Abstract
The capability of multi-level logic operations in biological diagnosis is far from being fully realized. In particular, the simplification of logic judgments to realize rapid, on-site complex diagnoses is still a key issue in bioelectronics. The authors here describe the construction of a colorimetric multilevel DNA circuit that incorporates two IMPLY gates and a sample extraction technology (SET) with anti-BPA aptamer as a co-recognizing element and the color of gold nanoparticles as the output signal. The circuit can perform multi-bioanalysis of the plasticizers and hormone mimetics bisphenol A (BPA) and bisphenol S (BPS). The assay is based on the finding that the aptamer against BPA can recognize both BPA and BPS. This DNA logic detection system is simple, fast, sensitive and selective because of the utilization of a co-recognition element which decreased input numbers. This, in turn, cascades multiplex Boolean logic gates and simplifies the diagnostic challenge. Both BPA and BPS can be determined by photometry at 620 nm, the limit of detection being 1.5 ng⋅mL−1 for BPA and 1.3 ng⋅mL−1 for BPS. Application to (spiked) water samples shows good analytical performance in terms of recovery (95.4 to 106.8%), linear range (4.4 to 66 ng⋅mL−1 for BPA, 2.5 to 75 ng⋅mL−1 for BPS) and correlation coefficients (>0.98). In our perception, the method represents a simple route for the fabrication of colorimetric multi-level DNA circuits. It may shorten the gap between bioelectronic logic circuits and high throughput real sample analysis.

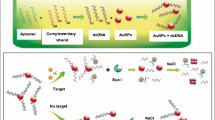
Illustration of sample extraction treatments (SET) of bisphenol A (BPA) and bisphenol S (BPS) and the three-input IMPLY1-IMPLY2 logic operation with BPA, BPS and anti-BPA aptamer as inputs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Q, Yoo SY, Chung YH, Lee JY, Min J, Choi JW (2016) Control of electrochemical signals from quantum dots conjugated to organic materials by using DNA structure in an analog logic gate. Bioelectrochemistry 111:–6
Zhang Y, Liu W, Zhang W, Yu S, Yue X, Zhu W, Zhang D, Wang Y, Wang J (2015) DNA-mediated gold nanoparticle signal transducers for combinatorial logic operations and heavy metal ions sensing. Biosens Bioelectron 72:218–224
Du J, Yin S, Jiang L, Ma B, Chen X (2013) A colorimetric logic gate based on free gold nanoparticles and the coordination strategy between melamine and mercury ions. Chem Commun 49:4196–4198
Park KS, Jung C, Park HG (2010) “Illusionary” polymerase activity triggered by metal ions: use for molecular logic-gate operations. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:9757–9760
Xianyu Y, Wang Z, Sun J, Wang X, Jiang X (2014) Colorimetric logic gates through molecular recognition and plasmonic nanoparticles. Small 10:4833–4838
Yang B, Zhang X, Kang L, Huang Z, Shen G, Yu R, Tan W (2014) Intelligent layered nanoflare:“lab-on-a-nanoparticle” for multiple DNA logic gate operations and efficient intracellular delivery. Nanoscale 6:8990–8996
Feng L, Lyu Z, Offenhausser A, Mayer D (2015) Multi-level logic gate operation based on amplified aptasensor performance. Angew Chem Int Ed 54:7693–7697
Yang J, Song Z, Liu S, Zhang Q, Zhang C (2016) Dynamically arranging gold nanoparticles on DNA origami for molecular logic gates. Appl Mater Interfaces 8:22451–22456
Qin C, Gao Y, Wen W, Zhang X, Wang S (2016) Visual multiple recognition of protein biomarkers based on an array of aptamer modified gold nanoparticles in biocomputing to strip biosensor logic operations. Biosens Bioelectron 79:522–530
Wang J, Lu J, Su S, Gao J, Huang Q, Wang L, Huang W, Zuo X (2015) Binding-induced collapse of DNA nano-assembly for naked-eye detection of ATP with plasmonic gold nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 65:171–175
Zhang Y, Li M, Liu H, Ge S, Yu J (2016) Label-free colorimetric logic gates based on free gold nanoparticles and the coordination strategy between cytosine and silver ions. New J Chem 40:5516–5522
Wu Z, Dong B, Zhou X, Shen A, Hu J (2015) INHIBIT-inspired two-output DNA logic gates based on surface-enhanced raman scattering volume. Chemistry 21:14301–14304
Chen JH, Fang ZY, Lie PC, Zeng LW (2012) Computational lateral flow biosensor for proteins and small molecules: a new class of strip logic gates. Anal Chem 84:6321–6325
Song T, Liang H (2012) Synchronized assembly of gold nanoparticles driven by a dynamic DNA-fueled molecular machine. J Am Chem Soc 134:10803–10806
Zhang L, Wang Z, Liang R, Qiu J (2013) Easy design of colorimetric logic gates based on nonnatural base pairing and controlled assembly of gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 29:8929–8935
Yang C, Wang Y, Marty JL, Yang X (2011) Aptamer-based colorimetric biosensing of Ochratoxin A using unmodified gold nanoparticles indicator. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2724–2727
Li J, Chang K, Wang C, Yang C, Shiesh S, Le G (2016) On-chip, aptamer-based sandwich assay for detection of glycated hemoglobins via magnetic beads. Biosens Bioelectron 79:887–893
Deng C, Zhong Y, He Y, Ge Y, Song G (2016) Selective determination of trace bisphenol a using molecularly imprinted silica nanoparticles containing quenchable fluorescent silver nanoclusters. Microchim Acta 183:431–439
Diao C, Yang X, Sun A, Liu R (2015) Vortex-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction of bisphenol S prior to its determination by HPLC with UV detection. Microchim Acta 182:2593–2600
Huang YQ, Wong CKC, Zheng J, Bouwman SH, Barra R, Wahlstrom B, Neretin L, Wong MH (2012) Bisphenol A (BPA) in China: a review of sources, environmental levels, and potential human health impacts. Environ Int 42:91–99
Kinch CD, Lbhazehiebo K, Jeong JH, Habibi HR, Kurrasch DM (2015) Low-dose exposure to bisphenol A and replacement bisphenol S induces precocious hypothalamic neurogenesis in embryonic zebrafish. PNAS 5:1475–1480
Gallart-Ayala H, Moyano E, Galceran MT (2011) Analysis of bisphenols in soft drinks by on-line solid phase extraction fast liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 683:227–233
Ragavan KV, Selvakumar LS, Thakur MS (2013) Functionalized aptamers as nano-bioprobes for ultrasensitive detection of bisphenol-A. Chem Commun 49:5960–5962
Xu J, Li Y, Bie J, Jiang W, Guo J, Luo Y, Shen F, Sun C (2015) Colorimetric method for determination of bisphenol A based on aptamer-mediated aggregation of positively charged gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182:2131–2138
Zhu Y, Zhou C, Yan X, Yan Y, Wang Q (2015) Aptamer-functionalized nanoporous gold film for high-performance direct electrochemical detection of bisphenol A in human serum. Anal Chim Acta 883:81–89
Vinas P, Campillo N, Martinez-Castillo N, Hernandez-Cordoba M (2010) Comparison of two derivatization-based methods for solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometric determination of bisphenol A, bisphenol S. Anal Bioanal Chem 397:115–125
Becerra V, Odermatt J (2012) Detection and quantification of traces of bisphenol A and bisphenol S in paper samples using analytical pyrolysis-GC/MS. Analyst 137:2250–2259
Xing H, Zhan S, Wu Y, He L, Zhou P (2013) Sensitive colorimetric detection of melamine in milk with an aptamer-modified nanogold probe. RSC Adv 3:17424–17430
Jo M, Ahn JY, Lee J, Lee S, Hong SW, Yoo JW, Kang J, Dua P, Lee D, Hong S, Kim S (2011) Development of single-stranded DNA aptamers for specific bisphenol A detection. Oligonucleotides 21:85–91
Mei Z, Chu H, Chen W, Xue F, Liu J, Xu H, Zhang R, Zheng L (2013) Ultrasensitive one-step rapid visual detection of bisphenol A in water samples by label-free aptasensor. Biosens Bioelectron 39:26–30
Acknowledgements
This research was financed by Grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21675127), the New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-13-0483), the Shaanxi Provincial Research Fund (2014KJXX-42, 2014 K02-13-03, 2014 K13-10) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Northwest A&F University of China (2014YB093, 2452015257).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 12.4 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Zhu, W. et al. Simultaneous colorimetric determination of bisphenol A and bisphenol S via a multi-level DNA circuit mediated by aptamers and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184, 951–959 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2092-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2092-8