Abstract
Purpose
The determination on how antineoplastic agents interfere on the progression of periodontitis is critical for improvement and even development of novel therapeutic approaches for periodontal management. This study evaluated the influence of chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) or cisplatin (CIS) on healthy periodontal tissues and on the progression of experimental periodontitis (EP).
Methods
One hundred forty-four male rats were divided into six groups (n = 24). Each group was treated with physiological saline solution (PSS) 0.9%, 5-FU, or CIS. Experimental periodontitis (EP) was induced by ligature placement. Animals were euthanized at 7, 15, and 30 days after treatment. Data were statistically analyzed (p ≤ 0.05).
Results
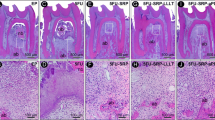
The groups with EP and treated with 5-FU or CIS showed lower percentage of bone volume in the furcation region and higher percentage of alveolar bone loss, higher number of TRAP-positive cells, and lower number of PCNA-positive cells when compared group with EP and treated with PSS (p ≤ 0.05). Groups with EP and treated with 5-FU or CIS showed high immunolabelling pattern of RANKL, TNF-α, and IL-1β, moderate of BAX, and low of HIF-1α. Histological analysis showed severe tissue breakdown in the groups with EP and treated with 5-FU or CIS.
Conclusions
Chemotherapy with antineoplastic agents 5-FU and CIS increased the intensity and duration of the inflammation and compromised tissue repair by reduction in cellular and vascular turnover. The more severe periodontal breakdown was caused by 5-FU.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
My manuscript has data included as electronic supplementary material if necessary.
Code availability
N/A.
Notes
5-FU: 5-fluorouracil.
CIS: cisplatin.
EP: experimental periodontitis.
SRP: scaling and root planning.
PABL: percentage of alveolar bone loss.
PSS: physiological saline solution.
µCT: microcomputed tomography.
TRAP: tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase.
RANKL: receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand.
OPG: osteoprotegerin.
TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-alfa.
IL-1β: interleukin 1 beta.
PCNA: proliferating cell nuclear antigen.
BAX: bcl-2-associated X protein.
HIF-1α: hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha.
PBTV: percentage of bone tissue volume.
References
Schenkein HA (2006) Host responses in maintaining periodontal health and determining periodontal disease. Periodontol 2000 40:77–93. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0757.2005.00144.x
Cekici A, Kantarci A, Hasturk H, Van Dyke TE (2014) Inflammatory and immune pathways in the pathogenesis of periodontal disease. Periodontol 2000 64:57–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12002
Nassar PO, Nassar CA, Guimarães MR, Aquino SG, Andia DC, Muscara MN, Spolidorio DMP, Rossa C Jr, Spolidorio LC (2009) Simvastatin therapy in cyclosporine A-induced alveolar bone loss in rats. J Periodontal Res 44:479–488. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0765.2008.01143.x
Fernandes LA, de Almeida JM, Theodoro LH, Bosco AF, Nagata MJH, Martins TM, Okamoto T, Garcia VG (2009) Treatment of experimental periodontal disease by photodynamic therapy in immunosuppressed rats. J Clin Periodontol 36:219–228. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01355.x
Guchelaar HJ, Vermes I, Koopmans RP, Reutelingsperger CP, Haanen C (1998) Apoptosis- and necrosis-inducing potential of cladribine, cytarabine, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil in vitro: a quantitative pharmacodynamic model. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 42:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002800050788
Arias JL (2008) Novel strategies to improve the anticancer action of 5-fluorouracil by using drug delivery system. Molecules 13:2340–2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules13102340
Wong HM (2014) Oral complications and management strategies for patients undergoing cancer therapy. Sci World J 2014:581795. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules13102340
Lorch JH, Goloubeva O, Haddad RI, Cullen K, Sarlis N, Tishler R, Tan M, Fasciano J, Sammartino DE, Posner MR, TAX 324 Study Group (2011) Induction chemotherapy with cisplatin and fluorouracil alone or in combination with docetaxel in locally advanced squamous-cell cancer of the head and neck: long-term results of the TAX 324 randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 12:153–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70279-5
Vermorken JB, Peyrade F, Krauss J, Mesía R, Remenar E, Gauler TC, Keilholz U, Delord JP, Schafhausen P, Erfán J, Brümmendorf TH, Iglesias L, Bethe U, Hicking C, Clement PM (2014) Cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil, and cetuximab (PFE) with or without cilengitide in recurrent/metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: results of the randomized phase I/II ADVANTAGE trial (phase II part). Ann Oncol 25:682–688. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdu003
Longley DB, Harkin DP, Johnston PG (2003) 5-fluorouracil: mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat Rev Cancer 3:330–338. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1074
Havelka AM, Berndtsson M, Olofsson MH, Shoshan MC, Linder S (2007) Mechanisms of action of DNA-damaging anticancer drugs in treatment of carcinomas: is acute apoptosis an “off-target” effect? Mini Rev Med Chem 7:1035–1039. https://doi.org/10.2174/138955707782110196
Garcia VG, Novaes VC, De Almeida JM, Longo M, Ervolino E, Bomfim SRM, Theodoro LH (2015) Evaluation of the progression and treatment of experimental periodontitis in rats subjected to chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil. Support Care Cancer 23:2007–2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-014-2563-y
Theodoro LH, Longo M, Ervolino E, Duque C, Ferro-Alves ML, Assem NZ, Louzada LM, Garcia VG (2016) Effect of low-level laser therapy as an adjuvant in the treatment of periodontitis induced in rats subjected to 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy. J Periodontal Res 51:669–680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-014-2563-y
Theodoro LH, Longo M, Novaes VCN, Miessi DMJ, Ferro-Alves E, de Almeida JM, Garcia VG (2017) Low-level laser and antimicrobial photodynamic therapy on experimental periodontitis in rats submitted to chemotherapy by 5-fluorouracil. Support Care Cancer 25:3261–3271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-017-3738-0
Gusman DJR, Ervolino E, Theodoro LH, Garcia VG, Nagata MJH, Alves BES, de Araujo NJ, Matheus HR, de Almeida JM (2019) Antineoplastic agents exacerbate periodontal inflammation and aggravate experimental periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 46:457–469. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13101
Percie du Sert N, Ahluwalia A, Alam S, Avey MT, Baker M, Browne WJ, Clark A, Cuthill IC, Dirnagl U, Emerson M, Garner P, Holgate ST, Howells DW, Hurst V, Karp NA, Lazic SE, Lidster K, MacCallum CJ, Macleod M, Pearl EJ, Petersen OH, Rawle F, Reynolds P, Rooney K, Sena ES, Silberberg SD, Steckler T, Würbel H (2020) Reporting animal research: explanation and elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0. PLoS Biol 18(7):e3000411. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000411
Johnson JH (1975) Effects of local irritation and dextran and sufphat administration on the periodontium of the rat. J Periodontal Res 10:332–345. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0765.1975.tb00042.x
de Almeida JM, Theodoro LH, Bosco AF, Nagata MJH, Oshiiwa M, Garcia VG (2007) Influence of photodynamic therapy on the development of ligature-induced periodontitis in rats. J Periodontol 78:566–575. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2007.060214
de Almeida JM, Theodoro LH, Bosco AF, Nagata MJ, Bonfante S, Garcia VG (2008) Treatment of experimental periodontal disease by photodynamic therapy in rats with diabetes. J Periodontol 79:2156–2165. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2008.080103
de Almeida J, Ervolino E, Bonfietti LH, Novaes VC, Theodoro LH, Fernandes LA, Martins TM, Faleiros PL, Garcia VG (2015) Adjuvant therapy with sodium alendronate for the treatment of experimental periodontitis in rats. J Periodontol 86:1166–1175. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2015.150166
Matheus HR, Ervolino E, Faleiros PL, Novaes VCN, Theodoro LH, Garcia VG, de Almeida JM (2018) Cisplatin chemotherapy impairs the peri-implant bone repair around titanium implants: an in vivo study in rats. J Clin Periodontol 45:241–252. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12824
Park CH, Abramson ZR, Taba MJR, Jin Q, Chang J, Kreider JM, Goldstein SA, Giannobile WV (2007) Three-dimensional micro-computed tomographic imaging of alveolar bone in experimental bone loss or repair. J Periodontol 78:273–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcma.2017.11.002
Zuza EP, Garcia VG, Theodoro LH, Ervolino E, Favero LFV, Longo M, Ribeiro FS, Martins AT, Spolidorio LC, Zuanon JAS, de Toledo BEC, Pires JR (2018) Influence of obesity on experimental periodontitis in rats: histopathological, histometric and immunohistochemical study. Clin Oral Investig 22:1197–1208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-017-2207-y
Garcia VG, Gualberto Júnior EC, Fernandes LA, Bosco AF, Hitomi Nagata MJ, Casatti CA, Ervolino E, Theodoro LH (2013) Adjunctive antimicrobial photodynamic treatment of experimentally induced periodontitis in rats with ovariectomy. J Periodontol 84:556–565. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2012.120163
Garcia VG, Longo M, Gualberto Júnior EC, Bosco AF, Nagata MJH, Ervolino E, Theodoro LH (2014) Effect of the concentration of phenothiazine photosensitizers in antimicrobial photodynamic therapy on bone loss and the immune inflammatory response of induced periodontitis in rats. J Periodontal Res 49:584–594. https://doi.org/10.1111/jre.12138
Graves D (2008) Cytokines that promote periodontal tissue destruction. J Periodontol 79:1585–1591. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2008.080183
Graves DT, Cochran D (2003) The contribution of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor to periodontal tissue destruction. J Periodontol 74:391–401. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2003.74.3.391
Raghu Nadhanan R, Abimosleh SM, Su YW, Scherer AM, Howarth GS, Xian CJ (2012) Dietary emu oil supplementation suppresses 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy-induced inflammation, osteoclast formation, and bone loss. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 302:E1440–E1449. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00587.2011
Stine KC, Wahl EC, Liu L, Skinner RA, Vanderschilden J, Bunn RC, Montgomery CO, Suva LJ, Aronson J, Becton DL, Nicholas RW, Swearingen CJ, Lumpkin CK Jr (2014) Cisplatin inhibits bone healing during distraction osteogenesis. J Orthop Res 32:464–470. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.22527
Graves DT, Li J, Cochran DL (2011) Inflammation and uncoupling as mechanisms of periodontal bone loss. J Dent Res 90:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034510385236
Preshaw PM, Taylor JJ (2011) How has research into cytokine interactions and their role in driving immune responses impacted our understanding of periodontitis? J Clin Periodontol 38:60–84. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2010.01671.x
Hamouda N, Sano T, Oikawa Y, Ozaki T, Shimakawa M, Matsumoto K, Amagase K, Higuchi K, Kato S (2017) Apoptosis, dysbiosis and expression of inflammatory cytokines are sequential events in the development of 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in mice. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 121:159–168. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.12793
de Araújo AA, Varela H, de Medeiros CA, Brito GAC, de Lima KC, de Moura LM, de Araújo Júnior RF (2015) Azilsartan reduced TNF-α and IL-1β levels, increased IL-10 levels and upregulated VEGF, FGF, KGF, and TGF-α in an oral mucositis model. PLoS ONE 17(10):e0116799. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0116799
Miller RP, Tadagavadi RK, Ramesh G, Reeves WB (2010) Mechanisms of Cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Toxins (Basel) 2:2490–2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2112490
Wisniewska-Jarosinska M, SliwinskI T, Kasznicki J, Krupa R, Bloch K, Drzewoski J, Chojnacki J, Blasiak J, Morawiec-Sztandera A (2011) A Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of capecitabine in head and neck cancer and normal cells. Mol Biol Rep 38:3679–3688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0482-7
Cho JM, Manandhar S, Lee HR, Park HM, Kwak MK (2008) Role of the Nrf2-antioxidant system in cytotoxicity mediated by anticancer cisplatin: Implication to cancer cell resistance. Cancer Lett 260:96–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2007.10.022
Mailand N, Gibbs-Seymour I, Bekker-Jensen S (2013) Regulation of PCNA-protein interactions for genome stability. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14:269–282. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3562
Mukhopadhyay S, Panda PK, Sinha N, Das DN, Bhutia SK (2014) Autophagy and apoptosis: where do they meet? Apoptosis 19:555–566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-0967-2
Al-Mahalawy H, Marei HF, Abuohashish H, Alhawaj H, Alrefaee M, Al-Jandan B (2016) Effects of cisplatin chemotherapy on the osseointegration of titanium implants. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 44:337–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2016.01.012
Ahluwalia A, Tarnawski AS (2012) Critical role of hypoxia sensor–HIF-1α in VEGF gene activation. Implications for angiogenesis and tissue injury healing. Curr Med Chem 19:90–97. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986712803413944
Wang Y, Wan C, Deng L, Liu X, Cao X, Gilbert SR, Bouxsein ML, Faugere MC, Guldberg RE, Gerstenfeld LC, Haase VH, Johnson RS, Schipani E, Clemens TL (2007) The hypoxia-inducible factor alpha pathway couples angiogenesis to osteogenesis during skeletal development. J Clin Invest 117:1616–1626. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI31581
Schmidt-Bleek K, Schell H, Lienau J, Schulz N, Hoff P, Pfaff M, Schmidt G, Martin C, Perka C, Buttgereit F, Volk HD, Duda G (2014) Initial immune reaction and angiogenesis in bone healing. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 8:120–130. https://doi.org/10.1002/term.1505
Garlet GP (2010) Destructive and protective roles of cytokines in periodontitis: a re-appraisal from host defense and tissue destruction viewpoints. J Dent Res 89:1349–1363. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034510376402
Hong BY, Sobue T, Choquette L, Dupuy AK, Thompson A, Burleson JA, Salner AL, Schauer PK, Joshi P, Fox E, Shin DG, Weinstock GM, Strausbaugh LD, Dongari-Bagtzoglou A, Peterson DE, Diaz PI (2019) Chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis is associated with detrimental bacterial dysbiosis. Microbiome 7(1):66. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-019-0679-5
Wang Y, Zeng X, Yang X, Que J, Du Q, Zhang Q, Zou J (2021) Oral health, caries risk profiles, and oral microbiome of pediatric patients with leukemia submitted to chemotherapy. Biomed Res Int 16(2021):6637503. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6637503
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Periodontics Division, the Department of Basic Sciences of the School of Dentistry, São Paulo State University (UNESP), Araçatuba, São Paulo, Brazil, and São Paulo State University (UNESP), School of Veterinary Medicine, Araçatuba. The authors also thank CAPES for providing scholarship to Dr. Vivian Novaes, and São Paulo State Foundation for Research (FAPESP) for the research grant conceded to Dr. Juliano Milanezi de Almeida (#2014/11427-8). Also, Clara Possarle Cunha (#2015/21332-7) and Giovani Lopes Fernandes (#2015/04639-1) received scholarships from FAPESP.
Funding
Dr. Juliano Milanezi de Almeida received a grant from the São Paulo State Foundation for Research- FAPESP (#2014/11427–8).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VCNN, EE, and JMA have made substantial contributions to conception and design of the study. GLF and CPC have been involved in animal surgery, laboratory processing, and data collection. VCNN have been involved in conception, study design, animal surgery, laboratory processing, data interpretation, and drafting the manuscript. EE have been involved in study design, histological and immunohistochemical analysis, and critically revised the manuscript. JMA have been involved in conception, study design, data interpretation, statistical procedures, and critically revised the manuscript. LHT and VGG have critically revised the manuscript. All authors have given final approval of the version to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All protocols were approved by Ethics Committee in Animal Use (#2014/00543) of the School of Dentistry of Araçatuba, São Paulo State University (UNESP).
Consent to participate
N/A.
Consent for publication
This manuscript has only been submitted to this journal. It was read and approved by all authors and, if accepted, it will not be published elsewhere in the same form, in English or in any other language, without the written consent of the copyright-holder.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Novaes, V.C.N., Ervolino, E., Fernandes, G.L. et al. Influence of the treatment with the antineoplastic agents 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin on the severity of experimental periodontitis in rats. Support Care Cancer 30, 1967–1980 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-021-06586-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-021-06586-y