Abstract
Background
Recently, there has been a burgeoning interest in radiofrequency ablation combined with stent (RFA + Stent) for unresectable malignant biliary obstruction (MBO). This study aimed to perform a meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy and safety of RFA + Stent compared with biliary stent alone.
Methods
We searched PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, and Web of Science databases from their inception dates to June 20, 2021, for studies that compared RFA + Stent and stent alone for unresectable MBO. The main outcomes were survival, patency, and adverse effects. All meta-analyses were calculated using the random-effects model.
Results
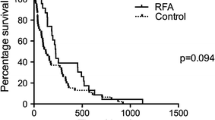
A total of 19 studies involving 1946 patients were included in this study. Compared with stent alone, RFA + Stent was significantly associated with better overall survival (HR 0.55; 95% CI 0.48, 0.63; P < 0.00001), longer mean survival time (SMD 2.20; 95% CI 1.17, 3.22; P < 0.0001), longer mean stent patency time (SMD 1.37; 95% CI 0.47, 2.26; P = 0.003), higher stent patency at 6 months (OR 2.82; 95% CI 1.54, 5.18; P = 0.0008). The two interventions had similar incidence of postoperative abdominal pain (OR 1.29; 95% CI 0.94, 1.78; P = 0.11), mild bleeding (OR 1.28; 95% CI 0.65, 2.54; P = 0.48), cholangitis (OR 1.09; 95% CI 0.76, 1.55; P = 0.65), pancreatitis (OR 1.39; 95% CI 0.82, 2.38; P = 0.22). Furthermore, the serum bilirubin levels and stricture diameter after operations were significantly alleviated than before operations, but the degree of alleviation between the two groups were not significantly different (all P > 0.05).
Conclusion
Although the alleviation of serum bilirubin and stricture diameter did not differ between the two interventions, RFA + Stent can significantly improve the survival and stent patency with comparable procedure-related adverse events than stent alone. Thus, RFA + Stent should be recommended as an attractive alternative to biliary stent alone for patients with unresectable MBO.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- GRADE:
-
Grading of recommendations assessment, development, and evaluation
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- I 2 :
-
I-Squared
- MBO:
-
Malignant biliary obstruction
- NOS:
-
Newcastle–Ottawa Scale
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis
- RCTs:
-
Randomized controlled studies
- RFA + Stent:
-
Radiofrequency ablation combined with stent
- ROB-2:
-
The revised cochrane risk of bias tool
- SMD:
-
Standardized mean differences
References
Banales JM, Marin JJG, Lamarca A et al (2020) Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: the next horizon in mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 17(9):557–588
Gupta N, Yelamanchi R (2021) Pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a review of recent paradigms and advances in epidemiology, clinical diagnosis and management. World J Gastroenterol 27(23):3158–3181
Rizvi S, Khan SA, Hallemeier CL et al (2018) Cholangiocarcinoma—evolving concepts and therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 15(2):95–111
Abraham NS, Barkun JS, Barkun AN (2002) Palliation of malignant biliary obstruction: a prospective trial examining impact on quality of life. Gastrointest Endosc 56(6):835–841
Khoo S, Do NDT, Kongkam P (2020) Efficacy and safety of EUS biliary drainage in malignant distal and hilar biliary obstruction: a comprehensive review of literature and algorithm. Endosc Ultrasound 9(6):369–379
Monkemuller K, Popa D, Wilcox CM (2014) Endoscopic treatment options for cholangiocarcinomas. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 14(4):407–418
Hamada T, Nakai Y, Isayama H et al (2021) Antireflux metal stent for biliary obstruction: any benefits? Dig Endosc 33(3):310–320
Zhu HD, Guo JH, Huang M et al (2018) Irradiation stents vs. conventional metal stents for unresectable malignant biliary obstruction: a multicenter trial. J Hepatol 68(5):970–977
Gao DJ, Yang JF, Ma SR et al (2020) Endoscopic radiofrequency ablation plus plastic stent placement versus stent placement alone for unresectable extrahepatic biliary cancer: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2020.12.016
Inoue T, Yoneda M (2021) Updated evidence on the clinical impact of endoscopic radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of malignant biliary obstruction. Dig Endosc. https://doi.org/10.1111/den.14059
Yang J, Wang J, Zhou H et al (2018) Efficacy and safety of endoscopic radiofrequency ablation for unresectable extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a randomized trial. Endoscopy 50(8):751–760
Kang H, Chung MJ, Cho IR et al (2021) Efficacy and safety of palliative endobiliary radiofrequency ablation using a novel temperature-controlled catheter for malignant biliary stricture: a single-center prospective randomized phase II TRIAL. Surg Endosc 35(1):63–73
Cho JH, Jeong S, Kim EJ et al (2018) Long-term results of temperature-controlled endobiliary radiofrequency ablation in a normal swine model. Gastrointest Endosc 87(4):1147–1150
Habert P, Di Bisceglie M, Bartoli A et al (2021) Description of morphological evolution of lung tumors treated by percutaneous radiofrequency ablation: long term follow-up of 100 lesions with chest CT. Int J Hyperth 38(1):786–794
Yang Y, Yu H, Tan X et al (2021) Liver resection versus radiofrequency ablation for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Hyperth 38(1):875–886
Laquiere A, Boustiere C, Leblanc S et al (2016) Safety and feasibility of endoscopic biliary radiofrequency ablation treatment of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Surg Endosc Other Interv Tech 30(3):1242–1248
Yang KH, Li XX, Bai Z (2018) Research methods of evidence-based social science: systematic review and meta-analysis. Lanzhou University Press, Lanzhou
Sofi AA, Khan MA, Das A et al (2018) Radiofrequency ablation combined with biliary stent placement versus stent placement alone for malignant biliary strictures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 87(4):944-951.e1
Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.2 (2021). Cochrane, 2021. [EB/OL]. www.training.cochrane.org/handbook
Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M et al (2015) Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ 350:g7647
Sterne JC, Savovic J, Page MJ et al (2019) RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ-Br Med J. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l4898
Stang A (2010) Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol 25(9):603–605
Wang Q, Wang J, Pan B et al (2020) Advance in the GRADE approach to rate the quality of evidence from a network meta-analysis. Chin J Evid Based Med 20(7):1–7
Liu Q, Ding L (2019) Accessibility and validation of survival data in survival curve for meta-analysis. Chin J Evid Based Med 19(9):1124–1130
Luo D, Wan X, Liu J et al (2018) Optimally estimating the sample mean from the sample size, median, mid-range, and/or mid-quartile range. Stat Methods Med Res 27(6):1785–1805
Wan X, Wang W, Liu J et al (2014) Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med Res Methodol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-14-135
Uyanık SA, Öğüşlü U, Çevik H et al (2021) Percutaneous endobiliary ablation of malignant biliary strictures with a novel temperature-controlled radiofrequency ablation device. Diagn Interv Radiol 27(1):102–108
Sharaiha RZ, Natov N, Glockenberg KS et al (2014) Comparison of metal stenting with radiofrequency ablation versus stenting alone for treating malignant biliary strictures: is there an added benefit? Dig Dis Sci 59(12):3099–3102
Kallis Y, Phillips N, Steel A et al (2015) Analysis of endoscopic radiofrequency ablation of biliary malignant strictures in pancreatic cancer suggests potential survival benefit. Dig Dis Sci 60(11):3449–3455
Li TF, Huang GH, Li Z et al (2015) Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography and intraductal radiofrequency ablation combined with biliary stent placement for malignant biliary obstruction. J Vasc Interv Radiol 26(5):715–721
Liang H, Peng Z, Cao L et al (2015) Metal stenting with or without endobiliary radiofrequency ablation for unresectable extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Cancer Ther 06(11):981–992
Kadayifci A, Atar M, Forcione DG et al (2016) Radiofrequency ablation for the management of occluded biliary metal stents. Endoscopy 48(12):1096–1101
Liu J, Di K, Xu S et al (2016) Radiofrequency ablation combined with stent implantation in treatment of malignant biliary obstruction. Chin J Interv Imaging Ther 13(10):587–591
Wang J, Zhao L, Zhou C et al (2016) Percutaneous Intraductal radiofrequency ablation combined with biliary stent placement for nonresectable malignant biliary obstruction improves stent patency but not survival. Medicine (Baltimore) 95(15):e3329
Cui W, Wang Y, Fan WZ et al (2017) Comparison of intraluminal radiofrequency ablation and stents vs. stents alone in the management of malignant biliary obstruction. Int J Hyperth 33(7):853–861
Dutta AK, Basavaraju U, Sales L et al (2017) Radiofrequency ablation for management of malignant biliary obstruction: a single-center experience and review of the literature. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 11(8):779–784
Wu TT, Li WM, Li HC et al (2017) Percutaneous intraductal radiofrequency ablation for extrahepatic distal cholangiocarcinoma: a method for prolonging stent patency and achieving better functional status and quality of life. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 40(2):260–269
Bokemeyer A, Matern P, Bettenworth D et al (2019) Endoscopic radiofrequency ablation prolongs survival of patients with unresectable hilar cholangiocellular carcinoma—a case-control study. Sci Rep 9(1):13685
Orozco MCG, Guerrero AH, Larraga JOA et al (2020) Efficacy and safety of radiofrequency ablation in patients with unresectable malignant biliary strictures. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. https://doi.org/10.17235/reed.2020.7023/2020
Yu TZ, Zhang W, Li CY et al (2020) Percutaneous intraductal radiofrequency ablation combined with biliary stent placement for treatment of malignant biliary obstruction. Abdom Radiol 45(11):3690–3697
Kong YL, Zhang HY, Liu CL et al (2021) Improving biliary stent patency for malignant obstructive jaundice using endobiliary radiofrequency ablation: experience in 150 patients. Surg Endosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-021-08457-3
Xia MX, Wang SP, Yuan JG et al (2021) Effect of endoscopic radiofrequency ablation on the survival of patients with inoperable malignant biliary strictures: a large cohort study. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhbp.960
Zheng X, Bo ZY, Wan W et al (2016) Endoscopic radiofrequency ablation may be preferable in the management of malignant biliary obstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dig Dis 17(11):716–724
Yang J, Wang J, Zhou H et al (2020) Endoscopic radiofrequency ablation plus a novel oral 5-fluorouracil compound versus radiofrequency ablation alone for unresectable extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc 92(6):1204–1212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2020.04.075
Yang Q, Liu J, Ma W et al (2019) Efficacy of different endoscopic stents in the management of postoperative biliary strictures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Gastroenterol 53(6):418–426
Tal AO, Vermehren J, Friedrich-Rust M et al (2014) Intraductal endoscopic radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of hilar non-resectable malignant bile duct obstruction. World J Gastrointest Endosc 6(1):13–19
Funding
This research is supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Nos. 2020jbkyzx001, lzujbky-2020-kb20); the Key Laboratory of Evidence-Based Medicine and Knowledge Translation Foundation of Gansu Province (Grant No. GSEBMKT-2021KFKT03); Key Laboratory of Molecular Diagnosis and Precision Therapy of Surgical Tumors of Gansu Province, Grant Number 2019GSZDSYS06.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All patients participated in the interpretation of study results and approved the final version of the manuscript. TG and KY contributed to studying concepts and design. SS, HJ, and QC, contributed to data collection, statistical analysis, data interpretation, and the paper's drafting. SG, KL, WY, CL, TL, HT, and XL contributed to data collection.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Shaoming Song, Haojie Jin, Qinghao Cheng, Shiyi Gong, Kun Lv, Wenwen Yang, Caining Lei, Ting Lei, Hongwei Tian, Xiaofei Li, Kehu Yang, and Tiankang Guo have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure S1
Forest plot of subgroup analysis illustrating the mean stent patency based on metal or plastic stent (PNG 19 KB)
Figure S2
Funnel plots. A: overall survival; B: mean survival time; C: mean stent patency time; D: abdominal pain; E: cholangitis (PNG 417 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, S., Jin, H., Cheng, Q. et al. Local palliative therapies for unresectable malignant biliary obstruction: radiofrequency ablation combined with stent or biliary stent alone? An updated meta-analysis of nineteen trials. Surg Endosc 36, 5559–5570 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-022-09181-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-022-09181-2