Abstract
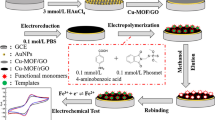
An electrochemiluminescence (ECL) sensor based on molecular imprinting polymer and SiO2 nanoparticles loaded Ru(bpy)3 and nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots (NCQDs) is constructed for citrinin detection. The Ru(bpy)3 acts as ECL emitter, and the NCQDs cooperate with tri-n-propylamine (TPA) in solution as a coreactant to facilitate the luminescence. The citrinin imprinted poly(p-aminothiophenol) film is deposited on the surface of the luminophore by electrochemical method, which can immobilize the luminophore besides recognizing the target. The obtained ECL sensor exhibits high sensitivity, stability, and reproducibility. The change of ECL intensity and the logarithm of citrinin concentration display a good linear relationship in the range 1.0 to 100 pg mL−1, and the detection limit is 5 fg mL−1. When it is applied to the detection of citrinin contents in food sample (i.e., rice and millet) solutions, the RSD is less than 6.1%, and the recoveries for spiked standards range from 95.5 to 102.0%. Hence, this work provides a promising alternative for citrinin detection.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh DK, Ganbold E-O, Cho E-M, Cho K-H, Kim D, Choo J, Kim S, Lee CM, Yang SI, Joo S-W (2014) Detection of the mycotoxin citrinin using silver substrates and Raman spectroscopy. J Hazard Mater 265:89–95
Atar N, Eren T, Yola ML (2015) A molecular imprinted SPR biosensor for sensitive determination of citrinin in red yeast rice. Food Chem 184:7–11
Ahmed N, Farag M, Soliman K, Abdel-Samed A, Naguib KM (2007) Evaluation of methods used to determine ochratoxin A in coffee beans. J Agric Food Chem 55:9576–9580
Flajs D, Peraica M (2009) Toxicological properties of citrinin. Arhiv za higijenu rada i toksikologiju 60:457
Markov K, Pleadin J, Bevardi M, Vahčić N, Sokolić-Mihalak D, Frece J (2013) Natural occurrence of aflatoxin B1, ochratoxin A and citrinin in Croatian fermented meat products. Food control 34:312–317
Franco C, Fente C, Vazquez B, Cepeda A, Lallaoui L, Prognon P, Mahuzier G (1996) Simple and sensitive high-performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence method for the determination of citrinin application to the analysis of fungal cultures and cheese extracts. J Chromatogr A 723:69–75
Hartl A, Stenzel W-R (2007) Development of a method for the determination of citrinin in barley, rye and wheat by solid phase extraction on aminopropyl columns and HPLC-FLD. Mycotoxin Res 23:127–131
Arroyo-Manzanares N, Huertas-Pérez JF, Gámiz-Gracia L, García-Campaña AM (2015) Simple and efficient methodology to determine mycotoxins in cereal syrups. Food Chem 177:274–279
Zhao-Hui D, Zhuang-Sen L, He-Rui Y, Yan-Hong G, Zhang K, Su-Qing Z, Zhen-Yu Z (2009) Preparation of artificial antigen and egg yolk-derived immunoglobulin (IgY) of citrinin for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Biomed Environ Sci 22:237–243
Hu X, Liu Y, Xia Y, Zhao F, Zeng B (2021) A novel ratiometric electrochemical sensor for the selective detection of citrinin based on molecularly imprinted poly (thionine) on ionic liquid decorated boron and nitrogen co-doped hierarchical porous carbon. Food Chem 363:130385
Fang G, Liu G, Yang Y, Wang S (2016) Quartz crystal microbalance sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer membrane and three-dimensional Au nanoparticles@ mesoporous carbon CMK-3 functional composite for ultrasensitive and specific determination of citrinin. Sens Actuators B Chem 230:272–280
Li L, Chen Y, Zhu J-J (2017) Recent advances in electrochemiluminescence analysis. Anal Chem 89:358–371
Valenti G, Rampazzo E, Kesarkar S, Genovese D, Fiorani A, Zanut A, Palomba F, Marcaccio M, Paolucci F, Prodi L (2018) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence from metal complexes-based nanoparticles for highly sensitive sensors applications. Coord Chem Rev 367:65–81
Richter MM (2004) Electrochemiluminescence (ecl). Chem Rev 104:3003–3036
Xu J, Huang P, Qin Y, Jiang D, Chen H-Y (2016) Analysis of intracellular glucose at single cells using electrochemiluminescence imaging. Anal Chem 88:4609–4612
Bard AJ, Debad JD, Leland JK, Sigal GB, Wilbur JL, Wohlstadter JN (2000) Chemiluminescence, electrogenerated. Wiley, New York, p 9842
Knight AW, Greenway GM (1994) Occurrence, mechanisms and analytical applications of electrogenerated chemiluminescence A review. Analyst 119:879–890
Debad JD, Glezer EN, Leland JK, Sigal GB (2004) Clinical and biological applications of ECL. In: Electrogenerated chemiluminescence. CRC Press, pp 370–407
He L, Cox KA, Danielson ND (1990) Chemiluminescence detection of amino acids, peptides, and proteins using tris-2, 2′-bipyridine ruthenium (III). Anal Lett 23:195–210
Zeng H, Yu X, Wan J, Cao X (2021) Synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymers based on boronate affinity for diol-containing macrolide antibiotics with hydrophobicity-balanced and pH-responsive cavities. J Chromatogr A 1642:461969
Fu D, Chen T, Cheng Y, Li A, Liu H, Cheng Z, Li P, Liu J (2021) A molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensing platform based on the signal amplification system fabricated with the theoretically optimized monomer for specific determination of formaldehyde. Sens Actuators B Chem 344:130260
Lian S, Huang Z, Lin Z, Chen X, Oyama M, Chen X (2016) A highly selective melamine sensor relying on intensified electrochemiluminescence of the silica nanoparticles doped with [Ru(bpy)3]2+/molecularly imprinted polymer modified electrode. Sens Actuators B Chem 236:614–620
Zhang W, Xiong H, Chen M, Zhang X, Wang S (2017) Surface-enhanced molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence sensor based on Ru@SiO(2) for ultrasensitive detection of fumonisin B(1). Biosens Bioelectron 96:55–61
Cao N, Zhao F, Zeng B (2020) A novel self-enhanced electrochemiluminescence sensor based on PEI-CdS/Au@ SiO2@ RuDS and molecularly imprinted polymer for the highly sensitive detection of creatinine. Sens Actuators B Chem 306:127591
Li J, Wang Q, Xiong C, Deng Q, Zhang X, Wang S, Chen MM (2022) An ultrasensitive CH(3)NH(3)PbBr(3) quantum dots@SiO(2)-based electrochemiluminescence sensing platform using an organic electrolyte for aflatoxin B1 detection in corn oil. Food Chem 390:133200
Cao N, Zeng P, Zhao F, Zeng B (2019) Au@ SiO2@ RuDS nanocomposite based plasmon-enhanced electrochemiluminescence sensor for the highly sensitive detection of glutathione. Talanta 204:402–408
Zorzi M, Pastore P, Magno F (2000) A single calibration graph for the direct determination of ascorbic and dehydroascorbic acids by electrogenerated luminescence based on Ru (bpy) 32+ in aqueous solution. Anal Chem 72:4934–4939
Zhang L, Dong S (2006) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence sensors using Ru (bpy) 32+ doped in silica nanoparticles. Anal Chem 78:5119–5123
Long Y-M, Bao L, Zhao J-Y, Zhang Z-L, Pang D-W (2014) Revealing carbon nanodots as coreactants of the anodic electrochemiluminescence of Ru (bpy) 32+. Anal Chem 86:7224–7228
Li L, Liu D, Mao H, You T (2017) Multifunctional solid-state electrochemiluminescence sensing platform based on poly (ethylenimine) capped N-doped carbon dots as novel co-reactant. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 89:489–495
Akyıldırım O, Kardaş F, Beytur M, Yüksek H, Atar N, Yola ML (2017) Palladium nanoparticles functionalized graphene quantum dots with molecularly imprinted polymer for electrochemical analysis of citrinin. J Mol Liq 243:677–681
Deng G, Xu K, Sun Y, Chen Y, Zheng T, Li J (2013) High sensitive immunoassay for multiplex mycotoxin detection with photonic crystal microsphere suspension array. Anal Chem 85:2833–2840
Luo L, Ma S, Li L, Liu X, Zhang J, Li X, Liu D, You T (2019) Monitoring zearalenone in corn flour utilizing novel self-enhanced electrochemiluminescence aptasensor based on NGQDs-NH2-Ru@ SiO2 luminophore. Food Chem 292:98–105
Wang D, Li Y, Lin Z, Qiu B, Guo L (2015) Surface-enhanced electrochemiluminescence of Ru@ SiO2 for ultrasensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Anal Chem 87:5966–5972
Liu Z, Zhang F, Cui L, Wang K, Zhan H (2017) Fabrication of a highly sensitive electrochemiluminescence chlorpromazine sensor using a Ru (bpy) 3 2+ incorporated carbon quantum dot–gelatin composite film. Anal Methods 9:1011–1017
Funding
This work was supported by the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 21775112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y., Wang, T., Cao, J. et al. Molecular imprinting electrochemiluminescence sensor based on nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots /Ru(bpy)3@SiO2 for the determination of citrinin. Microchim Acta 190, 155 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05735-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05735-w