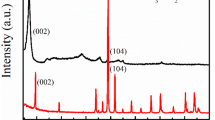
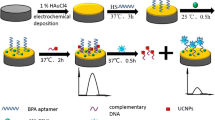
Abstract
MXene@Au as the base and Au@SiO2 as signal amplification factor were used for constructing an ultrasensitive “on–off” electrochemiluminescence (ECL) biosensor for the detection of Pb2+ in water. The use of MXene@Au composite provided a good interface environment for the loading of tris(2,2-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) (Ru(bpy)32+) on the electrode. Based on resonance energy transfer, the Au (core) SiO2 (shell) (Au@SiO2) nanoparticles stimulate electron transport and promote tripropylamine (TPrA) oxidation. The luminescence effect of Au@SiO2 was five times that of AuNPs and SiO2 nanomaterials alone, and the ECL intensity was greatly improved. In addition, Pb2+ activated the aptamer to exert its endonuclease activity, which realized the signal cycle amplification in the process of Pb2+ detection. When Pb2+ was added, the ECL signal weakened, and the Pb2+ concentration was detected according to the decreased ECL intensity. Under optimized experimental conditions, this aptamer sensor for Pb2+ has a wide detection range (0.1 to 1 × 106 ng L−1) and a low detection limit (0.059 ng L−1). The relative standard deviation (RSD) of the sensor is 0.39–0.99%, and the recovery of spiked standard is between 90.00 and 125.70%. The sensor shows good selectivity and high sensitivity in actual water sample analysis. This signal amplification strategy possibly provides a new method for the detection of other heavy metal ions and small molecules.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ziaee F, Ziaee M, Taseidifar M (2021) Synthesis and application of a green surfactant for the treatment of water containing PFAS/hazardous metal ions. J Hazard Mater 407:124800
Mukherjee I, Singh UK, Singh RP, Anshumali D, Kumari PK, Jha P. Mehta (2020) Characterization of heavy metal pollution in an anthropogenically and geologically influenced semi-arid region of east India and assessment of ecological and human health risks. Sc Total Environ. 705:135801
Rahman MATMT, Paul M, Bhoumik N, Hassan M, Alam MK, Aktar Z (2020) Heavy metal pollution assessment in the groundwater of the Meghna Ghat industrial area, Bangladesh, by using water pollution indices approach. Appl Water Sci. 10:186
Ubando AT, Africa ADM, Maniquiz-Redillas MC, Culaba AB, Chen WH, Chang JS (2021) Microalgal biosorption of heavy metals: a comprehensive bibliometric review. J Hazard Mater 402:123431
Jeong H, Choi YY, Lee J, Lim J, Ra K (2020) Heavy metal pollution by road-deposited sediments and its contribution to total suspended solids in rainfall runoff from intensive industrial areas. Environ Pollut 265:115028
Bozorgzadeh E, Pasdaran A, Ebrahimi-Najafabadi H (2021) Determination of toxic heavy metals in fish samples using dispersive micro solid phase extraction combined with inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy. Food Chem 346:128916
Subramanian V, Lee S, Jena S, Jana SK, Ray D, Kim SJ, Thalappil P (2020) Enhancing the sensitivity of point-of-use electrochemical microfluidic sensors by ion concentration polarisation-a case study on arsenic. Sens Actuators B Chem 304:127340
Khan MS, Ameer H, Ali A, Li YY, Yang L, Ren X, Wei Q (2020) Electrochemiluminescence behaviour of silver/ZnIn2S4/reduced graphene oxide composites quenched by Au@SiO2 nanoparticles for ultrasensitive insulin detection. Biosens Bioelectron 162:112235
Praoboon N, Siriket S, Taokaenchan N, Kuimalee S, Phaisaqnsuthichol S, Pookmanee P, Satienperakul S (2022) Paper-based electrochemiluminescence device for the rapid estimation of trimethylamine in fish via the quenching effect of thioglycolic acid-capped cadmium selenide quantum dots. Food Chem 366:130590
D’Alton L, Nguyen P, Carrara S, Hogan CF (2021) Intense near-infrared electrochemiluminescence facilitated by energy transfer in bimetallic Ir-Ru metallopolymers. Electrochim Acta 379:138117
AL-maskri AAA, Ye JW, Talap J, Hu HH, Sun LL, Yu LS, Cai S, Zeng S (2020) Reverse transcription-based loop-mediated isothermal amplification strategy for real-time miRNA detection with phosphorothioated probes, Anal Chim Acta. 1126 1-6
Jiang CM, Li XJ, Yao Y, Lan LY, Shao YZ, Zhao FN, Ying YB, Ping JF (2020) A multifunctional and highly flexible triboelectric nanogenerator based on MXene-enabled porous film integrated with laser-induced graphene electrode. Nano Energy 66:104121
Shao YZ, Yao Y, Jiang CM, Zhao FN, Liu XX, Ying YB, Ping JF (2019) Two-dimensional MXene nanosheets (types Ti3C2Tx and Ti2CTx) as new ion-to-electron transducers in solid-contact calcium ion-selective electrodes. Microchim Acta 186:750
Downs AM, Gerson J, Hossain MN, Ploense K, Pham M, Kraatz HB, Kippin T, Plaxco KW (2021) Nanoporous gold for the miniaturization of in vivo electrochemical aptamer-based sensors. ACS Sens 6:2299–2306
Idili A, Parolo C, Alvarez-Diduk R, Merkoci A (2021) Rapid and efficient detection of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein using an electrochemical aptamer-based sensor. ACS Sens 6:3093–3101
Hedarian SMT, Sani AT, Danesh NM, Ramezani M, Alibolandi M, Gerayelou G, Abnous K, Taghdisi SM (2021) A novel electrochemical approach for the ultrasensitive detection of fluoroquinolones based on a double-labelled aptamer to surpass complementary strands of aptamer lying flatSens. Actuators B Chem 334:129632
Sahin S, Caglayan MO, Ustundag Z (2020) A review on nanostructure-based mercury (II) detection and monitoring focusing on aptamer and oligonucleotide biosensors. Talanta 220:121437
Wang WR, Xu YC, Cheng N, Xie YX, Huang KL, Xu WT (2020) Dual-recognition aptazyme-driven DNA nanomachine for two-in-one electrochemical detection of pesticides and heavy metal ions. Sens Actuators B Chem 321:128598
Yu ZZ, Jiang L, Liu RY, Zhao WD, Yang ZH, Zhang JY, Jin SZ (2021) Versatile self-assembled MXene-Au nanocomposites for SERS detection of bacteria, antibacterial and photothermal sterilization. Chem Eng J 426:131914
Zhao FN, Yao Y, Jiang CM, Shao YZ, Barcelo D, Ying YB, Ping JF (2019) Self-reduction bimetallic nanoparticles on ultrathin MXene nanosheets as functional platform for pesticide sensing. Journal of Haardous Materials 384:121358–121358
Yao Y, Lan LY, Liu XX, Ying YB, Ping JF (2019) Spontaneous growth and regulation of noble metal nanoparticles on flexible biomimetic MXene paper for bioelectronics. Biosens Bioelectron 148:111799
Wang DF, Guo LH, Huang R, Qiu B, Lin ZY, Chen GN (2015) Surface enhanced electrochemiluminescence of Ru(bpy)32+. Sci Rep 5:7954
Huang JC, Xiang YD, Li JS, Kong QQ, Zhai HG, Xu R, Yang FZ, Sun X, Guo YM (2021) A novel electrochemiluminescence aptasensor based on copper-gold 5 bimetallic nanoparticles and its applications. Biosens Bioelectron 194:113601
Yadav, Y., Berlina, A.N., Zherdev, A.V., Gaur, M.S., Dzantiev, Rapid and selective electrochemical detection of Pb2+ ions using aptamer-conjugated alloy nanoparticles, SNAS 2077 (2020).
Abu-Ali H, Nabok A, Smith TJ (2019) Development of novel and highly specific ssDNA-aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for rapid detection of mercury (II) and lead (II) ions in water. Chemosensors 27:2–14
Oliveira VHB, Rechotnek F, Silva E, Marques VDS (2020) A sensitive electrochemical sensor for Pb2+ ions based on ZnO nanofibers functionalized by L-cysteine. J Mol Liq 309:113041
Fall B, Diaw AKD, Fall M, Sall ML (2021) Synthesis of highly sensitive rGO@CNT@Fe2O3/polypyrrole nanocomposite for the electrochemical detection of Pb2+. Mater Today Commun 334:102005
Mourya A, Sinha SK, Mazumdar B (2019) Glassy carbon electrode modified with blast furnace slag for electrochemical investigation of Cu2+ and Pb2+ metal ions. Microchemical J 149:113041
Raj SK, Yadav V, Bhadu GR, Patidar R, Kumar M, Kulshrestha V (2021) Synthesis of highly fluorescent and water soluble graphene quantum dots for detection of heavy metal ions in aqueous media. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:46336–46342
Vekateswarlu S, Reddy AS, Panda A, Sarkar D, Son YH, Yoon MY (2020) Reversible fluorescence switching of metal-organic framework nanoparticles for use as security ink and detection of Pb2+ ions in aqueous media. ACS Appl Nano Mater 4:3684–3692
Zhang Y, Xu JM, Zhou S, Zhu L, Lv X, Zhang J, Zhang LN, Zhu PW, Yu JH (2020) DNAzyme-triggered visual and ratiometric electrochemiluminescence dual-readout assay for Pb(II) based on an assembled paper device. Anal Chem 92:3874–3881
Wang YH, Shi HH, Zhang LN, Ge SG, Xu ML, Wang X, Yu JH (2021) Two-dimensional black phosphorus nanoflakes: a coreactant-free electrochemiluminescence luminophors for selective Pb2+ detection based on resonance energy transfer. J Hazard Mater 403:123601
Feng DF, Li PH, Tan XC, Wu YY, Wei FC, Du FK, Ai CH, Luo YN, Chen QY, Han HY (2020) Electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for multiple determination of Hg2+ and Pb2+ ions by using the MIL-53(Al)@CdTe-PEI modified electrode. Anal Chim Acta 1100:232–239
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2018BC055) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32161133008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, H., Wang, Y., Yin, J. et al. Electrochemiluminescence biosensor for determination of lead(II) ions using signal amplification by Au@SiO2 and tripropylamine-endonuclease assisted cycling process. Microchim Acta 189, 317 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05429-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05429-9