Abstract
A fluorescent nanoprobe consisting of CdTe quantum dots (QDs) and coated with molecularly imprinted layers was prepared and successfully applied to the determination of norfloxacin (NOR) in seawater and wastewater samples. The 3-mercaptopropionic acid capped QDs were prepared and then covered with a protective silica shell. A molecularly imprinted layer was finally synthesized around the silanized QDs using 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane as functional monomer and norfloxacin as the template. Compared with the non-imprinted polymer, the fluorescence of the nanoprobe with imprinted polymer (measured at excitation/emission wavelengths of 300/596 nm) is strongly reduced in the presence of NOR, and the imprinting factor is 8.8. Under the optimal experimental conditions, the detection limit of the nanoprobe is 0.18 μM, and response is linear between 0.5 - 28 μM of NOR. The relative standard deviation of the detection of NOR is <7.2%. In order to evaluate the practicality of the probe, wastewater and seawater samples spiked with norfloxacin were analyzed by this method, and recoveries ranged from 96.2 - 106.0%.

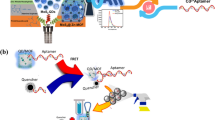
Schematic presentation and fluorescence spectrum of fluorescent nanoprobe with selectivity for norfloxacin (NOR). CdTe quantum dots (QDs) are used as fluorescent carriers, 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) as template molecules, tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) as crosslinking agent, and aqueous ammonia as initiator.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hou AX, Gao WY, Yang X, Lei KL, Qu SS (2003) Mechanism of inhibition of norfloxacin against Escherichia coli. J Wuhan Univ 49:167–170
Wei X, Zhou ZP, Hao TF, Li HJ, Dai JD, Gao L, Zheng XD, Wang JX, Yan YS (2015) Simple synthesis of thioglycolic acid-coated CdTe quantum dots as probes for Norfloxacin lactate detection. J Lumin 161:47–53
Mansilla AE, PeñaD MDL, Salinas GGF (2005) HPLC determination of enoxacin, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin with photoinduced fluorimetric (PIF) detection and multiemission scanning: Application to urine and serum. J Chromatogr B 822:185–193
Liu YM, Cao JT, Tian W, Zheng YL (2008) Determination of levofloxacin and norfloxacin by capillary electrophoresis with electrochemiluminescence detection and applications in human urine. Electrophoresis 29:3207–3212
Jiang QQ, Zhang HT, Liu JW, Li JM, Wang ZL (2011) Development and Optimization of an Indirect Competitive ELISA for Detection of Norfloxacin Residue in Chicken Liver. Procedia Environ Sci 8:128–133
Huang KJ, Liu X, Xie WZ, Yuan HX (2008) Electrochemical behavior and voltammetric determination of norfloxacin at glassy carbon electrode modified with multi walled carbon nanotubes/Nafion. Colloid Surface B 64:269–274
González DM, Campaña AMG, Casado AG (2010) Peroxyoxalate Photoinduced Chemiluminescence Detection of Norfloxacin in Pharmaceutical Products by Flow Injection Analysis. Anal Lett 43:2399–2410
Darwish IA, Sultan MA, Al-Arfaj HA (2009) Novel selective kinetic spectrophotometric method for determination of norfloxacin in its pharmaceutical formulations. Talanta 78:1383–1388
Yuan C, Zhang K, Zhang ZP, Wang SH (2012) Highly selective and sensitive detection of mercuric ion based on a visual fluorescence method. Anal Chem 84:9792–9801
Chullasat K, Nurerk P, Kanatharana P, Davis F, Bunkoed O (2018) A facile optosensing protocol based on molecularly imprinted polymer coated on CdTe quantum dots for highly sensitive and selective amoxicillin detection. Sensor Actuat B Chem 254:255–263
Ensafi AA, Kazemifard N, Rezaei B (2017) Development of a nano plastic antibody for determination of propranolol using CdTe quantum dots. Sensor Actuat B Chem 252:846–853
Habimana JDD, Ji J, Pi FW, Karangwa E, Sun JD, Guo W, Cui FC, Shao JD, Ntakirutimana C, Sun XL (2018) A class-specific artificial receptor-based on molecularly imprinted polymer-coated quantum dot centers for the detection of signaling molecules, N-acyl-homoserine lactones present in gram-negative bacteria. Anal Chim Acta 1031:134–144
Ensafi AA, Kazemifard N, Rezaei B (2017) Development of a selective prilocaine optical sensor based on molecularly imprinted shell on CdTe quantum dots. Sensor Actuat B Chem 242:835–841
Chen L, Xu S, Li J (2011) Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem Soc Rev 40:2922–2942
Huy BT, Seo MH, Zhang XF, Lee YI (2014) Selective optosensing of clenbuterol and melamine using molecularly imprinted polymer-capped CdTe quantum dots. Biosens Bioelectron 57:310–316
Jia MF, Zhang Z, Li JH, Shao HJ, Chen LX, Yang XB (2017) A molecular imprinting fluorescence sensor based on quantum dots and a mesoporous structure for selective and sensitive detection of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Sensor Actuat B Chem 251:934–943
Lia XJ, Jiao HF, Shi XZ, Sun AL, Wang XJ, Chai JY, Li DX, Chen J (2018) Development and application of a novel fluorescent nanosensor based on FeSe quantum dots embedded silica molecularly imprinted polymer for the rapid optosensing of cyfluthrin. Biosens Bioelectron 99:268–273
Wu L, Lin ZZ, Zhong HP, Chen XM, Huang ZY (2017) Rapid determination of malachite green in water and fish using a fluorescent probe based on CdTe quantum dots coated with molecularly imprinted polymer. Sensor Actuat B Chem 239:69–75
Chang LF, Wu HC, He XW, Chen LX, Zhang YK (2017) A highly sensitive fluorescent turn-on biosensor for glycoproteins based on boronic acid functional polymer capped Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots. Anal Chim Acta 995:91–98
Li L, Cheng Y, Ding YP, Gu SQ, Zhang FF, Yu WJ (2013) Synthesis of Functionalized Core–Shell CdTe/ZnS Nanoparticles and Their Application as a Fluorescence Probe for Norfloxacin Determination. J Inorg Chem 14:2564–2570
Hua JH, Jiao Y, Wang M, Yang YL (2018) Determination of norfloxacin or ciprofloxacin by carbon dots fluorescence enhancement using magnetic nanoparticles as adsorbent. Microchim Acta 185(2):137
Moreira FTC, Freitas VAP, Sales MGF (2011) Biomimetic norfloxacin sensors made of molecularly-imprinted materials for potentiometric transduction. Microchimi Acta 172(1-2):15–23
Ding H, Jiao HF, Shi XZ, Sun AL, Guo XQ, Li DX, Chen J (2017) Molecularly imprinted optosensing sensor for highly selective and sensitive recognition of sulfadiazine in seawater and shrimp samples. Sensor Actuat B Chem 246:510–517
Gomes SAO, Vieira CS, Almeida DB, Santos-Mallet JR, Menna-Barreto RFS, Cesar CL, Feder D (2011) CdTe and CdSe quantum dots cytotoxicity: a comparative study on microorganisms. Sensors 11:11664–11678
Martín-Esteban A (2001) Molecularly imprinted polymers: new molecular recognition materials for selective solid-phase extraction of organic compounds, Fresen. Anal Chem 370:795–802
Zu FL, Yan FY, Bai ZJ, Xu JX, Wang YY, Huang YC, Zhou XG (2017) The quenching of the fluorescence of carbon dots: A review on mechanisms and applications. Microchimi Acta 184(7):1899–1914
Xu S, Lu H, Li J, Song X, Wang A, Chen L, Han S (2013) Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers-capped CdTe quantum dots for the fluorescent sensing of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. ACS Appl Mater Inter 5:8146–8154
Zhou ZP, Li T, Xu WZ, Huang WH, Wang NW, Yang WM (2017) Synthesis and characterization of fluorescence molecularly imprinted polymers as sensor for highly sensitive detection of dibutyl phthalate from tap water samples. Sensor Actuat B Chem 240:1114–1122
Coverly S, Kérouel R, Aminot A (2012) A re-examination of matrix effects in the segmented-flow analysis of nutrients in sea and estuarine water. Anal Chim Acta 712:94–100
Hong JJ, Chen QL, Yi QT, Chen M, Yuan DX (2013) Evaluation and improvement of multi-residual determination accuracy of trace veterinary drugs in seawater. J Xiamen University 52:0438–0479
Yang SG, Li ZX, Wang QY, Guo MM, Tan ZJ, Xing LH, Yao JH (2010) Determination of quinolones drug residues in aquacultural seawater using HPLC method. Progress in Fishery Sciences 31(2):95–101
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41876078), the Public Science and Technology Research Funds Projects of Ocean (No. 201505034), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (ZR2018MD016) and the Special Fund for Basic Scientific Research in Central Colleges and Universities (No. 201713059). We especially thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive commends.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
No conflict of interest exits in this manuscript, and the manuscript is approved by all authors for publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 856 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, T., Fu, H., Tan, L. et al. CdTe quantum dots coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer for fluorometric determination of norfloxacin in seawater. Microchim Acta 186, 362 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3440-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3440-7