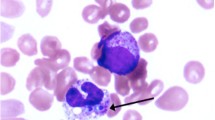
Summary
Toxoplasma gondii is a widespread protozoan parasite that infects one third of the global human population. Very little information is known about the impact of T. gondii on patients with heart disease. The aim of the present study was to determine the association between T. gondii exposure and patients suffering from myocardial infarction.
The infection rate of anti-Toxoplasma IgG antibodies in 86 patients with myocardial infarction (troponin‑T positive) and 86 age and gender-matched controls (troponin‑T negative) was examined using enzyme-linked immunoassays. The DNA extraction was performed on separated buffy coats of serologically positive blood samples (32 samples with high titer of anti-Toxoplasma IgG). The GRA6 gene of T. gondii was amplified using PCR. The existence of polymorphic restriction sites for endonuclease MseI was used with the PCR-RFLP method and the bases of GRA6 gene were sequenced to determine the type of strains (I, II and III).
A positive anti-Toxoplasma IgG level was found in 61.6% of the myocardial infarction samples and in 24.4% of the healthy controls (P- value < 0.05). The PCR results showed that only 3 of the anti-Toxoplasma IgG positive patients were found to be positive with GRA6 gene for T. gondii. The PCR-RFLP results showed that 2 of the 3 positive sample had 75bp and 623 bp DNA fragments belonging to type II genotype. The sequencing result confirmed the genotype II of T. gondii. Toxoplasma infection should be considered in myocardial infarction cases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dubey JP. Toxoplasmosis of animals and humans. 2nd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2010.
Montoya JG, Liesenfeld O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet. 2004;363:1965–76.
Maenz M, Schlüter D, Liesenfeld O, Schares G, Gross U, Pleyer U. Ocular toxoplasmosis past, present and new aspects of an old disease. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2014;39:77–106.
Remington JS, McLeod R, Wilson CB, Desmonts G. Infectious diseases of the fetus and newborn. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2011. pp. 918–1041. Ch.31.
Moncada PA, Montoya JG. Toxoplasmosis in the fetus and newborn: an update on prevalence, diagnosis and treatment. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2012;10:815–28.
Ferreira SM, Borges SA. Some aspects of protozoan infections in immune compromised patients—a review. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2004;97(4):443–57.
Pereira-Chioccola VL, Vidal JE, Su C. T. gondii infection and cerebral toxoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients. Future Microbiol. 2004;4(10):1363–79.
Mann D, Zipes D, Libby P, Bonow R. Braunwald’s heart disease. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2014. p. 433.
Feldman AM, McNamara D. Myocarditis. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1388–98.
Hidron A, Vogenthaler N, Santos-Preciado JI, Rodriguez-Morales AJ, Franco-Paredes C, Rassi A. Cardiac involvement with parasitic infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010;23(2):324–49.
Kirchoff LV, Weiss LM, Wittneer M, Tanowitz HB. Parasitic diseases of the heart. Front Biosci. 2004;9:706–23.
Kean BH, Grocott RG. Sarcosporidiosis and toxoplasmosis in man and guinea pig. Am J Pathol 1945;21:467–83.
Mullan DP, Henry L, Beverley JKA. Toxoplasmosis and myocarditis. Br Heart J. 1968;4:559–60.
Chandenier J, Jarry G, Nassif D, Douadi Y, Paris L, Thulliez P, et al. Congestive heart failure and myocarditis after seroconversion for toxoplasmosis in two immunocompetent patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000;19(5):375–9.
Lesenne M, Asseman P, Fortier B, de Groote P, Bauchart JJ, Millaire A, et al. Acute myocarditis caused by toxoplasmosis simulating infarction. A propose of a case. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 1996;89(7):923–5.
Lanjewar DN, Agate SV, Chitale AR, Joshi SR. Sudden death due to cardiac toxoplasmosis. J Assoc Physicians India. 2006;54:244–5.
Mary AS, Hamilton M. Ventricular tachycardia in a patient with toxoplasmosis. Br Heart J. 1973;35:349–52.
De la Gastine G, Dupont P, Maragnes P, Jokic M, Krayem L, Guillois B, et al. Acute myocarditis with T. gondii. A case report in a newborn. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2005;98(5):582–5.
Paulley JW, Jones R, Green WPD, Kane EP. Myocardial toxoplasmosis. Br Heart J. 1956;18(1):55–64.
Chapman N, MacLennan WJ, Rahilly M. T. gondii: an unusual cause of myocarditis in old age. Postgrad Med J. 1995;71:168–9.
Shee JC. Stokes-Adams attacks due to T. myocarditis. Br Heart J. 1964;26:151.
Negaratnam N, Stephen J. Chronic constrictive pericarditis associated with toxoplasmosis. Br Heart J. 1973;35:868–70.
Leak D, Meghji M. Toxoplasmic infection in cardiac disease. Am J Cardiol. 1979;43(4):841–9.
Sano J, Saitoh H, Kobayashi Y, Ikeda M, Kodani E, Takayama M, et al. Toxoplasma pericarditis without immunosuppressant disorder detected by polymerase chain reaction of pericardial fluid: a case report. J Cardiol. 2000;35(1):47–54.
Alvarado-Esquivel C, Salcedo-Jaquez M, Sanchez-Anguiano LF, Hernandez-Tinoco J, Rabago-Sanchez E, Beristain-Garcia I, et al. Association between Toxoplasma gondii exposure and heart disease: A case-control study. J Clin Med Res. 2016;8(5):402.
Gallino A, Maggiorini M, Kiowski W, Martin X, Wunderli W, Schneider J, et al. Toxoplasmosis in heart transplant recipients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1996;15(5):389–93.
Mayes JT, O’Connor BJ, Avery R, Castellani W, Carey W. Transmission of Toxoplasma gondii infection by liver transplantation. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;21(3):511–5.
Hamidinejat H, Mirmoemen SH, Ghorbanpour M, Borojeni MP, Jafari H, Dashtegol S, et al. Probable role of Toxoplasma gondii in misdiagnosing of acute myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 2013;167(1):285–6.
Samojlowicz D, Borowska-Solonynko A, Golab E. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii parasite infection among people who died due to sudden death in the capital city of Warsaw and its vicinity. Przegl Epidemiol. 2013;67(1):29–118.
Arrizabalaga G, Boothroyd JC. Role of calcium during Toxoplasma gondii invasion and egress. Int J Parasitol. 2004;34(3):361–8.
Hofman P, Drici MD, Gibelin P, Michiels JF, Thyss A. Prevalence of T. myocarditis in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Br Heart J. 1993;70(4):376–81.
Hofman P, Bernard E, Michiels J, Thyss A, Le Fichoux Y, Loubiere R. Extracerebral toxoplasmosis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Pathol Res Pract. 1993;189(8):894–901.
Wagner F, Reichenspurner H, Uberfuhr P, Weiss M, Fingerle V, Reichart B. Toxoplasmosis after heart transplantation: diagnosis by endomyocardial biopsy. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1994;13(5):916–8.
Mary A, Hamilton M. Ventricular tachycardia in a patient with toxoplasmosis. Br Heart J. 1973;35(3):349.
Wreghitt T, Gray J, Pavel P, Balfour A, Fabbri A, Sharples L, et al. Efficacy of pyrimethamine for the prevention of donor-acquired Toxoplasma gondii infection in heart and heart-lung transplant patients. Transpl Int. 1992;5(4):197–200.
Franco-Paredes C, Rouphael N, Méndez J, Folch E, Rodríguez-Morales AJ, Santos JI, et al. Cardiac manifestations of parasitic infections part 2: Parasitic myocardial disease. Clin Cardiol. 2007;30(5):218–22.
Yazar S, Eser B, Yay M. Prevalence of anti-Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in Turkish blood donors. Ethiop Med J. 2006;44:257–61.
Fazaeli A, Carter P, Darde M, Pennington T. Molecular typing of Toxoplasma gondii strains by GRA6 gene sequence analysis. Int J Parasitol. 2000;30(5):637–42.
Saeij JP, Boyle JP, Boothroyd JC. Differences among the three major strains of Toxoplasma gondii and their specific interactions with the infected host. Trends Parasitol. 2005;21(10):476–81.
Dubey JP. The history and life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. Toxoplasma gondii. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2014. pp. 1–17.
Howe DK, Sibley LD. Toxoplasma gondii comprises three clonal lineages: correlation of parasite genotype with human disease. J Infect Dis. 1995;172(6):1561–6.
Ajzenberg D, Cogné N, Paris L, Bessières M‑H, Thulliez P, Filisetti D, et al. Genotype of 86 Toxoplasma gondii isolates associated with human congenital toxoplasmosis, and correlation with clinical findings. J Infect Dis. 2002;186(5):684–9.
Zia-Ali N, Fazaeli A, Khoramizadeh M, Ajzenberg D, Dardé M, Keshavarz-Valian H. Isolation and molecular characterization of Toxoplasma gondii strains from different hosts in Iran. Parasitol Res. 2007;101(1):111–5.
Gebremedhin EZ, Abdurahaman M, Tessema TS, Tilahun G, Cox E, Goddeeris B, et al. Isolation and genotyping of viable Toxoplasma gondii from sheep and goats in Ethiopia destined for human consumption. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7(1):425.
Nourmohammadi M, Hamidinejat H, Tabandeh M, Goraninejad S, Bahrami S. Genotyping of zoonotic toxoplasm gondii isolated from aborted fetuses of ewes of Lorestan province based on SAG2 SAG3 and GRA6 molecular markers. J Ardabil Univer Med Sci. 2017;17(3):343–52.
Swierzy IJ, Muhammad M, Kroll J, Abelmann A, Tenter AM, Lüder CG. Toxoplasma gondii within skeletal muscle cells: a critical interplay for food-borne parasite transmission. Inter J Parasitol. 2014;44(2):91–8.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the personnel and staff of the Parasitology Department of Medical Sciences, Faculty of Tarbiat Modares University for their kind help during this research.
Funding
The present work is part of an MSc thesis, funded by Tarbiat Modares University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
O. Gohari, A. Dalimi, and M. Pirestani declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
The study was approved by the Tarbiat Modares University Ethical Review Board, Tehran, Iran. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants or on human tissue were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1975 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent: for this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gohari, O., Dalimi, A. & Pirestani, M. Toxoplasma infection in patients with myocardial infarction. Wien Klin Wochenschr 132, 736–741 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-020-01682-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-020-01682-1