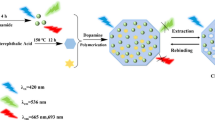
Abstract
Based on the designed inverted Y-shaped peptide and MXene nanocomposite (MXene-Au@ZIF-67), a ratiometric anti-pollution electrochemical biosensor was designed and applied to the detection of biomarkers in serum. Au@ZIF-67 inserted into the interior of MXene can not only prevent the accumulation of MXene but also provide a large amounts of binding sites for capturing biomolecules. A designed multifunctional Y-shaped peptide containing anchoring, antifouling, and recognition sequences was anchored onto MXene-Au@ZIF-67 through Au–S bonds. Electrochemical signal molecules, ferrocenecarboxylic acid (Fc) and methylene blue (MB), were modified to another end of multifunctional peptide and interior of MXene-Au@ZIF-67, respectively, to produce a ratiometric electrochemical signal. We selected prostate specific antigen (PSA) as the model compound. PSA specifically recognizes and cleaves the recognition segment in the Y-shaped peptide, and the signal of Fc is reduced, while the signal of MB remains unchanged. The ratiometric strategy endows the present biosensor high accuracy and sensitivity with a detection limit of 0.85 pg/mL. In addition, the sensing surface has good antifouling ability due to the antifouling sequence of the two branching parts of the Y-shaped peptide. More importantly, by replacing the recognition segment of peptides also other targets are accessible, indicating the potential application of the universal detection strategy to the detection of various biomarkers in clinical diagnosis.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Dejous C, Krishnan UM (2020) Sensors for diagnosis of prostate cancer: looking beyond the prostate specific antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 173:112790
Zheng K, Liu X, Liu H, Dong D, Li L, Jiang L, Huang M, Ding C (2021) Novel pH-triggered doxorubicin-releasing nanoparticles self-assembled by functionalized β-cyclodextrin and amphiphilic phthalocyanine for anticancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:10674–10688
He Y, Xie S, Yang X, Yuan R, Chai Y (2015) Electrochemical peptide biosensor based on in situ silver deposition for detection of prostate specific antigen. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:13360–13366
Roberts A, Tripathi PP, Gandhi S (2019) Graphene nanosheets as an electric mediator for ultrafast sensing of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor-a biomarker of cancer. Biosens Bioelectron 141:111398
Chikkaveeraiah BV, Bhirde AA, Morgan NY, Eden HS, Chen X (2012) Electrochemical immunosensors for detection of cancer protein biomarkers. ACS Nano 6:6546–6561
Qi H, Li M, Dong M, Ruan S, Gao Q, Zhang C (2014) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence peptide-based biosensor for the determination of prostate-specific antigen based on target-induced cleavage of peptide. Anal Chem 86:1372–1379
Wei B, Mao K, Liu N, Zhang M, Yang Z (2018) Graphene nanocomposites modified electrochemical aptamer sensor for rapid and highly sensitive detection of prostate specific antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 121:41–46
Matthew JA, Vincent CT, Richard BK (2010) Honeycomb carbon: a review of graphene. Chem Rev 110:132–145
Roberts A, Gandhi S (2022) A concise review on potential cancer biomarkers and advanced manufacturing of smart platform-based biosensors for early-stage cancer diagnostics. Biosensors Bioelectronics X 11:100178
Wang HB, Maiyalagan T, Wang X (2012) Review on recent progress in nitrogen-doped graphene: synthesis, characterization, and its potential applications. ACS Catal 2:781–794
Ji XY, Kong N, Wang JQ, Li WL (2018) A novel top-down synthesis of ultrathin 2D boron nanosheets for multimodal imaging-guided cancer therapy. Adv Mater 36:1803031
David C, Daniel LA, Akhilesh KG (2015) Two-dimensional nanomaterials for biomedical applications: emerging trends and future prospects. Adv Mater 45:7261–7284
Wang GX, Han R, Li Q, Han YF, Luo XL (2020) Electrochemical biosensors capable of detecting biomarkers in human serum with unique long-term antifouling abilities based on designed multifunctional peptides. Anal Chem 92:7186–7193
Gooding JJ (2019) Finally, a simple solution to biofouling. Nat Nanotechnol 14:1089–1090
Luo XL, Xu Q, James T, Davis JJ (2014) Redox and label-free array detection of protein markers in human serum. Anal Chem 86:5553–5558
Pino PD, Yang F, Pelaz B, Zhang Q (2016) Basic physicochemical properties of polyethylene glycol coated gold nanoparticles that determine their interaction with cells. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 18:5573–5577
Knop K, Hoogenboom R, Fischer D, Schubert US (2010) Poly(ethylene glycol) in drug delivery: pros and cons as well as potential alternatives. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 49:6288–6308
Luo XL, Xu MY, Freeman C, James T, Davis JJ (2013) Ultrasensitive label free electrical detection of insulin in neat blood serum. Anal Chem 85:4129–4134
Mi L, Jiang SY (2014) Integrated antimicrobial and nonfouling zwitterionic polymers. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 53:1746–1754
Wang JJ, Xu GY, Wang W, Xu SH, Luo XL (2015) Nitrite oxidation with copper–cobalt nanoparticles on carbon nanotubes doped conducting polymer PEDOT composite. Chemistry 9:1892–1897
Chen M, Han R, Wang WQ, Li Y, Luo XL (2021) Antifouling aptasensor based on self-assembled loop-closed peptides with enhanced stability for CA125 assay in complex biofluids. Anal Chem 93:13555–13563
Zhao SJ, Liu NZ, Wang WQ, Xu ZY, Wu YM, Luo XL (2021) An electrochemical biosensor for alpha-fetoprotein detection in human serum based on peptides containing isomer D-amino acids with enhanced stability and antifouling property. Biosens Bioelectron 190:113466
Wang WQ, Han R, Chen M, Luo XL (2021) Antifouling peptide hydrogel based electrochemical biosensors for highly sensitive detection of cancer biomarker HER2 in human serum. Anal Chem 93:7355–7361
Liu NZ, Ma YH, Han R, Lv SP, Wang PP, Luo XL (2021) Antifouling biosensors for reliable protein quantification in serum based on designed all-in-one branched peptides. Chem Commun (Camb) 57:777–780
Li Y, Wang L, Ding CF, Luo XL (2019) Highly selective ratiometric electrogenerated chemiluminescence assay of DNA methyltransferase activity via polyaniline and anti-fouling peptide modified electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 142:111553
Lin Y, Jia J, Yang R, Chen D, Wang J, Luo F, Guo L, Qiu B, Lin Z (2019) Ratiometric immunosensor for GP73 detection based on the ratios of electrochemiluminescence and electrochemical signal using DNA tetrahedral nanostructure as the carrier of stable reference signal. Anal Chem 91:3717–3724
Xu Y, Wang Z, Ding CF, Luo XL (2020) Ratiometric antifouling electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on bi-functional peptides and low toxic quantum dots. Sens Actuators B 322:128613
Hao QX, Wang L, Niu SY, Ding CF, Luo XL (2020) Ratiometric electrogenerated chemiluminescence sensor based on a designed antifouling peptide for the detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Anal Chim Acta 1136:134–140
Shao K, Wang B, Nie A, Ye SY, Ma J, Li ZH, Lv ZC, Han HY (2018) Target-triggered signal-on ratiometric electrochemiluminescence sensing of PSA based on MOF/Au/G-quadruplex. Biosens Bioelectron 118:160–166
Chouhan RS, Shah M, Prakashan D, Kolhe RPRP, Gandhi S (2023) Emerging trends and recent progress of MXene as a promising 2D material for point of care (POC) diagnostics. Diagnostics 13:697
Yuri N, Yasuhiko I, Masato U, Sachiro K (2020) Surfaces immobilized with oligo-prolines prevent protein adsorption and cell adhesion. J Mater Chem B 8:2233–2237
Hostert JD, Loney CN, Pramounmat N, Yan K, Su ZH, Renner JN (2021) Self-assembly and rearrangement of a polyproline II helix peptide on gold. Langmuir 37:6115–6122
Schnitzer T, Paenurk E, Trapp N, Gershoni-Poranne R, Wennemers H (2021) Peptide-metal frameworks with metal strings guided by dispersion interactions. J Am Chem Soc 143:644–648
Denmeade SR, Lou W, Lövgren J, Malm J, Lilja H, Isaacs JT (1997) Specific and efficient peptide substrates for assaying the proteolytic activity of prostate-specific antigen. Cancer Res 57:4924–4930
Zhao N, He YQ, Mao X, Sun YH, Zhang XB, Li CZ, Lin YH, Liu GD (2010) Electrochemical assay of active prostate-specific antigen (PSA) using ferrocene-functionalized peptide probes. Electrochem Commun 12:471–474
Alhabeb M, Maleski K, Anasori B, Lelyukh P, Clark L, Sin S, Gogotsi Y (2017) Guidelines for synthesis and processing of two-dimensional titanium carbide (Ti3C2Tx MXene). Chem Mater 29:7633–7644
Becerra J, Nguyen D-T, Gopalakrishnan V-N, Do T-O (2020) Plasmonic Au nanoparticles incorporated in the zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-67) for the efficient sunlight-driven photoreduction of CO2. ACS Appl Energy Mater 3:7659–7665
Liu L, Hao Y-J, Li Z, Chen C, Wu M-Y, Feng S (2019) Visible colorimetric sensing of cysteine based on Au nanoparticle modified ZIF-67. Chem Pap 74:1839–1847
Zhang YJ, Wang L, Zhang NN, Zhou ZJ (2018) Adsorptive environmental applications of MXene nanomaterials: a review. RSC Adv 8:19895
Zhang RY, Liu J, Li YC (2019) MXene with great adsorption ability toward organic dye: an excellent material for constructing a ratiometric electrochemical sensing platform. ACS Sens 4:2058–2064
Funding
The authors greatly acknowledge the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22074074), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2020MB065), and the Major Scientific and Technological Innovation Project of Shandong Province (2021ZDSYS30).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YD: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, and writing—original draft. SZ: conceptualization, supervision, validation, and visualization. XZ: investigation, validation, and supervision. MD: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, and methodology. CD: conceptualization and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• A multifunctional Y-shaped peptide containing anchoring, antifouling, and recognition sequences was designed.
• Electrochemical signal molecules, ferrocenecarboxylic acid (Fc) and methylene blue (MB), were used to produce ratiometric electrochemical signal.
• An antifouling ratiometric biosensor was constructed and can be used for the detection in complex samples with high sensitivity and accurate.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Y., Zhang, S., Zang, X. et al. Ratiometric antifouling electrochemical biosensors based on designed Y-shaped peptide and MXene loaded with Au@ZIF-67 and methylene blue. Microchim Acta 191, 5 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06079-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06079-1