Abstract
By introducing functional groups such as quaternary amine groups, sulfonic acid groups, triazine groups, and other mespore nanomaterials into the hydrogel, better separation effect of some organic framework materials has been obtained. Due to a reasonable design and preparation strategy, the hydrogel composite-modified silica can be used in the selective separation of various analytes such as pesticides, alkylbenzenes, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, nucleosides/bases, benzoic acids, antibiotics, and carbohydrates. Through the exploration of chromatographic retention behavior, it is proved that the column can be used in mixed-mode liquid chromatography. The intra-day relative standard deviation for retention time of this new stationary phase is 0.12–0.16% (n = 10), and the inter-day relative standard deviation is less than 0.39% (n = 5). This new stationary phase can also be used for separation in complex samples. The limit of detection (LOD) for chlorotoluron in farm irrigation water is 0.21 µg/L and the linear range is 2–250 µg/L. After optimizing the chromatographic conditions, the highest efficiency of the hydrogel column in RPLC and HILIC modes has reached 32,400 plates/m (chlorobenzuron) and 41,300 plates/m (galactose). This new type of hydrogel composite is a porous network material with flexible functional design and simple preparation method and its application has been expanded in liquid chromatography separation successfully.
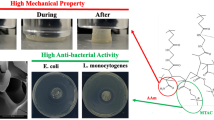
Graphical abstract
The hydrogel composed of triallyl cyanate cross-linking agent and 3-(2-(methacryloyloxy) ethyl) dimethylamine) propane-1-sulfonate (SBMA) monomer which were co-modified on the surface of mesoporous silica with MOF-919 for separation in mixed-mode liquid chromatography.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang Y, Liu J, Wang J, Hu M, Mo F, Liang G, Zhi C (2018) An intrinsically self-healing NiCo vertical bar vertical bar Zn rechargeable battery with a self-healable ferric-ion-crosslinking sodium polyacrylate hydrogel electrolyte. Angew Chem Int Ed 57(31):9810–9813
Zhang YZ, Lee KH, Anjum DH, Sougrat R, Jiang Q, Kim H, Alshareefit HN (2018) MXenes stretch hydrogel sensor performance to new limits. Sci Adv 4(6):eaat0098. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aat0098
Le X, Shang H, Yan H, Zhang J, Lu W, Liu M, Wang L, Lu G, Xue Q, Chen T (2021) A Urease-containing fluorescent hydrogel for transient information storage. Angew Chem Int Ed 60(7):3640–3646
Jiao L, Xu W, Yan H, Wu Y, Gu W, Li H, Du D, Lin Y, Zhu C (2019) A dopamine-induced Au hydrogel nanozyme for enhanced biomimetic catalysis. Chem Commun 55(66):9865–9868
Zhou Q, Dong X, Xiong Y, Zhang B, Lu S, Wang Q, Liao Y, Yang Y, Wang H (2020) Multi-responsive lanthanide-based hydrogel with encryption, naked eye sensing, shape memory, self-healing, and antibacterial activity. ACS Appl Mater Inter 12(25):28539–28549
Zhao Z, Wang Z, Li G, Cai Z, Wu J, Wang L, Deng L, Cai M, Cui W (2021) Injectable microfluidic hydrogel microspheres for cell and drug delivery. Adv Funct Mater 31(31):2103339. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202103339
Ma Y, Hua M, Wu S, Du Y, Pei X, Zhu X, Zhou F, He X (2020) Bioinspired high-power-density strong contractile hydrogel by programmable elastic recoil. Sci Adv 6(47):2520–2530
Li J, Mooney DJ (2016) Designing hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Nat Rev Mater 1(12):16071
Liu J, Qu S, Suo Z, Yang W (2021) Functional hydrogel coatings. Natl Sci Rev 8(2):254–272
Okubo K, Ikeda K, Oaku A, Hiruta Y, Nagase K, Kanazawa H (2018) Protein purification using solid-phase extraction on temperature-responsive hydrogel-modified silica beads. J Chromatogr A 1568:38–48
Fan F, Liang X, Wang S, Wang L, Guo Y (2020) A facile process for the preparation of organic gel-assisted silica microsphere material for multi-mode liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1628:461472–461480
Fan F, Lu X, Wang S, Liang X, Wang L, Guo Y (2021) Non-conjugated flexible network for the functional design of silica-based stationary phase for mixed-mode liquid chromatography. Talanta 233:122548–212555
Wang X, Xu D, Jaquet B, Yang Y, Wang J, Huang H, Chen Y, Gerhard C, Zhang K (2020) Structural colors by synergistic birefringence and surface plasmon resonance. ACS Nano 14(12):16832–16839
Kim I, Bang W-Y, Park WH, Han EH, Lee E (2019) Photo-crosslinkable elastomeric protein-derived supramolecular peptide hydrogel with controlled therapeutic CO-release. Nanoscale 11(37):17327–17333
Lee TH, Oh JY, Jang JK, Moghadam F, Roh JS, Yoo SY, Kim YJ, Choi TH, Lin H, Kim HW, Park HB (2020) Elucidating the role of embedded metal-organic frameworks in water and ion transport properties in polymer nanocomposite membranes. Chem Mater 32(23):10165–10175
Jiang H, Yang K, Zhao X, Zhang W, Liu Y, Jiang J, Cui Y (2021) Highly stable Zr(IV)-based metal-organic frameworks for chiral separation in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J Am Chem Soc 143(1):390–398
Liu Q, Song Y, Ma Y, Zhou Y, Cong H, Wang C, Wu J, Hu G, O’Keeffe M, Deng H (2019) Mesoporous cages in chemically robust MOFs created by a large number of vertices with reduced connectivity. J Am Chem Soc 141(1):488–496
Jiao C, Majeed Z, Wang G-H, Jiang H (2018) A nanosized metal-organic framework confined inside a functionalized mesoporous polymer: an efficient CO2 adsorbent with metal defects. J Mater Chem A 6(35):17220–17226
Zuo H, Guo Y, Zhao W, Hu K, Wang X, He L, Zhang S (2019) Controlled fabrication of silica@covalent triazine polymer core shell spheres as a reversed-phase/hydrophilic interaction mixed mode chromatographic stationary phase. ACS Appl Mater Inter 11(49):46149–46156
Li X, Li B, Liu M, Zhou Y, Zhang L, Qiao X (2019) Core-shell metal-organic frameworks as the mixed-mode stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction/reversed-phase chromatography. ACS Appl Mater Inter 11(10):10320–10327
Huang J, Han X, Yang S, Cao Y, Yuan C, Liu Y, Wang J, Cui Y (2019) Microporous 3D covalent organic frameworks for liquid chromatographic separation of xylene isomers and ethylbenzene. J Am Chem Soc 141(22):8996–9003
Yang F, Yang C-X, Yan X-P (2015) Post-synthetic modification of MIL-101(Cr) with pyridine for high-performance liquid chromatographic separation of tocopherols. Talanta 137:136–142
Zhao W, Hui K, Hub C, Wang X, Yu A, Zhang S (2017) Silica gel microspheres decorated with covalent triazine-based frameworks as an improved stationary phase for high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1487:83–88
Du W, Zhang Z, Fan W, Gao W, Su H, Li Z (2018) Fabrication and evaluation of polydimethylsiloxane modified gelatin/silicone rubber asymmetric bilayer membrane with porous structure. Mater Des 158:28–38
Li P, Yu H, Liu N, Wang F, Lee G-B, Wang Y, Liu L, Li WJ (2018) Visible light induced electropolymerization of suspended hydrogel bioscaffolds in a microfluidic chip. Biomater Sci 6(6):1371–1378
Zhao L, Ren Z, Liu X, Ling Q, Li Z, Gu H (2021) A multifunctional, self-healing, self-adhesive, and conductive sodium alginate/poly(vinyl alcohol) composite hydrogel as a flexible strain sensor. ACS Appl Mater Inter 13(9):11344–11355
Fan F, Nie X, Fan C, Liang X, Lu X, Guo Y (2020) L-cysteine and 5-norbornene-2-carboxylic acid decorated mesoporous silica spheres as liquid chromatographic material. Micropor Mesopor Mat 299:110102–110108
Fan F, Wang L, Li Y, Wang X, Lu X, Guo Y (2020) A novel process for the preparation of Cys-Si-NIPAM as a stationary phase of hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC). Talanta 218:121154–121160
Tsopelas F, Ochsenkuehn-Petropoulou M, Tsantili-Kakoulidou A (2010) Void volume markers in reversed-phase and biomimetic liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1217(17):2847–2854
Al-Massaedh AA, Pyell U (2016) Mixed-mode acrylamide-based continuous beds bearing tert-butyl groups for capillary electrochromatography synthesized via complexation of N-tert-butylacrylamide with a water-soluble cyclodextrin. Part I: Retention properties. J Chromatogr A 1477:114–126
Vasilevskaya VV, Klochkov AA, Lazutin AA, Khalatur PG, Khokhlov AR (2004) HA (hydrophobic/amphiphilic) copolymer model: coil-globule transition versus aggregation. Macromolecules 37(14):5444–5460
Feng T, Ji W, Zhang Y, Wu F, Tang Q, Wei H, Mao L, Zhang M (2020) Zwitterionic polydopamine engineered interface for in vivo sensing with high biocompatibility. Angew Chem Int Ed 59(52):23445–23449
Tan W, Chen Y, Xiong X, Huang S, Fang Z, Chen Y, Ma M, Chen B (2020) Synthesis of a poly(sulfobetaine-co-polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane) hybrid monolith via an in-situ ring opening quaternization for use in hydrophilic interaction capillary liquid chromatography. Microchim Acta 187:109
Obradovic D, Komsta L, Agbabaa D (2020) Novel computational approaches to retention modeling in dual hydrophilic interactions/reversed phase chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1619:460951–460962
Abbood A, Smadja C, Herrenknecht C, Alahmad Y, Tchapla A, Taverna M (2009) Retention mechanism of peptides on a stationary phase embedded with a quaternary ammonium group: a liquid chromatography study. J Chromatogr A 1216(15):3244–3251
Sliwka-Kaszynska M, Jaszczolt K, Witt D, Rachon J (2004) High-performance liquid chromatography of di- and trisubstituted aromatic positional isomers on 1,3-alternate 25,27-dipropoxy-26,28-bis-3-propyloxy-calix 4 arene-bonded silica gel stationary phase. J Chromatogr A 1055(1–2):21–28
Fan C, Liu B, Li H, Quan K, Chen J, Qiu H (2021) N-Vinyl pyrrolidone and undecylenic acid copolymerized on silica surface as mixed-mode stationary phases for reversed-phase and hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1655:462534–462539
Ren X, Zhang K, Gao D, Fu Q, Zeng J, Zhou D, Wang L, Xia Z (2018) Mixed-mode liquid chromatography with a stationary phase co-functionalized with ionic liquid embedded C18 and an aryl sulfonate group. J Chromatogr A 1564:137–144
Wu Q, Hou X, Zhang X, Li H, Zhao L, Lv H (2021) Amphipathic carbon quantum dots-functionalized silica stationary phase for reversed phase/hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Talanta 226:122148–122156
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21575149, 21575148).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fangbin Fan: conceptualization, method, investigation, data curation, and writing—original draft.
Xiaofeng Lu: formal analysis.
Shuai Wang: software and resources.
Licheng Wang: validation and formal analysis.
Xiaojing Liang: writing—review and editing.
Yong Guo: funding acquisition and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, F., Lu, X., Wang, S. et al. Mesoporous nanomaterial-assisted hydrogel double network composite for mixed-mode liquid chromatography. Microchim Acta 188, 433 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05094-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05094-4