality (both intact phosphoprotein and phosphopeptides). We also realized the fine tuning of the recognition at peptide level of the imprinted nanoparticles by adjusting the imprinting time. Based on the selective enrichment of the imprinted nanoparticles, the MS identification of both the intact phosphoprotein (Tau) and phosphopeptides (angiotensin II and peptides of Tau) in real complex samples could be achieved. Therefore, we believe that the in situ digestion-assisted multi-template imprinting strategy holds promising future in both phosphorylation analysis and proteomics applications.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blom N, Sicheritz-Ponten T, Gupta R, Gammeltoft S, Brunak S (2004) Prediction of post-translational glycosylation and phosphorylation of proteins from the amino acid sequence. Proteomics 11:1633–1649. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.200300771
Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, Macek B, Kumar C, Mortensen P, Mann M (2006) Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks. Cell 217:635–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026
Ptacek J, Devgan G, Michaud G, Zhu H, Zhu X, Fasolo J, Guo H, Jona G, Breitkreutz A, Sopko R, McCartney RR, Schmidt MC, Rachidi N, Lee SJ, Mah AS, Meng L, Stark MJ, Stern DF, De VC, Tyers M (2005) Global analysis of protein phosphorylation in yeast. Nature 438:679–684. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04187
Kalume DE, Molina H, Pandey A (2003) Tackling the phosphoproteome: Tools and strategies. Curr Opin Chem Biol 7:64–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1367-5931(02)00009-1
Hubbard MJ, Cohen P (1993) On target with a new mechanism for the regulation of protein phosphorylation. Trends Biochem Sci 18:172–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/0968-0004(93)90109-z
Graves JD, Krebs EG (1999) Protein phosphorylation and signal transduction. Pharmacol Ther 82:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0163-7258(98)00056-4
Van Simaeys D, Turek D, Champanhac C, Vaizer J, Sefah K, Zhen J, Sutphen R, Tan WH (2014) Identification of cell membrane protein stress-induced phosphoprotein 1 as a potential ovarian cancer biomarker using aptamers selected by cell systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment. Anal Chem 86:4521–4527. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac500466x
Chen IH, Xue L, Hsu CC, Paez SJ, Pan L, Andaluz H, Wendt MK, Lliuk AB, Zhu JK, Tao WA (2016) Phosphoproteins in extracellular vesicles as candidate markers for breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114:3175–3180. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1618088114
Iqbal K, Liu F, Gong CX, Grundke-Iqbal I (2010) Tau in Alzheimer disease and related tauopathies. Curr Alzheimer Res 7:656–64. https://doi.org/10.2174/156720510793611592
Fraser KB, Moehle MS, Alcalay RN, West AB (2016) Urinary LRRK2 phosphorylation predicts parkinsonian phenotypes in G2019S LRRK2 carriers. Neurology 86:994–999. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000002436
Riley NM, Coon JJ (2016) Phosphoproteomics in the age of rapid and deep proteome profiling. Anal Chem 88:74–94. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04123
Solari FA, Dell’Aica M, Sickmann A, Zahedi RP (2015) Why phosphoproteomics is still a challenge. Mol Biosyst 11:1487–1493. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5mb00024f
Li XS, Yuan BF, Feng YQ (2016) Recent advances in phosphopeptide enrichment: Strategies and techniques. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 78:70–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2015.11.001
Yaffe MB (2002) Phosphotyrosine-binding domains in signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:177–186. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm759
Li Y, Wang Y, Dong M, Zou HF, Ye ML (2017) Sensitive approaches for the assay of the global protein tyrosine phosphorylation in complex samples using a mutated SH2 domain. Anal Chem 89:2304–2311. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b03812
Wang MY, Deng CH, Li Y, Zhang XM (2014) Strengthening alginate/polyacrylamide hydrogels using various multivalent cations. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 21:10418–10422. https://doi.org/10.1021/am403966x
Chi A, Huttenhower C (2007) Analysis of phosphorylation sites on proteins from saccharomyces cerevisiae by electron transfer dissociation (ETD) mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:2193−2198. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0607084104
Larsen MR, Thingholm TE, Jensen ON, Roepstorff P, Jørgensen TJD (2005) Highly selective enrichment of phosphorylated peptides from peptide mixtures using titanium dioxide microcolumns. Mol Cell Proteomics 4:873–886. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.T500007-MCP200
Liu FJ, Wan H, Liu ZS, Wang HW, Mao JW, Ye ML, Zou HF (2016) Preparation of polypropylene spin tips filled with immobilized titanium(IV) ion monolithic adsorbent for robust phosphoproteome analysis. Anal Chem 88:5058–5064. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b00701
Qin WJ, Zhang WJ, Song LN, Zhang YJ, Qian XH (2010) Surface initiated atom transfer radical polymerization: Access to three dimensional wavelike polymer structure modified capillary columns for online phosphopeptide enrichment. Anal Chem 82:9461–9468. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac1021437
Zhou HJ, Ye ML, Dong J, Corrandini E, Cristobal A, Heck AJR, Zou HF, Mohanmmed S (2013) Robust phosphoproteome enrichment using monodisperse microsphere-based immobilized titanium (IV) ion affinity chromatography. Nat Protoc 8:461–480. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2013.010
Rush J, Moritz A, Lee KA, Guo A, Goss VL, Spek EJ, Zhang H, Zha XM, Polakiewicz RD, Comb MJ (2005) Immunoaffinity profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation in cancer cells. Nat Biotechnol 23:94–101. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1046
Oda Y, Nagasu T, Chait BT (2001) Enrichment analysis of phosphorylated proteins as a tool for probing the phosphoproteome. Nat Biotechnol 19:379–382. https://doi.org/10.1038/86783
Zhang Y, Liu RJ, Hu YL, Li GK (2009) Microwave heating in preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer beads for trace triazines analysis in complicated samples. Anal Chem 81:967–976. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac8018262
Yang HH, Zhang SQ, Yang W, Chen XL, Zhuang ZX, Xu JG, Wang XR (2004) Molecularly imprinted sol−gel nanotubes membrane for biochemical separations. J Am Chem Soc 126:4054–4055. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0389570
Zhang W, Liu W, Li P, Xiao HB, Wang H, Tang B (2014) A fluorescence nanosensor for glycoproteins with activity based on the molecularly imprinted spatial structure of the target and boronate affinity. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:12489–12493. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201405634
Kunath S, Panagiotopoulou M, Maximilien J, Marchyk N, Sänger J, Haupt K (2015) Cell and tissue imaging with molecularly imprinted polymers as plastic antibody mimics. Adv Healthc Mater 4:1322–1326. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201500145
Takeuchi T, Mori K, Sunayama H, Takano E, KitayamamY ST, Hirose Y, Inubushi S, Sasaki R, Tanino H (2020) Antibody-conjugated signaling nanocavities fabricated by dynamic molding for detecting cancers using small extracellular vesicle markers from tears. J Am Chem Soc 142:6617–6624. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b13874
Rangel PXM, Moroni E, Merlier F, Gheber LA, Vago R, Bui BTS, Haupt K (2020) Chemical antibody mimics inhibit cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion: A promising strategy for cancer therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed 59:2816–2822. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201910373
Emgenbroich M, Vilela F, Courtois J, Borrelli C, Hall AJ, Simanova A, Shinde S, Oxelbark J, Verhage J, Lorenzi DE, Irgum K, Lazraq I, Karim K, Sellergren B (2008) A phosphotyrosine-imprinted polymer receptor for the recognition of tyrosine phosphorylated peptides. Chem A Eur J 14:9516–9529. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.200801046
Helling S, Shinde S, Brosseron F, Schnabel A, Meyer HE, Marcus K, Sellergren B (2011) Ultratrace enrichment of tyrosine phosphorylated peptides on an imprinted polymer. Anal Chem 83:1862–1865. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac103086v
Chen J, Shinde S, Koch MH, Eisenacher M, Galozzi S, Lerari T, Barkovits K, Subedi P, Krüger R, Kuhlmann K, Sellergren B, Helling S, Marcus K (2015) Low-bias phosphopeptide enrichment from scarce samples using plastic antibodies. Sci Rep 5:11438. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11438
Emgenbroich M, Borrelli C, Shinde S, Lazraq I, Vilela F, Hall AJ, Oxelbark J, De Lorenzi E, Courtois J, Simanova A, Verhage J, Irgum K, Karim K, Sellergren B (2008) A phosphotyrosine-imprinted polymer receptor for the recognition of tyrosine phosphorylated peptides. Chem - Eur J 14:9516–9529. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.200801046
Li QS, Shen F, Zhang X, Hu YF, Ren XQ (2013) One-pot synthesis of phenylphosphonic acid imprinted polymers for tyrosine phosphopeptides recognition in aqueous phase. Anal Chim Acta 795:82–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.07.040
Chen Y, Li DJ, Bie ZJ, He XP, Liu Z (2016) Coupling of phosphate-imprinted mesoporous silica nanoparticles-based selective enrichment with matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry for highly efficient analysis of protein phosphorylation. Anal Chem 88:1447–1454. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04343
Li DY, Qin YP, Li HY, He XW, Li WY, Zhang YK (2015) A “turn-on” fluorescent receptor for detecting tyrosine phosphopeptide using the surface imprinting procedure and the epitope approach. Biosens Bioelectron 66:224–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.11.023
Chen Y, Li DJ, Bie ZJ, He XP, Liu Z (2016) Coupling of phosphate-imprinted mesoporous silica nanoparticles-based selective enrichment with matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry for highly efficient analysis of protein phosphorylation. Anal Chem 88:1447–1454. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04343
Zhao JL, He H, Guo ZC, Liu Z (2021) Molecularly imprinted and cladded nanoparticles provide better phosphorylation recognition. Anal Chem 93:16194–16202. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04070
Xing RR, Wang SS, Bie ZJ, He H, Liu Z (2017) Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers specific to glycoproteins, glycans and monosaccharides via boronate affinity controllable-oriented surface imprinting. Nat Protoc 12:964–987. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2017.015
Bie ZJ, Xing RR, He XP, Ma YY, Chen Y, Liu Z (2018) Precision imprinting of glycopeptides for facile preparation of glycan-specific artificial antibodies. Anal Chem 90:9845–9852. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b01903
Bie ZJ, Chen Y (2021) Selective analysis of interferon-alpha in human serum with boronate affinity oriented imprinting based plastic antibody. Talanta 230:122338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122338
Bie ZJ, Zhao WM, Lv ZY, Liu SL, Chen Y (2019) Preparation of salbutamol imprinted magnetic nanoparticles via boronate affinity oriented surface imprinting for the selective analysis of trace salbutamol residues. Analyst 144:3128–3135. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9AN00198K
Wagner U, Utton M, Gallo JM, Miller CCJ (1996) Cellular phosphorylation of tau by GSK-3 beta influences tau binding to microtubules and microtubule organisation. J Cell Sci 109:1537–1543. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.109.6.1537
Hanger DP, Noble W (2011) Functional implications of glycogen synthase kinase-3-mediated tau phosphorylation. Int J Alzheimer’s Dis 2011:352805. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/352805
Tan YJ, Sui DX, Wang WH, Kuo MH, Reid GE, Bruening ML (2013) Phosphopeptide enrichment with TiO2-modified membranes and investigation of tau protein phosphorylation. Anal Chem 85:5699–5706. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac400198n
Funding
The authors received financial support of the 512 Talent Cultivation Plan of Bengbu Medical College (by51202305), the Natural Science Research Project of Bengbu Medical college (2022byfy003), and the Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Educational Committee (2022AH051537, 2022AH051424, 2023AH030091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhao, X., Zhang, H. et al. In situ digestion-assisted multi-template imprinted nanoparticles for efficient analysis of protein phosphorylation. Microchim Acta 190, 490 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06081-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06081-7