Abstract
A competitive fluorescent lateral flow assay (CFLFA) is proposed for direct, ultrasensitive, quantitative detection of common pesticides imidacloprid (IMI) and carbendazim (CBZ) in complex food samples by using silica–core multilayered quantum dot nanobeads (SiO2-MQB) as liquid fluorescent tags. The SiO2-MQB nanostructure comprises a 200-nm SiO2 core and a shell of hundreds of carboxylated QDs (excitation/emission maxima ~365/631 nm), and can generate better stability, superior dispersibility, and higher luminescence than traditional fluorescent beads, greatly improving the sensitivity of current LFA methods for pesticides. Moreover, using liquid SiO2-MQB directly instead of via the conjugate pad both simplifies the structure of LFA system and improves the efficiency of immunobinding reactions between nanotags and the targets. Applying these methods, the established CFLFA realized the stable and accurate detection of IMI and CBZ in 12 min, with detection limits down to 1.94 and 14.79 pg/mL, respectively. The SiO2-MQB-CFLFA is practicable for application to real food samples (corn, apple, cucumber, and cabbage), and undoubtedly a promising and low-cost tool for on-site monitoring of trace pesticide residues.
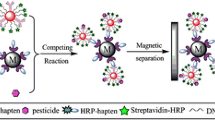
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
Data is contained within the article.
References
Li ZR, Lin H, Wang L, Cao LM, Sui JX, Wang KQ (2022) Optical sensing techniques for rapid detection of agrochemicals: strategies, challenges, and perspectives. Sci Total Environ 838:156515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156515
Bilal M, Iqbal HMN, Barcelo D (2019) Persistence of pesticides-based contaminants in the environment and their effective degradation using laccase-assisted biocatalytic systems. Sci Total Environ 695:133896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133896
Craddock HA, Huang D, Turner PC, Quiros-Alcala L, Payne-Sturges DC (2019) Trends in neonicotinoid pesticide residues in food and water in the United States, 1999-2015. Environ Health 18:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-018-0441-7
He J, Li H, Zhang L, Zhi X, Li X, Wang X, Feng Z, Shen G, Ding X (2021) Silver microspheres aggregation-induced Raman enhanced scattering used for rapid detection of carbendazim in Chinese tea. Food Chem 339:128085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128085
Narenderan ST, Meyyanathan SN, Babu B (2020) Review of pesticide residue analysis in fruits and vegetables. Pre-treatment, extraction and detection techniques. Food Res Int 133:109141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109141
Ding XK, Zhang W, Cheng D, He JZ, Yang KL (2012) Oligopeptides functionalized surface plasmon resonance biosensors for detecting thiacloprid and imidacloprid. Biosens Bioelectron 35:271–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.02.060
Aslantas S, Golge O, González-Curbelo MÁ, Kabak B (2023) Determination of 355 Pesticides in Lemon and Lemon Juice by LC-MS/MS and GC-MS/MS. Foods 12:1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091812
Lopez-Ruiz R, Romero-Gonzalez R, Martin-Torres S, Jimenez-Carvelo AM, Cuadros-Rodriguez L, Frenich AG (2022) Applying an instrument-agnostizing methodology for the standardization of pesticide quantitation using different liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry platforms: A case study. J Chromatogr A 1664:462791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2021.462791
Ramezani S, Mahdavi V, Gordan H, Rezadoost H, Conti GO, Khaneghah AM (2022) Determination of multi-class pesticides residues of cow and human milk samples from Iran using UHPLC-MS/MS and GC-ECD: A probabilistic health risk assessment. Environ Res 208:112730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.112730
Tang X, Zhang Q, Zhang Z, Ding X, Jiang J, Zhang W, Li P (2019) Rapid, on-site and quantitative paper-based immunoassay platform for concurrent determination of pesticide residues and mycotoxins. Anal Chim Acta 1078:142–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.06.015
Wang W, Yu Q, Zheng S, Li J, Wu T, Wang S, Wang C, Gu B (2023) Ultrasensitive and simultaneous monitoring of multiple small-molecule pollutants on an immunochromatographic strip with multilayered film-like fluorescent tags. Sci Total Environ 878:162968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162968
Chen X, Ding L, Huang X, Xiong Y (2022) Tailoring noble metal nanoparticle designs to enable sensitive lateral flow immunoassay. Theranostics 12:574–602. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.67184
Mahmoudi T, de la Guardia M, Baradaran B (2020) Lateral flow assays towards point -of -care cancer detection: a review of current progress and future trends. Trac-Trend Anal Chem 125:115842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.115842
Wang W, Yang X, Rong Z, Tu Z, Zhang X, Gu B, Wang C, Wang S (2022) Introduction of graphene oxide-supported multilayer-quantum dots nanofilm into multiplex lateral flow immunoassay: a rapid and ultrasensitive point-of-care testing technique for multiple respiratory viruses. Nano Res 16:3063–3073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5043-6
Huang L, Zhang Y, Liao T, Xu K, Jiang C, Zhuo D, Wang Y, Wen H-M, Wang J, Ao L et al (2021) Compact magneto-fluorescent colloids by hierarchical assembly of dual-components in radial channels for sensitive point-of-care immunoassay. Small 17:2100862. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202100862
Parolo C, Sena-Torralba A, Bergua JF, Calucho E, Fuentes-Chust C, Hu L, Rivas L, Álvarez-Diduk R, Nguyen EP, Cinti S, Quesada-González D (2020) Tutorial: design and fabrication of nanoparticle-based lateral-flow immunoassays. Nat Protoc 15:3788–3816. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-020-0357-x
Tu J, Wu T, Yu Q, Li J, Zheng S, Qi K, Sun G, Xiao R, Wang C (2023) Introduction of multilayered magnetic core-dual shell SERS tags into lateral flow immunoassay: a highly stable and sensitive method for the simultaneous detection of multiple veterinary drugs in complex samples. J Hazard Mater 448:130912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.130912
Wang C, Wang C, Li J, Tu Z, Gu B, Wang S (2022) Ultrasensitive and multiplex detection of four pathogenic bacteria on a bi-channel lateral flow immunoassay strip with three-dimensional membrane-like SERS nanostickers. Biosens Bioelectron 214:114525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114525
Guan T, Shen Y, Jiang Z, Wang J, Zhang S, Koidis A, Yao X, Yan Y, Lei H (2022) Facile fabrication of highly quantum dot/AuNP-loaded tags for a dual-modal colorimetric/reversed ratiometric fluorescence immunochromatographic assay. Anal Chem 94:13463–13472. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c02544
Wang C, Cheng X, Liu L, Zhang X, Yang X, Zheng S, Rong Z, Wang S (2021) Ultrasensitive and simultaneous detection of two specific SARS-CoV-2 antigens in human specimens using direct/enrichment dual-mode fluorescence lateral flow immunoassay. Acs Appl Mater Inter 13:40342–40353. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c11461
Wu Y, Sun J, Huang X, Lai W, Xiong Y (2021) Ensuring food safety using fluorescent nanoparticles-based immunochromatographic test strips. Trends Food Sci Tech 118:658–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.10.025
Huang L, Jin J, Ao L, Jiang C, Zhang Y, Wen HM, Wang J, Wang H, Hu J (2020) Hierarchical plasmonic-fluorescent labels for highly sensitive lateral flow immunoassay with flexible dual-modal switching. ACS Appl Mater Inter 12:58149–58160. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c18667
Yang X, Yu Q, Cheng X, Wei H, Zhang X, Rong Z, Wang C, Wang S (2023) Introduction of multilayered dual-signal nanotags into a colorimetric-fluorescent coenhanced immunochromatographic assay for ultrasensitive and flexible monitoring of SARS-CoV-2. ACS Appl Mater Inter 15:12327–12338. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c21042
Gao F, Liu Y, Lei C, Liu C, Song H, Gu Z, Jiang P, Jing S, Wan J, Yu C (2021) The role of dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles' size for quantum dots enrichment and lateral flow immunoassay performance. Small Methods 5:2000924. https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202000924
Wang J, Jiang C, Jin J, Huang L, Yu W, Su B, Hu J (2021) Ratiometric fluorescent lateral flow immunoassay for point-of-care testing of acute myocardial infarction. Angew Chem Int Ed 60:13042–13049. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202103458
Liu T, Li D, Yang D, Jiang M (2011) An improved seed-mediated growth method to coat complete silver shells onto silica spheres for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Colloid Surface A 387:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2011.07.030
Sheng EZ, Lu YX, Xiao Y, Li ZX, Wang HS, Dai ZH (2021) Simultaneous and ultrasensitive detection of three pesticides using a surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based lateral flow assay test strip. Biosens Bioelectron 181:113149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113149
Xian J, Luo S, Xue J, Zhang L, Fu Z, Ouyang H (2022) Synergetic dual-site atomic catalysts for sensitive chemiluminescent immunochromatographic test strips. Anal Chem 94:11449–11456. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c02914
Wang Y, Zhang M, Bu T, Bai F, Zhao S, Cao Y, He K, Wu H, Xi J, Wang L (2023) Immunochromatographic Assay based on Sc-TCPP 3D MOF for the rapid detection of imidacloprid in food samples, 13413f1. Food Chem 401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134131
Xue J, Yang H, Li J, Ouyang H, Fu Z (2023) Smartphone-based pressure signal readout device combined with bidirectional immunochromatographic test strip for dual-analyte detection. Anal Chem 95:1359–1365. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c04322
Ruiyi L, Yanhong J, Qinsheng W, Yongqiang Y, Nana L, Xiulan S, Zaijun L (2021) Serine and histidine-functionalized graphene quantum dot with unique double fluorescence emission as a fluorescent probe for highly sensitive detection of carbendazim. Sens Actuators B Chem 343:130099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130099
Tan G, Zhao Y, Wang M, Chen X, Wang B, Li QX (2020) Ultrasensitive quantitation of imidacloprid in vegetables by colloidal gold and time-resolved fluorescent nanobead traced lateral flow immunoassays. Food Chem 311:126055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.126055
Zhang Q, Zhang Z, Xu S, Liu A, Da L, Lin D, Jiang C (2023) Photoinduced electron transfer-triggered g-C(3)N(4)\Rhodamine B sensing system for the ratiometric fluorescence quantitation of carbendazim. Anal Chem 95:4536–4542. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c05691
Xu Y, Pu Y, Jiang H, Huang Y, Shen C, Cao J, Jiang W (2022) Highly sensitive fluorescent sensing platform for imidacloprid and thiamethoxam by aggregation-induced emission of the Zr(IV) metal - organic framework. Food Chem 375:131879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131879
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 32200076), the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (Grant no. 2208085MB29), and the Medical instrument supervise program of Hefei institute of physical science.CAS (YZJJ2021-J-YQ4).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhenmei Wang: Conceptualization, methodology, writing original draft; Shuai Zheng: Methodology, writing original draft; Chijian Zhang and Wenqi Wang: Methodology, data curation; Qian Wang and Zhigang Li.: Methodology; Yong Liu: Writing review & editing, supervision; Long Zhang.:Conceptualization, writing review & editing, supervision; Shu Wang: Funding acquisition, writing review & editing, supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Zhenmei Wang and Shuai Zheng contributed equally to this work.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
Additional experimental description (S1. Reagents, materials, and instruments; S2. Synthesis of SiO2 nanomicrospheres; S3. Preparation of SiO2-MQB nanomaterial complexes; S4. Preparation of colloidal AuNP-based LFA strip; S5. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; S6. Calculation of maximum number of QDs onto SiO2-MQB), and supporting figures (Figures S1-S13) mentioned in the main text. (DOCX 32310 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Zheng, S., Zhang, C. et al. Introduction of multilayered quantum dot nanobeads into competitive lateral flow assays for ultrasensitive and quantitative monitoring of pesticides in complex samples. Microchim Acta 190, 361 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05913-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05913-w